目录
一些轻量级的网络,如mobilenet中,会有深度可分离卷积depthwise separable convolution,由depthwise(DW)和pointwise(PW)两个部分结合起来,用来提取特征feature map,相比常规的卷积操作,其参数数量和运算成本比较低
常规卷积操作
对于一张5×5像素、三通道(shape为5×5×3),经过3×3卷积核的卷积层(假设输出通道数为4,则卷积核shape为3×3×3×4,最终输出4个Feature Map,
如果有same padding则输出尺寸与输入层相同(5×5×4),如果没有则为尺寸变为3×3×4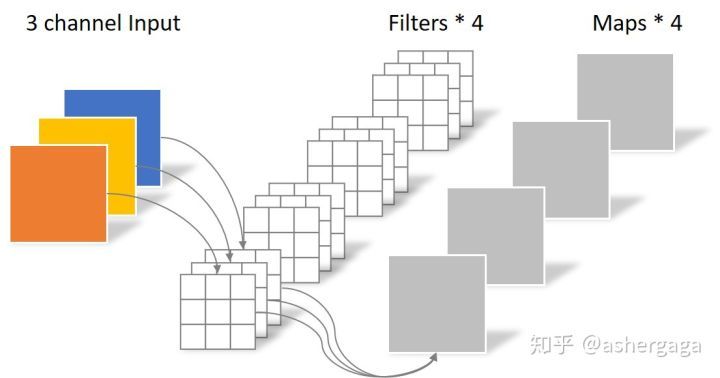
卷积层共4个Filter,每个Filter包含了3个Kernel,每个Kernel的大小为3×3。因此卷积层的参数数量可以用如下公式来计算:N_std = 4 × 3 × 3 × 3 = 108
深度可分离卷积 = 逐通道卷积+逐点卷积
1.逐通道卷积
Depthwise Convolution的一个卷积核负责一个通道,一个通道只被一个卷积核卷积
一张5×5像素、三通道彩色输入图片(shape为5×5×3),Depthwise Convolution首先经过第一次卷积运算,DW完全是在二维平面内进行。卷积核的数量与上一层的通道数相同(通道和卷积核一一对应)。所以一个三通道的图像经过运算后生成了3个Feature map(如果有same padding则尺寸与输入层相同为5×5),如下图所示。
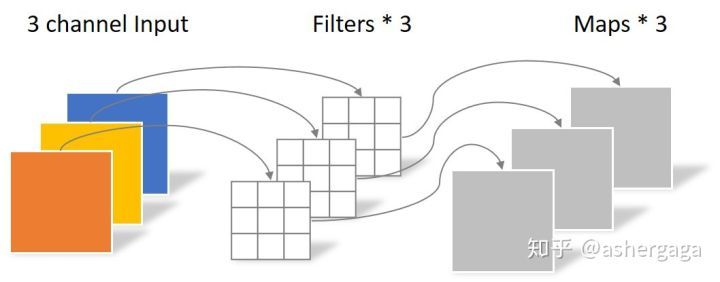
其中一个Filter只包含一个大小为3×3的Kernel,卷积部分的参数个数计算如下:N_depthwise = 3 × 3 × 3 = 27
Depthwise Convolution完成后的Feature map数量与输入层的通道数相同,无法扩展Feature map。而且这种运算对输入层的每个通道独立进行卷积运算,没有有效的利用不同通道在相同空间位置上的feature信息。因此需要Pointwise Convolution来将这些Feature map进行组合生成新的Feature map
2.逐点卷积
Pointwise Convolution的运算与常规卷积运算非常相似,它的卷积核的尺寸为 1×1×M,M为上一层的通道数。所以这里的卷积运算会将上一步的map在深度方向上进行加权组合,生成新的Feature map。有几个卷积核就有几个输出Feature map
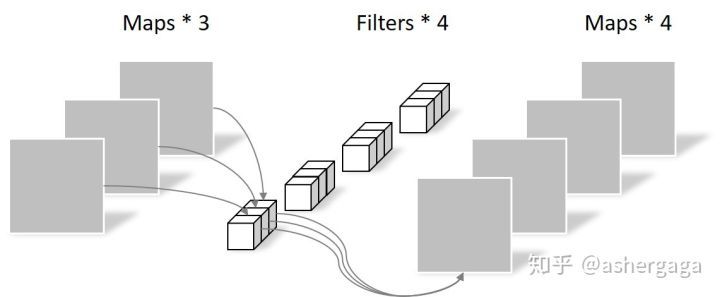
由于采用的是1×1卷积的方式,此步中卷积涉及到的参数个数可以计算为:N_pointwise = 1 × 1 × 3 × 4 = 12
经过Pointwise Convolution之后,同样输出了4张Feature map,与常规卷积的输出维度相同
参数对比
回顾一下,常规卷积的参数个数为:
N_std = 4 × 3 × 3 × 3 = 108
Separable Convolution的参数由两部分相加得到:
N_depthwise = 3 × 3 × 3 = 27
N_pointwise = 1 × 1 × 3 × 4 = 12
N_separable = N_depthwise + N_pointwise = 39
相同的输入,同样是得到4张Feature map,Separable Convolution的参数个数是常规卷积的约1/3。因此,在参数量相同的前提下,采用Separable Convolution的神经网络层数可以做的更深。
介绍
depthwise_conv2d来源于深度可分离卷积:
tf.nn.depthwise_conv2d(input,filter,strides,padding,rate=None,name=None,data_format=None)除去name参数用以指定该操作的name,data_format指定数据格式,与方法有关的一共五个参数:
input:
指需要做卷积的输入图像,要求是一个4维Tensor,具有[batch, height, width, in_channels]这样的shape,具体含义是[训练时一个batch的图片数量, 图片高度, 图片宽度, 图像通道数]filter:
相当于CNN中的卷积核,要求是一个4维Tensor,具有[filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, channel_multiplier]这样的shape,具体含义是[卷积核的高度,卷积核的宽度,输入通道数,输出卷积乘子],同理这里第三维in_channels,就是参数value的第四维strides:
卷积的滑动步长。padding:
string类型的量,只能是”SAME”,”VALID”其中之一,这个值决定了不同边缘填充方式。rate:
这个参数的详细解释见【Tensorflow】tf.nn.atrous_conv2d如何实现空洞卷积?
结果返回一个Tensor,shape为[batch, out_height, out_width, in_channels * channel_multiplier],注意这里输出通道变成了 in_channels * channel_multiplier
实验
为了形象的展示depthwise_conv2d,我们必须要建立自定义的输入图像和卷积核
img1 = tf.constant(value=[[[[1],[2],[3],[4]],[[1],[2],[3],[4]],[[1],[2],[3],[4]],[[1],[2],[3],[4]]]],dtype=tf.float32)
img2 = tf.constant(value=[[[[1],[1],[1],[1]],[[1],[1],[1],[1]],[[1],[1],[1],[1]],[[1],[1],[1],[1]]]],dtype=tf.float32)
img = tf.concat(values=[img1,img2],axis=3)filter1 = tf.constant(value=0, shape=[3,3,1,1],dtype=tf.float32)
filter2 = tf.constant(value=1, shape=[3,3,1,1],dtype=tf.float32)
filter3 = tf.constant(value=2, shape=[3,3,1,1],dtype=tf.float32)
filter4 = tf.constant(value=3, shape=[3,3,1,1],dtype=tf.float32)
filter_out1 = tf.concat(values=[filter1,filter2],axis=2)
filter_out2 = tf.concat(values=[filter3,filter4],axis=2)
filter = tf.concat(values=[filter_out1,filter_out2],axis=3)建立好了img和filter,就可以做卷积了
out_img = tf.nn.conv2d(input=img, filter=filter, strides=[1,1,1,1], padding='VALID')好了,用一张图来详细展示这个过程

这是普通的卷积过程,我们再来看深度卷积。
out_img = tf.nn.depthwise_conv2d(input=img, filter=filter, strides=[1,1,1,1], rate=[1,1], padding='VALID')

现在我们可以形象的解释一下depthwise_conv2d卷积了。看普通的卷积,我们对卷积核每一个out_channel的两个通道分别和输入的两个通道做卷积相加,得到feature map的一个channel,而depthwise_conv2d卷积,我们对每一个对应的in_channel,分别卷积生成两个out_channel,所以获得的feature map的通道数量可以用in_channel* channel_multiplier来表达,这个channel_multiplier,就可以理解为卷积核的第四维。
代码清单
import tensorflow as tf
img1 = tf.constant(value=[[[[1],[2],[3],[4]],[[1],[2],[3],[4]],[[1],[2],[3],[4]],[[1],[2],[3],[4]]]],dtype=tf.float32)
img2 = tf.constant(value=[[[[1],[1],[1],[1]],[[1],[1],[1],[1]],[[1],[1],[1],[1]],[[1],[1],[1],[1]]]],dtype=tf.float32)
img = tf.concat(values=[img1,img2],axis=3)
filter1 = tf.constant(value=0, shape=[3,3,1,1],dtype=tf.float32)
filter2 = tf.constant(value=1, shape=[3,3,1,1],dtype=tf.float32)
filter3 = tf.constant(value=2, shape=[3,3,1,1],dtype=tf.float32)
filter4 = tf.constant(value=3, shape=[3,3,1,1],dtype=tf.float32)
filter_out1 = tf.concat(values=[filter1,filter2],axis=2)
filter_out2 = tf.concat(values=[filter3,filter4],axis=2)
filter = tf.concat(values=[filter_out1,filter_out2],axis=3)
out_img = tf.nn.depthwise_conv2d(input=img, filter=filter, strides=[1,1,1,1], rate=[1,1], padding='VALID')
输出:
rate=1, VALID mode result:
[[[[ 0. 36. 9. 27.]
[ 0. 54. 9. 27.]]
[[ 0. 36. 9. 27.]
[ 0. 54. 9. 27.]]]]原文连接:https://blog.csdn.net/mao_xiao_feng/article/details/78003476








 本文介绍了深度可分离卷积,包括逐通道卷积和逐点卷积的操作原理,参数对比,以及在MobileNet等轻量网络中的应用。通过代码实例展示了如何使用TensorFlow实现depthwise_conv2d,并对比了常规卷积的参数节省。
本文介绍了深度可分离卷积,包括逐通道卷积和逐点卷积的操作原理,参数对比,以及在MobileNet等轻量网络中的应用。通过代码实例展示了如何使用TensorFlow实现depthwise_conv2d,并对比了常规卷积的参数节省。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










