C语言实现 Base64 和 Base32 编解码
作者:Bright Xu
Base64 编解码
定义头文件 base64.h
#ifndef _BASE64_H
#define _BASE64_H
#include <stdint.h>
static const char BASE64_MAP[] = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789+/=";
static const uint8_t BASE64_REVERSE_MAP[] = {
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 62, 0, 0, 0, 63, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4,
5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 26, 27, 28, 29,
30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51,
};
char *base64encode(const char *str, uint64_t len);
char *base64parse(const char *base64Str, uint64_t len);
#endif //_BASE64_H
思路
Base64编码就是用64个可打印字符表示二进制数据。
64
=
2
6
64 = 2^6
64=26,所以需要6 Bit来表示一个base64字符。一个字节8 Bit,6和8的最小公倍数是24。编码的过程中,以3个字节为一组转为4个base64字符,不足3个字节以0代替。为方便转换,以一个无符号32位整数(uint32_t)为中间载体。先由高位到低位将这三个字节填充到这个整数中,然后由高位到低位依次读取6位,获取对应数值的字母,共读取4次。如下图所示。解码的过程是上述的逆过程。
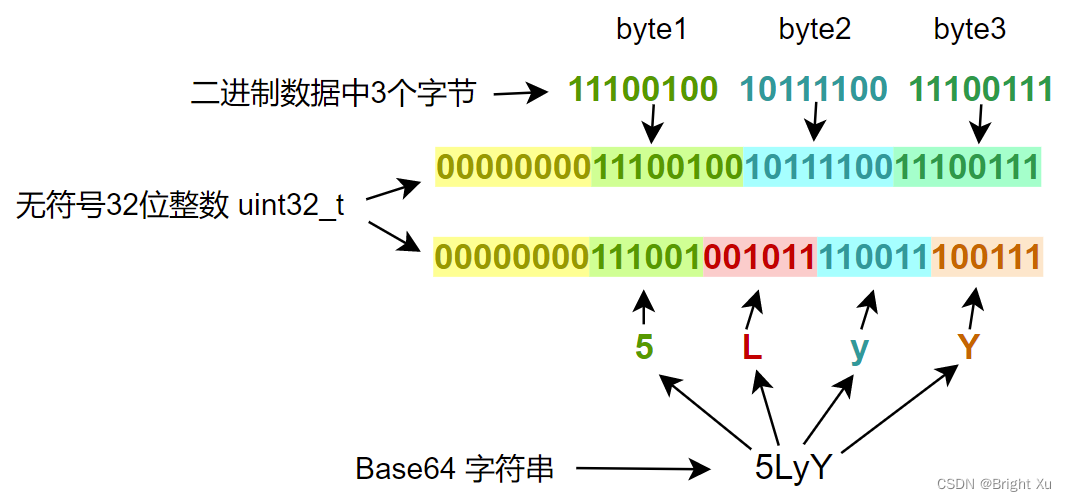
实现
#include "base64.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
#ifndef CEIL_POS
// 正数向上取整 CEIL_POS(2.345) => 3
#define CEIL_POS(X) (X > (uint64_t)(X) ? (uint64_t)(X+1) : (uint64_t)(X))
#endif
char *base64encode(const char *str, uint64_t len) {
uint64_t length = CEIL_POS(len * 4 / 3) + 1;
char *base64Chars = (char *) malloc(sizeof(char) * length);
uint64_t idx = 0;
for (uint64_t i = 0; i < len; i += 3) {
uint32_t byte1 = (uint8_t) str[i];
uint16_t byte2 = (i + 1 < len) ? (uint8_t) str[i + 1] : 0;
uint8_t byte3 = (i + 2 < len) ? (uint8_t) str[i + 2] : 0;
uint32_t triplet = (byte1 << 16) | (byte2 << 8) | byte3;
for (uint64_t j = 0; (j < 4) && (i + j * 0.75 < len); j++) {
base64Chars[idx] = BASE64_MAP[(triplet >> (6 * (3 - j))) & 0x3f];
idx++;
}
}
char paddingChar = BASE64_MAP[64];
if (paddingChar) {
while (idx % 4) {
base64Chars[idx] = paddingChar;
idx++;
}
}
base64Chars[idx] = 0;
return base64Chars;
}
char *base64parse(const char *base64Str, uint64_t len) {
while (base64Str[len - 1] == BASE64_MAP[64]) {
len--;
}
uint64_t length = CEIL_POS(len * 3 / 4) + 1;
char *str = (char *) malloc(sizeof(char) * length);
uint64_t idx = 0;
for (uint64_t i = 0; i < len; i += 4) {
uint32_t triplet = 0;
for (uint8_t j = 0; j < 4; ++j) {
if (i + j < len) triplet = (triplet << 6) | ((uint8_t) BASE64_REVERSE_MAP[base64Str[i + j]] & 0x3f);
else triplet = triplet << 6;
}
for (uint8_t j = 0; (j < 3); ++j) {
str[idx] = (triplet >> (8 * (2 - j))) & 0xff;
idx++;
}
}
str[idx] = 0;
return str;
}
使用
// test_b64.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "base64.h"
int main() {
char str1[] = "Man is distinguished, not only by his reason, but by this singular passion from other animals, which is a lust of the mind, that by a perseverance of delight in the continued and indefatigable generation of knowledge, exceeds the short vehemence of any carnal pleasure.";
char *encoded = base64encode(str1, strlen(str1));
puts(encoded);
char str2[] = "TWFuIGlzIGRpc3Rpbmd1aXNoZWQsIG5vdCBvbmx5IGJ5IGhpcyByZWFzb24sIGJ1dCBieSB0aGlzIHNpbmd1bGFyIHBhc3Npb24gZnJvbSBvdGhlciBhbmltYWxzLCB3aGljaCBpcyBhIGx1c3Qgb2YgdGhlIG1pbmQsIHRoYXQgYnkgYSBwZXJzZXZlcmFuY2Ugb2YgZGVsaWdodCBpbiB0aGUgY29udGludWVkIGFuZCBpbmRlZmF0aWdhYmxlIGdlbmVyYXRpb24gb2Yga25vd2xlZGdlLCBleGNlZWRzIHRoZSBzaG9ydCB2ZWhlbWVuY2Ugb2YgYW55IGNhcm5hbCBwbGVhc3VyZS4=";
char *decoded = base64parse(str2, strlen(str2));
puts(decoded);
return 0;
}
Base32 编解码
定义头文件 base32.h
#ifndef _BASE32_H
#define _BASE32_H
#include <stdint.h>
static const char BASE32_MAP[] = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ234567=";
static const uint8_t BASE32_REVERSE_MAP[] = {
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6,
7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25,
};
char *base32encode(const char *str, uint64_t len);
char *base32parse(const char *base32Str, uint64_t len);
#endif //_BASE32_H
思路
Base32编码就是用32个可打印字符表示二进制数据。
32
=
2
5
32 = 2^5
32=25,所以需要5 Bit来表示一个base32字符。一个字节8 Bit,5和8的最小公倍数是40。编码的过程中,以5个字节为一组转为8个base32字符,不足5个字节以0代替。为方便转换,以一个无符号64位整数(uint64_t)为中间载体。先由高位到低位将这5个字节填充到这个整数中,然后由高位到低位依次读取5位,获取对应数值的字母,共读取8次。如下图所示。解码的过程是上述的逆过程。
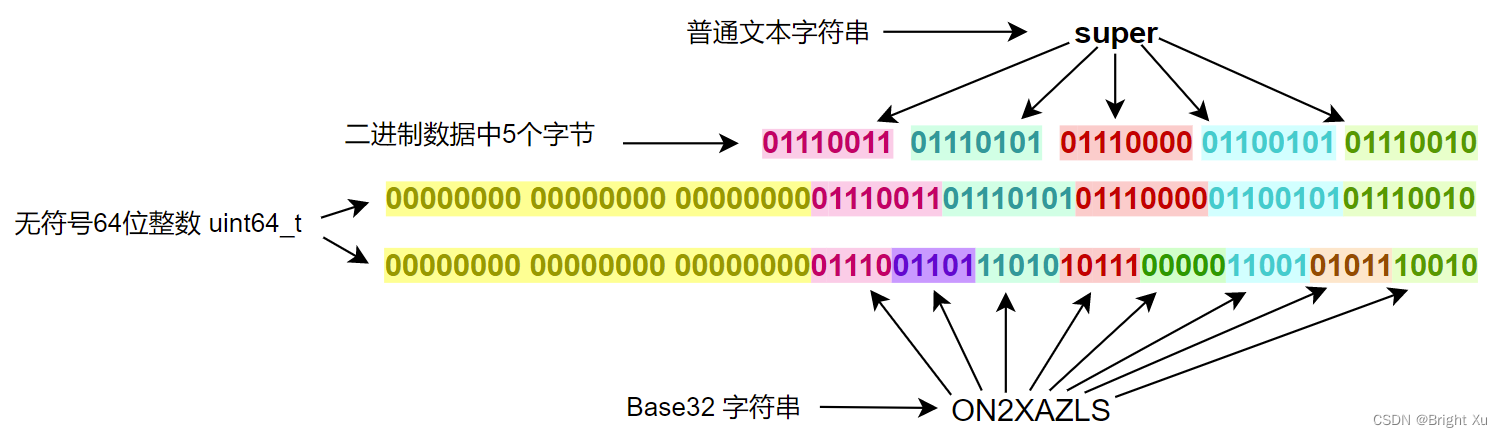
实现
#include "base32.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
#ifndef CEIL_POS
#define CEIL_POS(X) (X > (uint64_t)(X) ? (uint64_t)(X+1) : (uint64_t)(X))
#endif
char *base32encode(const char *str, uint64_t len) {
uint64_t length = CEIL_POS(len * 8 / 5) + 1;
char *base32Chars = (char *) malloc(sizeof(char) * length);
uint64_t idx = 0;
for (uint64_t i = 0; i < len; i += 5) {
uint64_t byte1 = (uint8_t) str[i];
uint64_t byte2 = (i + 1 < len) ? (uint8_t) str[i + 1] : 0;
uint32_t byte3 = (i + 2 < len) ? (uint8_t) str[i + 2] : 0;
uint16_t byte4 = (i + 3 < len) ? (uint8_t) str[i + 3] : 0;
uint8_t byte5 = (i + 4 < len) ? (uint8_t) str[i + 4] : 0;
uint64_t quintuple = (byte1 << 32) | (byte2 << 24) | (byte3 << 16) | (byte4 << 8) | byte5;
for (uint64_t j = 0; (j < 8) && (i + j * 0.625 < len); j++) {
base32Chars[idx] = BASE32_MAP[(quintuple >> (5 * (7 - j))) & 0x1f];
idx++;
}
}
char paddingChar = BASE32_MAP[32];
if (paddingChar) {
while (idx % 8) {
base32Chars[idx] = paddingChar;
idx++;
}
}
base32Chars[idx] = 0;
return base32Chars;
}
char *base32parse(const char *base32Str, uint64_t len) {
while (base32Str[len - 1] == BASE32_MAP[32]) {
len--;
}
uint64_t length = CEIL_POS(len * 5 / 8) + 1;
char *str = (char *) malloc(sizeof(char) * length);
uint64_t idx = 0;
for (uint64_t i = 0; i < len; i += 8) {
uint64_t quintuple = 0;
for (uint8_t j = 0; j < 8; ++j) {
if (i + j < len) quintuple = (quintuple << 5) | ((uint8_t) BASE32_REVERSE_MAP[base32Str[i + j]] & 0x1f);
else quintuple = quintuple << 5;
}
for (uint8_t j = 0; (j < 5); ++j) {
str[idx] = (quintuple >> (8 * (4 - j))) & 0xff;
idx++;
}
}
str[idx] = 0;
return str;
}
使用
// test_b32.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "base32.h"
int main() {
char str1[] = "Man is distinguished, not only by his reason, but by this singular passion from other animals, which is a lust of the mind, that by a perseverance of delight in the continued and indefatigable generation of knowledge, exceeds the short vehemence of any carnal pleasure.";
char *encoded = base32encode(str1, strlen(str1));
puts(encoded);
char str2[] = "JVQW4IDJOMQGI2LTORUW4Z3VNFZWQZLEFQQG433UEBXW43DZEBRHSIDINFZSA4TFMFZW63RMEBRHK5BAMJ4SA5DINFZSA43JNZTXK3DBOIQHAYLTONUW63RAMZZG63JAN52GQZLSEBQW42LNMFWHGLBAO5UGSY3IEBUXGIDBEBWHK43UEBXWMIDUNBSSA3LJNZSCYIDUNBQXIIDCPEQGCIDQMVZHGZLWMVZGC3TDMUQG6ZRAMRSWY2LHNB2CA2LOEB2GQZJAMNXW45DJNZ2WKZBAMFXGIIDJNZSGKZTBORUWOYLCNRSSAZ3FNZSXEYLUNFXW4IDPMYQGW3TPO5WGKZDHMUWCAZLYMNSWKZDTEB2GQZJAONUG64TUEB3GK2DFNVSW4Y3FEBXWMIDBNZ4SAY3BOJXGC3BAOBWGKYLTOVZGKLQ=";
char *decoded = base32parse(str2, strlen(str2));
puts(decoded);
return 0;
}






















 252
252











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








