本文提出了两种特征压缩方法:
- 减少每个像素的颜色位深度
- 使用空间平滑来减少各个像素之间的差异
特征压缩通过将与原始空间中许多不同特征向量相对应的样本合并为单个样本,从而减少了对手可用的搜索空间。通过将DNN模型对原始输入的预测与对压缩输入的预测进行比较,特征压缩可以很好的检测出对抗样本。本方法对于计算资源要求不高,可以与其他防御措施互补,并且可以结合联合检测框架使用。
Our approach, which we call feature squeezing, is driven by the observation that the feature input spaces are often unnecessarily large, and this vast input space provides extensive opportunities for an adversary to construct adversarial examples. Our strategy is to reduce the degrees of freedom available to an adversary by “squeezing” out unnecessary input features. The key idea is to compare the model’s prediction on the original sample with its prediction on the sample after squeezing, as depicted in Figure 1. If the original and squeezed inputs produce substantially different outputs from the model, the input is likely to be adversarial. By comparing the difference between predictions with a selected threshold value, our system outputs the correct prediction for legitimate examples and rejects adversarial inputs.
特征压缩核心思想:特征输入空间通常不需要太大,因为过大的特征输入空间会为对手生成对抗样本提供更多可能。 策略是通过“压缩”不必要的特征来降低对手生成对抗样本的自由度。 关键思想是将模型对原始样本的预测与压缩后对样本的预测进行比较。如果原始输入和压缩后的输入产生了与模型实质上不同的输出,则输入可能是对抗性的。 通过将预测之间的差异与选定的阈值进行比较,系统会为合法样本输出正确的预测,并拒绝对抗样本的输入。
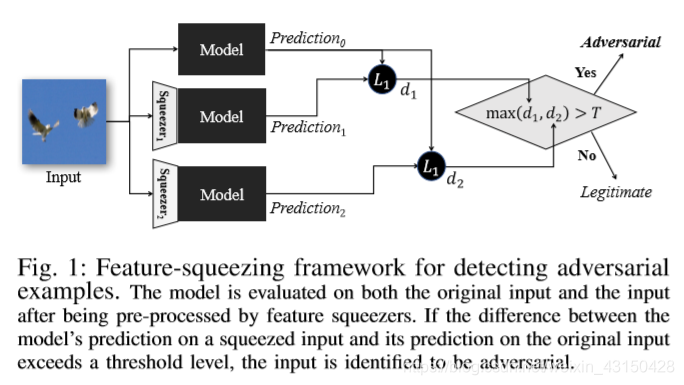
本文证明,通过预测非自适应对抗样本的正确标签,特征压缩可以显著增强模型的鲁棒性,同时保留合法输入的准确性,从而可以准确的检测静态对抗样本。
主要贡献是通过研究了特征压缩的两个方法:减少颜色位深度以及局部和非局部空间平滑实验表明,特征压缩可帮助DNN模型对11种不同的对抗样本攻击(不了解防御的情况)进行防御。 特征压缩是其他对抗防御的补充,因为不会改变基础模型,并且可以很容易地与其他防御(例如对抗训练)组合在一起。
L ∞ L_\infty L








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 589
589











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








