文章目录
R flow control
- flow control often used in function block
guideline of flow control
conditional statement
if
else if
switch
vectorized if
looping statement
repeat
while
for
advanced looping
apply
if
used for conditional execution
- usage if(condition){body}
codes:
GetPerformance=function(student.scores){
average.score=mean(student.scores)
Std=average.score>=75
print(paste("average.score: ",average.score))
if(Std){
print("the student is brilliant!")
}
print("academic work completed!")
}
student1=c(100L,98L,0L,96L)
student2=c(89L,90L,87L,76L)
GetPerformance(student1)
GetPerformance(student2)
- if the condition is false, R will not execute the block
else if
- incorporate different conditions
- act accordingly
codes:
GetReport=function(student.scores){
average.scores=mean(student.scores)
print(paste("student average score is : ",average.scores))
if(average.scores>=75){
print("student is brilliant! ")
}
else if(average.scores>=60){
print("student is satisfactory.")
}
else{
print("student is failed in academic.")
}
}
student1=c(100L,98L,0L,96L)
student2=c(89L,90L,87L,76L)
student3=c(0L,10L,45L,23L)
GetReport(student1)
GetReport(student2)
GetReport(student3)

switch
-
usage: switch(expression,
option1={
},
option2={
},
default value) -
expression above can only be an integer or a string
codes:
GetSummary=function(student.scores,summary.type){
result=switch(summary.type,
"mean"={
mean(student.scores)
},
"total"={
sum(student.scores)
},
"variance"={
var(student.scores)
},
"the biggest"={
max(student.scores)
},
"No implemention")
result
}
student1=c(100L,98L,0L,96L)
GetSummary(student1,"mean")
GetSummary(student1,"total")
GetSummary(student1,"variance")
GetSummary(student1,"the biggest")
GetSummary(student1,"the smallest")
GetSummary(stduent1,"")

vectorized if
used for if condition without explicit looping
used when multiple objects needing to be judged
not applicable in multiple conditions
multiple objects are vectorized
- usage: ifelse (test.vector, true.vector, false.vector)
- true.vector or false.vector is recycled if its length is shorter than test.vector
- if test.vector contains NA, the ifelse() will returned a NA
codes:
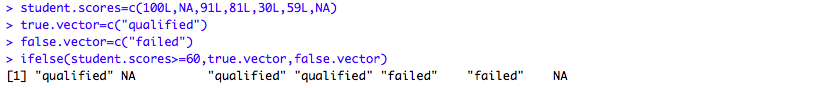
student.scores=c(100L,NA,91L,81L,30L,59L,NA)
true.vector=c("qualified")
false.vector=c("failed")
ifelse(student.scores>=60,true.vector,false.vector)
repeat
- repeat{} is a statement that designed for recycling for eternity
break
- normally we use break to break the loop at certain point and never begin
codes:
WriteOnNotebook=function(total.page){
count=0
repeat{
count=count+1
print(paste("The total page number is :",count))
if(count>=total.page){
break
}
}
print("the notebook is completed.")
}
WriteOnNotebook(10)

next
- normally we use next to break the loop and begin again
codes:
WriteOnOddPage=function(total.page.number){
count=0
repeat{
count=count+1
if(count>total.page.number){
break
}
if(count%%2==0){
print(paste("skipped page number :",count))
next
}
print(paste("the total page number is:",count))
}
}
WriteOnOddPage(6)
WriteOnOddPage(5)

- “break” and “next” to control the loop on desired condition
- in repeat,the loop is entered first and then use if to judge when to continue or break
while loop
- check the condition, check the logic value before entering the loop
- usage:while(){
}
codes;
WriteOnOddPage=function(total.page.number){
count=0
while(count<total.page.number){
count=count+1
if(count%%2==0){
print(paste("the skipped page number is :",count))
}
else{
print(paste("the total page number is :",count))
}
}
}
WriteOnOddPage(6)

for loop
loop in a vector
- usage of for loop
- for(iterator in vector ){
##execute body
}
codes:
WriteOnOddPage=function(total.page.number){
page.range=1:total.page.number
odd.page=page.range[page.range%%2!=0]
even.page=page.range[page.range%%2==0]
for (count in odd.page) {
print(paste("the total page number is : ",count))
}
for (count in even.page) {
print(paste("the skipped page number is :",count))
}
}
WriteOnOddPage(6)

apply
an advanced flow control mechanism
mainly used on matrix and array
but returned a list , a vector or an array
usage: apply(data, margin, function)
- margin means direction
- 1 represent row wise
- 2 represent column wise
- 1:2 represent every element
codes:
create a matrix
student.scores=matrix(c(1,2,3,4,
5,6,7,8,
9,10,11,12,
13,14,15,16),ncol=4,nrow=4,byrow=TRUE)
rownames(student.scores)=c("KD","Curry","KT","Green")
colnames(student.scores)=c("cs","math","English","Debate")
student.scores

apply(student.scores, 1, sum)
apply(student.scores, 1, max)
apply(student.scores,1,mean)
apply(student.scores,1,which.max)

-
which.max return the position of the max value
-
but for most time we need to where and what the max value is
codes:colnames(student.scores[,apply(student.scores,1,which.max)])

like rowSums(), rowMeans()
rowSums(student.scores)
rowMeans(student.scores)

-some examples of column wise
codes:
apply(student.scores,2,max)
rownames(student.scores[apply(student.scores, 2, which.max),])























 779
779











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








