引言
多目标粒子群优化算法(Multi-Objective Particle Swarm Optimization, MOPSO)是将传统的粒子群优化算法(PSO)扩展到多目标优化问题中的一种算法。
基本原理
MOPSO算法通过外部存档和Pareto支配关系来处理多目标优化问题。每个粒子在搜索空间中移动,其位置和速度根据个人最佳位置和全局最佳位置进行更新。全局最佳位置是从外部存档中选择的非支配解之一
算法步骤
-
粒子群初始化:创建一组粒子,每个粒子有一个初始位置和速度。位置在给定的边界范围内随机生成,初始速度设为零
-
适应度评估:对每个粒子计算其适应度值,即每个目标函数在该粒子位置上的值。更新粒子的个人最佳位置和个人最佳适应度
-
速度和位置更新:根据认知项(粒子自身的最佳位置)和社会项(全局最佳位置)更新粒子的速度。根据新的速度更新粒子的位置,并确保位置在搜索空间内
-
非支配解选择:使用支配关系判断粒子之间的优劣,找到一组非支配解。随机选择一个非支配解作为全局最佳位置
-
多目标优化:在指定的迭代次数内重复执行适应度评估、速度和位置更新以及非支配解选择。最终返回找到的所有非支配解的位置
参考文献
Matlab代码下载
微信搜索并关注-优化算法侠(英文名:Swarm-Opti),或扫描下方二维码关注,以算法名字搜索历史文章即可下载。
% 请关注微信公众号:优化算法侠,发现更多精彩
% MOPSO
% ----------------------------------------------------------------------- %
% ----------------------------------------------------------------------- %
function REP = MOPSO(params,MultiObj)
% Parameters
Np = params.Np;
Nr = params.Nr;
maxgen = params.maxgen;
W = params.W;
C1 = params.C1;
C2 = params.C2;
ngrid = params.ngrid;
maxvel = params.maxvel;
u_mut = params.u_mut;
fun = MultiObj.fun;
nVar = MultiObj.nVar;
var_min = MultiObj.var_min(:);
var_max = MultiObj.var_max(:);
% Initialization
POS = repmat((var_max-var_min)',Np,1).*rand(Np,nVar) + repmat(var_min',Np,1);
VEL = zeros(Np,nVar);
POS_fit = fun(POS);
if size(POS,1) ~= size(POS_fit,1)
warning(['The objective function is badly programmed. It is not returning' ...
'a value for each particle, please check it.']);
end
PBEST = POS;
PBEST_fit= POS_fit;
DOMINATED= checkDomination(POS_fit);
REP.pos = POS(~DOMINATED,:);
REP.pos_fit = POS_fit(~DOMINATED,:);
REP = updateGrid(REP,ngrid);
maxvel = (var_max-var_min).*maxvel./100;
gen = 1;
% Plotting and verbose
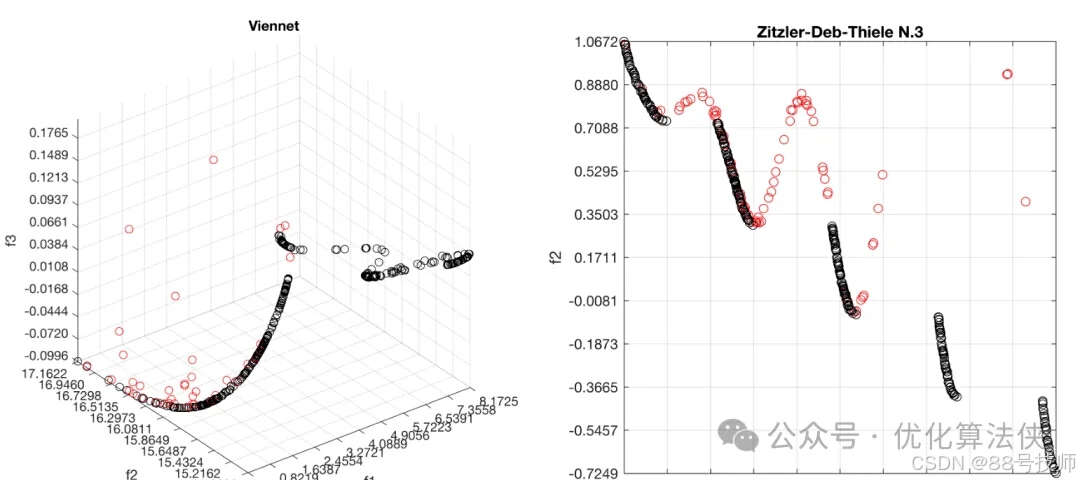
if(size(POS_fit,2)==2)
h_fig = figure(1);
h_par = plot(POS_fit(:,1),POS_fit(:,2),'or'); hold on;
h_rep = plot(REP.pos_fit(:,1),REP.pos_fit(:,2),'ok'); hold on;
try
set(gca,'xtick',REP.hypercube_limits(:,1)','ytick',REP.hypercube_limits(:,2)');
axis([min(REP.hypercube_limits(:,1)) max(REP.hypercube_limits(:,1)) ...
min(REP.hypercube_limits(:,2)) max(REP.hypercube_limits(:,2))]);
grid on; xlabel('f1'); ylabel('f2');
end
drawnow;
end
if(size(POS_fit,2)==3)
h_fig = figure(1);
h_par = plot3(POS_fit(:,1),POS_fit(:,2),POS_fit(:,3),'or'); hold on;
h_rep = plot3(REP.pos_fit(:,1),REP.pos_fit(:,2),REP.pos_fit(:,3),'ok'); hold on;
try
set(gca,'xtick',REP.hypercube_limits(:,1)','ytick',REP.hypercube_limits(:,2)','ztick',REP.hypercube_limits(:,3)');
axis([min(REP.hypercube_limits(:,1)) max(REP.hypercube_limits(:,1)) ...
min(REP.hypercube_limits(:,2)) max(REP.hypercube_limits(:,2))]);
end
grid on; xlabel('f1'); ylabel('f2'); zlabel('f3');
drawnow;
axis square;
end
display(['Generation #0 - Repository size: ' num2str(size(REP.pos,1))]);
% Main MPSO loop
stopCondition = false;
while ~stopCondition
% Select leader
h = selectLeader(REP);
% Update speeds and positions
VEL = W.*VEL + C1*rand(Np,nVar).*(PBEST-POS) ...
+ C2*rand(Np,nVar).*(repmat(REP.pos(h,:),Np,1)-POS);
POS = POS + VEL;
% Perform mutation
POS = mutation(POS,gen,maxgen,Np,var_max,var_min,nVar,u_mut);
% Check boundaries
[POS,VEL] = checkBoundaries(POS,VEL,maxvel,var_max,var_min);
% Evaluate the population
POS_fit = fun(POS);
% Update the repository
REP = updateRepository(REP,POS,POS_fit,ngrid);
if(size(REP.pos,1)>Nr)
REP = deleteFromRepository(REP,size(REP.pos,1)-Nr,ngrid);
end
% Update the best positions found so far for each particle
pos_best = dominates(POS_fit, PBEST_fit);
best_pos = ~dominates(PBEST_fit, POS_fit);
best_pos(rand(Np,1)>=0.5) = 0;
if(sum(pos_best)>1)
PBEST_fit(pos_best,:) = POS_fit(pos_best,:);
PBEST(pos_best,:) = POS(pos_best,:);
end
if(sum(best_pos)>1)
PBEST_fit(best_pos,:) = POS_fit(best_pos,:);
PBEST(best_pos,:) = POS(best_pos,:);
end
% Plotting and verbose
if(size(POS_fit,2)==2)
figure(h_fig); delete(h_par); delete(h_rep);
h_par = plot(POS_fit(:,1),POS_fit(:,2),'or'); hold on;
h_rep = plot(REP.pos_fit(:,1),REP.pos_fit(:,2),'ok'); hold on;
try
set(gca,'xtick',REP.hypercube_limits(:,1)','ytick',REP.hypercube_limits(:,2)');
axis([min(REP.hypercube_limits(:,1)) max(REP.hypercube_limits(:,1)) ...
min(REP.hypercube_limits(:,2)) max(REP.hypercube_limits(:,2))]);
end
if(isfield(MultiObj,'truePF'))
try delete(h_pf); end
h_pf = plot(MultiObj.truePF(:,1),MultiObj.truePF(:,2),'.','color',0.8.*ones(1,3)); hold on;
end
grid on; xlabel('f1'); ylabel('f2');
drawnow;
axis square;
end
if(size(POS_fit,2)==3)
figure(h_fig); delete(h_par); delete(h_rep);
h_par = plot3(POS_fit(:,1),POS_fit(:,2),POS_fit(:,3),'or'); hold on;
h_rep = plot3(REP.pos_fit(:,1),REP.pos_fit(:,2),REP.pos_fit(:,3),'ok'); hold on;
try
set(gca,'xtick',REP.hypercube_limits(:,1)','ytick',REP.hypercube_limits(:,2)','ztick',REP.hypercube_limits(:,3)');
axis([min(REP.hypercube_limits(:,1)) max(REP.hypercube_limits(:,1)) ...
min(REP.hypercube_limits(:,2)) max(REP.hypercube_limits(:,2)) ...
min(REP.hypercube_limits(:,3)) max(REP.hypercube_limits(:,3))]);
end
if(isfield(MultiObj,'truePF'))
try delete(h_pf); end
h_pf = plot3(MultiObj.truePF(:,1),MultiObj.truePF(:,2),MultiObj.truePF(:,3),'.','color',0.8.*ones(1,3)); hold on;
end
grid on; xlabel('f1'); ylabel('f2'); zlabel('f3');
drawnow;
axis square;
end
display(['Generation #' num2str(gen) ' - Repository size: ' num2str(size(REP.pos,1))]);
% Update generation and check for termination
gen = gen + 1;
if(gen>maxgen), stopCondition = true; end
end
hold off;
end
% Function that updates the repository given a new population and its
% fitness
function REP = updateRepository(REP,POS,POS_fit,ngrid)
% Domination between particles
DOMINATED = checkDomination(POS_fit);
REP.pos = [REP.pos; POS(~DOMINATED,:)];
REP.pos_fit= [REP.pos_fit; POS_fit(~DOMINATED,:)];
% Domination between nondominated particles and the last repository
DOMINATED = checkDomination(REP.pos_fit);
REP.pos_fit= REP.pos_fit(~DOMINATED,:);
REP.pos = REP.pos(~DOMINATED,:);
% Updating the grid
REP = updateGrid(REP,ngrid);
end
% Function that corrects the positions and velocities of the particles that
% exceed the boundaries
function [POS,VEL] = checkBoundaries(POS,VEL,maxvel,var_max,var_min)
% Useful matrices
Np = size(POS,1);
MAXLIM = repmat(var_max(:)',Np,1);
MINLIM = repmat(var_min(:)',Np,1);
MAXVEL = repmat(maxvel(:)',Np,1);
MINVEL = repmat(-maxvel(:)',Np,1);
% Correct positions and velocities
VEL(VEL>MAXVEL) = MAXVEL(VEL>MAXVEL);
VEL(VEL<MINVEL) = MINVEL(VEL<MINVEL);
VEL(POS>MAXLIM) = (-1).*VEL(POS>MAXLIM);
POS(POS>MAXLIM) = MAXLIM(POS>MAXLIM);
VEL(POS<MINLIM) = (-1).*VEL(POS<MINLIM);
POS(POS<MINLIM) = MINLIM(POS<MINLIM);
end
% Function for checking the domination between the population. It
% returns a vector that indicates if each particle is dominated (1) or not
function dom_vector = checkDomination(fitness)
Np = size(fitness,1);
dom_vector = zeros(Np,1);
all_perm = nchoosek(1:Np,2); % Possible permutations
all_perm = [all_perm; [all_perm(:,2) all_perm(:,1)]];
d = dominates(fitness(all_perm(:,1),:),fitness(all_perm(:,2),:));
dominated_particles = unique(all_perm(d==1,2));
dom_vector(dominated_particles) = 1;
end
% Function that returns 1 if x dominates y and 0 otherwise
function d = dominates(x,y)
d = all(x<=y,2) & any(x<y,2);
end
% Function that updates the hypercube grid, the hypercube where belongs
% each particle and its quality based on the number of particles inside it
function REP = updateGrid(REP,ngrid)
% Computing the limits of each hypercube
ndim = size(REP.pos_fit,2);
REP.hypercube_limits = zeros(ngrid+1,ndim);
for dim = 1:1:ndim
REP.hypercube_limits(:,dim) = linspace(min(REP.pos_fit(:,dim)),max(REP.pos_fit(:,dim)),ngrid+1)';
end
% Computing where belongs each particle
npar = size(REP.pos_fit,1);
REP.grid_idx = zeros(npar,1);
REP.grid_subidx = zeros(npar,ndim);
for n = 1:1:npar
idnames = [];
for d = 1:1:ndim
REP.grid_subidx(n,d) = find(REP.pos_fit(n,d)<=REP.hypercube_limits(:,d)',1,'first')-1;
if(REP.grid_subidx(n,d)==0), REP.grid_subidx(n,d) = 1; end
idnames = [idnames ',' num2str(REP.grid_subidx(n,d))];
end
REP.grid_idx(n) = eval(['sub2ind(ngrid.*ones(1,ndim)' idnames ');']);
end
% Quality based on the number of particles in each hypercube
REP.quality = zeros(ngrid,2);
ids = unique(REP.grid_idx);
for i = 1:length(ids)
REP.quality(i,1) = ids(i); % First, the hypercube's identifier
REP.quality(i,2) = 10/sum(REP.grid_idx==ids(i)); % Next, its quality
end
end
% Function that selects the leader performing a roulette wheel selection
% based on the quality of each hypercube
function selected = selectLeader(REP)
% Roulette wheel
prob = cumsum(REP.quality(:,2)); % Cumulated probs
sel_hyp = REP.quality(find(rand(1,1)*max(prob)<=prob,1,'first'),1); % Selected hypercube
% Select the index leader as a random selection inside that hypercube
idx = 1:1:length(REP.grid_idx);
selected = idx(REP.grid_idx==sel_hyp);
selected = selected(randi(length(selected)));
end
% Function that deletes an excess of particles inside the repository using
% crowding distances
function REP = deleteFromRepository(REP,n_extra,ngrid)
% Compute the crowding distances
crowding = zeros(size(REP.pos,1),1);
for m = 1:1:size(REP.pos_fit,2)
[m_fit,idx] = sort(REP.pos_fit(:,m),'ascend');
m_up = [m_fit(2:end); Inf];
m_down = [Inf; m_fit(1:end-1)];
distance = (m_up-m_down)./(max(m_fit)-min(m_fit));
[~,idx] = sort(idx,'ascend');
crowding = crowding + distance(idx);
end
crowding(isnan(crowding)) = Inf;
% Delete the extra particles with the smallest crowding distances
[~,del_idx] = sort(crowding,'ascend');
del_idx = del_idx(1:n_extra);
REP.pos(del_idx,:) = [];
REP.pos_fit(del_idx,:) = [];
REP = updateGrid(REP,ngrid);
end
% Function that performs the mutation of the particles depending on the
% current generation
function POS = mutation(POS,gen,maxgen,Np,var_max,var_min,nVar,u_mut)
% Sub-divide the swarm in three parts [2]
fract = Np/3 - floor(Np/3);
if(fract<0.5), sub_sizes =[ceil(Np/3) round(Np/3) round(Np/3)];
else sub_sizes =[round(Np/3) round(Np/3) floor(Np/3)];
end
cum_sizes = cumsum(sub_sizes);
% First part: no mutation
% Second part: uniform mutation
nmut = round(u_mut*sub_sizes(2));
if(nmut>0)
idx = cum_sizes(1) + randperm(sub_sizes(2),nmut);
POS(idx,:) = repmat((var_max-var_min)',nmut,1).*rand(nmut,nVar) + repmat(var_min',nmut,1);
end
% Third part: non-uniform mutation
per_mut = (1-gen/maxgen)^(5*nVar); % Percentage of mutation
nmut = round(per_mut*sub_sizes(3));
if(nmut>0)
idx = cum_sizes(2) + randperm(sub_sizes(3),nmut);
POS(idx,:) = repmat((var_max-var_min)',nmut,1).*rand(nmut,nVar) + repmat(var_min',nmut,1);
end
end完整代码

👇👇👇
点击链接跳转:
375种群优化算法免费下载-matlab
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/AsFTBmaZ8UOgES9TQuL0Kg?token=1339859150&lang=zh_CN
求解cec测试函数-matlab
cec2022测试函使用教程及matlab代码免费下载
绘制cec2017/018/2019/2020/2021/2022函数的三维图像教程,SO EASY!


























 1844
1844

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








