提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档
文章目录
JDBC
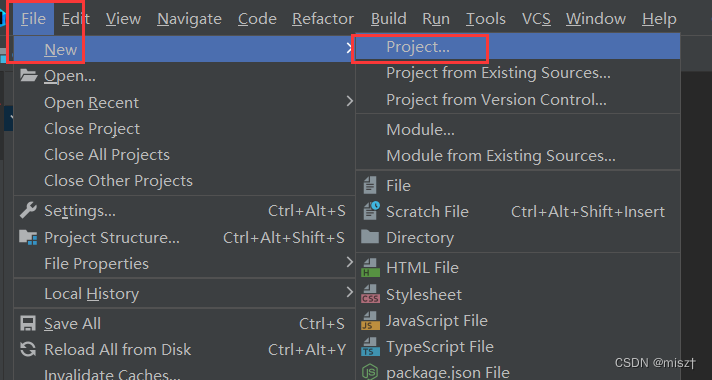
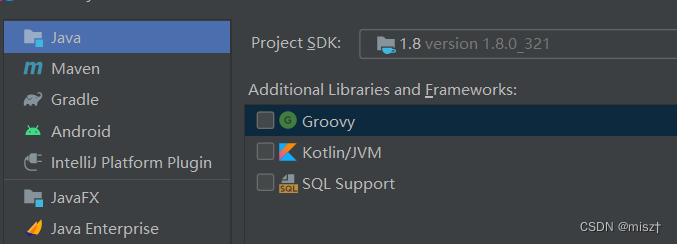
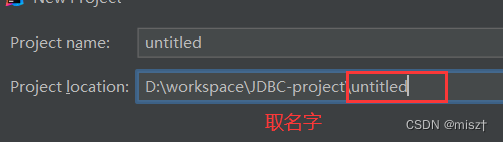
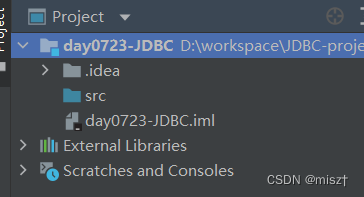
1.JDBC概念
JDBC是一种用于执行SQL语句的Java API(开发接口)。可以为多种关系型数据库提供统一的访问。
JDBC本身就是由Java语言编写的。
2.JDBC本质
其实JDBC是Java官方提供的一套规范(接口)。用于帮助程序员快速的实现不同数据库的链接和操作
3.JDBC入门
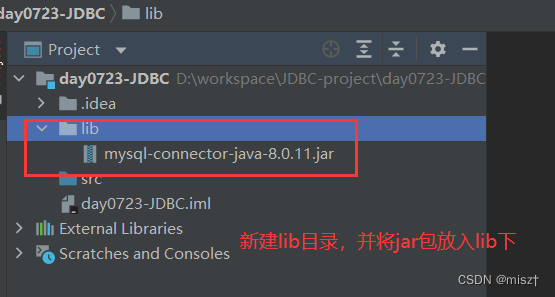
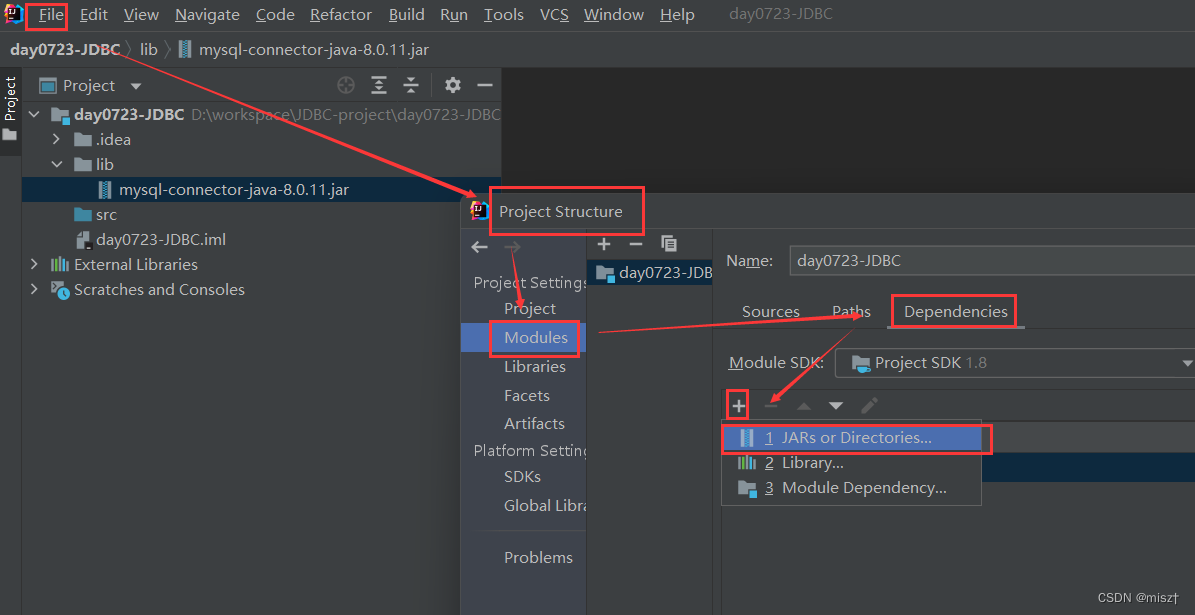
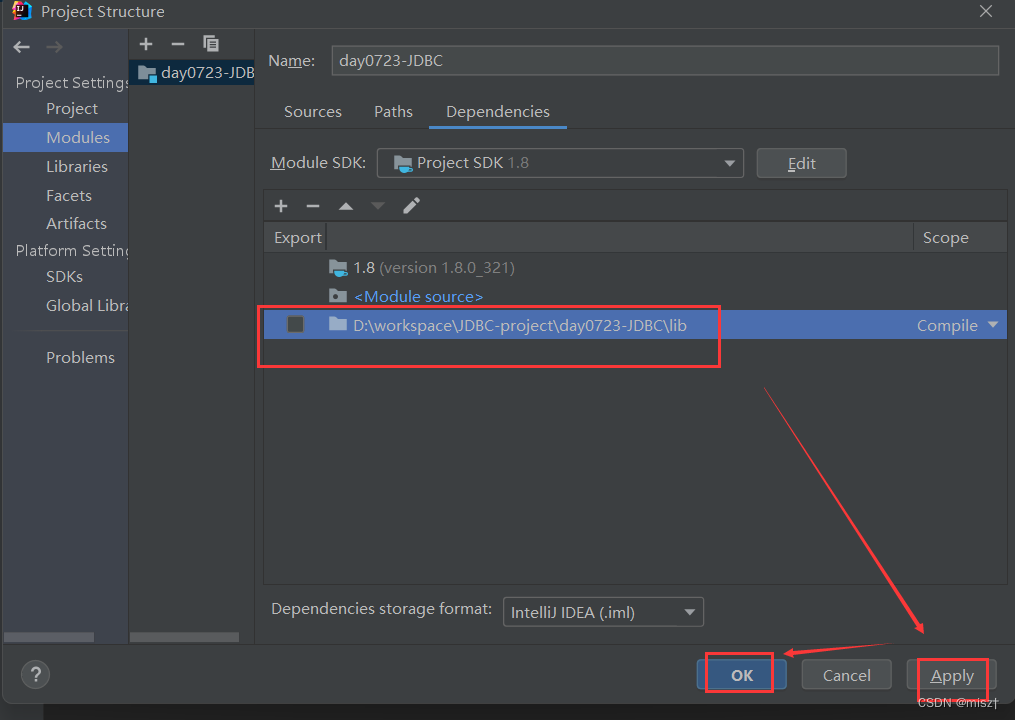
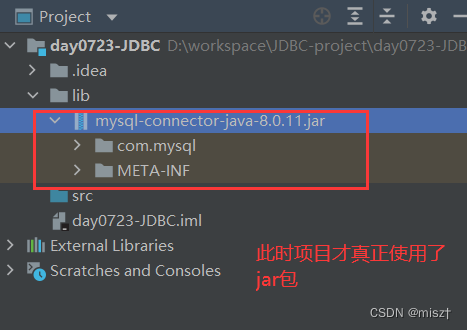
3.1 导入依赖
我的jar包的文件路径:D:\workspace\implement
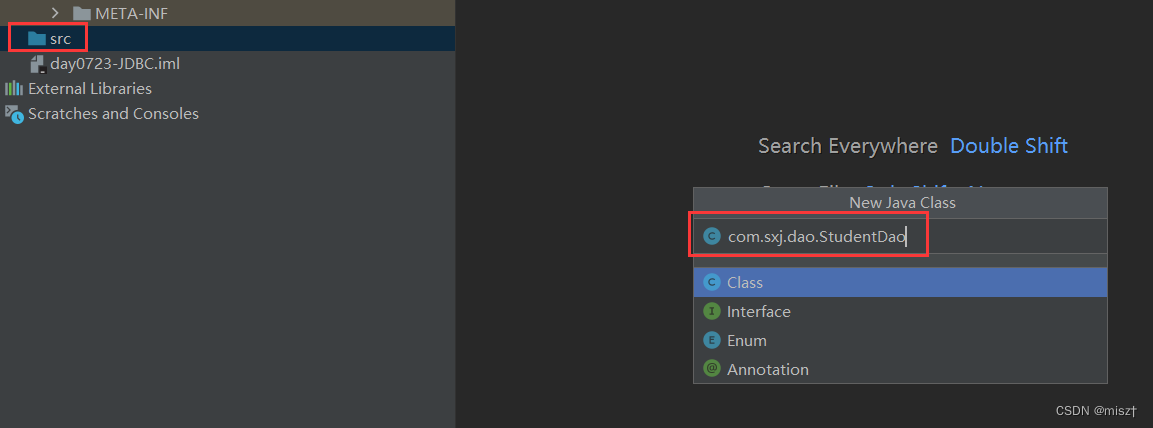
3.2 注册驱动
com.sxj.dao.StudentDao
package com.sxj.dao;
public class StudentDao {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
}
}
3.3 获取链接
//3.获取链接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/school?characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=UTC","root", "1234");
3.4 获取执行对象
3.5 执行SQL并且返回结果
3.6 处理结果
3.7 释放资源
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//2.注册驱动 反射机制
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//3.获取链接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/school?characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=UTC",
"root", "1234");
//获取执行对象
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
//拼写SQL
String sql = "select * from student";
//执行SQL并且接收返回结果
ResultSet rs = statement.executeQuery(sql);
//处理结果
while(rs.next()){
int student_id = rs.getInt("student_id");
String student_name = rs.getString("student_name");
String student_gender = rs.getString("student_gender");
Date birthday = rs.getDate("birthday");
String address = rs.getString("address");
String student_card = rs.getString("student_card");
System.out.println(student_id+","+student_name+","+student_gender+","+
birthday+","+address+","+student_card);
}
//释放资源
rs.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
4.JDBC API详解
在MySQL的JDBC驱动中,com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver和com.mysql.jdbc.Driver`是不同版本的驱动程序,并且存在一些区别。
com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver是MySQL Connector/J
8.x版本的驱动程序。这是MySQL官方推荐的最新版本,具有更好的性能和功能。它支持新的连接协议(如MySQL协议8.0和X协议),具有更好的兼容性和安全性,还包含了一些新特性(例如支持数据类型的时区转换)。此外,Connector/J
8.x还引入了新的配置属性和一些改进。
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver是MySQL Connector/J
5.x版本的驱动程序。这是过时的版本,不再被MySQL官方支持和推荐使用。虽然它仍然能够正常工作,但可能存在较旧的缺陷和限制,不支持新的特性和协议。因此,推荐使用
com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver,以获得更好的性能和功能,并且确保与最新的MySQL版本兼容。如果你正在迁移应用程序,需要注意更新相关的连接字符串和配置属性。
4.1DriverManager:驱动管理对象
作用:注册驱动(告诉程序使用哪一个数据库驱动)
mysql5以后的数据库连接可以省略注册驱动的步骤。因为在jar中存在一个java.sql.Driver的配置文件,此配置文件中指定了驱动的配置。
获取数据库连接对象的方法(getConnection())
getConnection()
返回值:Connection对象
参数:url(数据库地址) jdbc:mysql://ip地址:端口号/数据库名?参数…;
user:用户名;password:密码
4.2Connection
作用1:获取执行对象
普通执行对象:使用createStatement()获取Statement对象
预编译执行对象:prepareStatement()方法获取prepareStatement对象
预编译对象(可以调用存储过程):prepareCall()获取CallableStatement对象
作用2::事务管理
开启事务:setAutoCommit(boolean); 参数为false的时候则开启事务
提交事务:commit();
回滚事务:rollback();
作用3:释放资源
close()
//3.获取链接
// 参数:url(数据库地址) jdbc:mysql://ip地址:端口号/数据库名?参数...;user:用户名;password:密码
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/school?characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=UTC",
"root", "123456");
// Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/day0721?characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=UTC",
// "root", "123456");
// 4.获取执行对象
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
// 拼写SQL
String sql = "select * from student";
// 开启事务
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
// 提交事务
// ResultSet rs = statement.executeQuery(sql);
connection.commit();
// 回滚事务
// 执行并且接收返回结果
ResultSet rs = statement.executeQuery(sql);
4.3 Statement
执行DML:进行insert,update,delete操作使用的executeUpdate(sql)。返回int
执行DQL:进行select操作的时候使用executeQuery(sql)。返回的是ResultSet
4.4 ResultSet
判断结果集中是否还存在数据:next();
返回true:说明当前索引还有数据,并且将索引下移
返回false:说明结果集中已经没有数据
getXXX(String 字段名):根据结果集中的字段名获取对应的数据
getXXX(int 字段索引):根据结果集中的字段索引获取对应的数据
5.JDBC完成CRUD
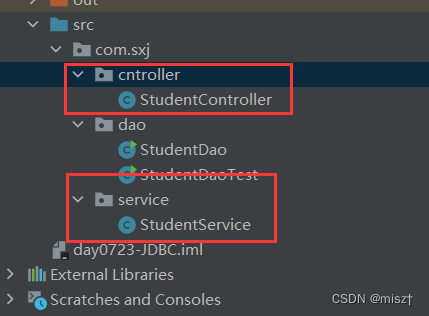
用户请求—>业务层Service---->控制层controller—>dao层—>数据库
prepareStatement和createStatement的区别
prepareStatement和createStatement都是用于执行SQL语句的方法,但它们之间有一些重要的区别。
-
语法结构:
createStatement方法用于创建一个Statement对象,该对象用于执行静态的SQL语句。而prepareStatement方法用于创建一个PreparedStatement对象,该对象用于执行带有参数的SQL语句。 -
预编译:
prepareStatement方法在执行之前会预编译SQL语句,将其编译为一个可重复使用的执行计划。这样做的好处是可以提高执行效率,并且防止SQL注入攻击。而createStatement方法在执行每个SQL语句时都会进行编译,不会进行预编译。 -
参数绑定:
prepareStatement方法允许你使用占位符(如?)来代表参数,在执行之前,你可以使用setXXX()方法将实际的参数值绑定到占位符上。这样做的好处是可以方便地处理参数,并且避免了拼接字符串引起的安全问题。而createStatement方法不支持参数绑定,你需要手动将参数值拼接到SQL语句中。 -
执行效率:由于
prepareStatement方法预编译了SQL语句,因此在重复执行相同的SQL语句时,PreparedStatement对象的执行速度通常会比Statement对象更快。这对于需要反复执行的SQL语句来说是非常有用的。
基于这些区别,通常情况下,如果你需要执行动态的、带有参数的SQL语句,你应该使用prepareStatement方法。如果你只需要执行静态的SQL语句,则可以使用createStatement方法。而且,由于prepareStatement具有更好的性能和安全性,它更受推荐和广泛使用。
executeUpdate()和executeQuery()
executeUpdate()和executeQuery()都是用于执行SQL语句的方法,但它们之间有一些重要的区别。
-
返回值类型:
executeUpdate()方法返回一个整数,表示受影响的行数 (即执行 INSERT、UPDATE 或 DELETE 语句时影响的行数)。而executeQuery()方法返回一个ResultSet对象,其中包含了查询结果的数据。 -
使用场景:
executeUpdate()方法通常用于执行更新数据库的操作,如插入数据、修改数据或删除数据。它不适用于执行查询操作。而executeQuery()方法用于执行查询语句,获取查询结果。 -
参数传递:
executeUpdate()方法不支持参数传递,因此你需要在SQL语句中直接写入参数的值。而executeQuery()方法可以与PreparedStatement一起使用,允许你使用占位符(如?)作为参数,并使用setXXX()方法将实际的参数值绑定到占位符上。 -
结果处理:
executeUpdate()方法执行后,可以使用返回的受影响行数进行进一步处理,例如判断是否有成功执行的操作。而executeQuery()方法执行后,你需要通过遍历ResultSet对象来获取查询的结果集。
总结来说,executeUpdate()方法适用于更新数据库操作,而executeQuery()方法适用于查询操作。你应该根据你的具体需求选择正确的方法进行执行。需要注意的是,无论是哪种方法,在执行前都需要使用Statement或PreparedStatement对象将SQL语句发送给数据库。
5.1 查看所有
public List<Student> findAllStudent() {
Connection conn=null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet rs=null;
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
try {
conn= DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/school?characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=UTC",
"root", "1234");
statement=conn.createStatement();
String sql = "select * from student";
rs = statement.executeQuery(sql);
while(rs.next()){
Student student = new Student();
student.setStudentId(rs.getInt("student_id"));
student.setStudentName(rs.getString("student_name"));
student.setStudentGender(rs.getString("student_gender"));
student.setBirthday(rs.getDate("birthday"));
student.setAddress(rs.getString("address"));
student.setGradeId(rs.getInt("grade_id"));
student.setStudentCard(rs.getString("student_card"));
list.add(student);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if (rs != null) {
rs.close();
}
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return list;
}
5.2 条件查询
public List<Student> findStudentByGender(String gender){
Connection conn=null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet rs=null;
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
try {
conn= DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/school?characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=UTC",
"root", "1234");
//拼接sql写法 缺点:会造成sql注入 sql没有参数的时候使用
// select * from user where uname=root and upwd= 1 or 1=1
/* statement=conn.createStatement();
String sql = "select * from student where student_gender="+gender;
rs = statement.executeQuery(sql);*/
//预编译 有占位符的 sql有参数的时候使用
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement("select * from student where student_gender=?");
ps.setString(1,gender);
rs = ps.executeQuery();
while(rs.next()){
Student student = new Student();
student.setStudentId(rs.getInt("student_id"));
student.setStudentName(rs.getString("student_name"));
student.setStudentGender(rs.getString("student_gender"));
student.setBirthday(rs.getDate("birthday"));
student.setAddress(rs.getString("address"));
student.setGradeId(rs.getInt("grade_id"));
student.setStudentCard(rs.getString("student_card"));
list.add(student);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if (rs != null) {
rs.close();
}
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return list;
}
5.3 添加
public Integer addStudent(Student student){
//注册驱动
//获取链接对象
//获取执行对象
//执行sql
//处理结果
Connection conn=null;
Integer i = null;
PreparedStatement ps=null;
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/school?characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai", "root", "1234");
ps = conn.prepareStatement("insert into student (student_name,student_gender,birthday,address,grade_id,student_card) VALUES(?,?,?,?,?,?)");
//给占位符赋值
ps.setString(1,student.getStudentName());
ps.setString(2,student.getStudentGender());
//参数需要的java.sql.Date 实例化此对象需要的long的数据
//student.getBirthday()得到的是java.util.Date类型数据
ps.setDate(3,new java.sql.Date(student.getBirthday().getTime()));
ps.setString(4,student.getAddress());
ps.setInt(5,student.getGradeId());
ps.setString(6,student.getStudentCard());
i = ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if (ps != null) {
ps.close();
}
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return i;
}
5.4修改
public Integer updateStudentById(Student student){
Connection conn=null;
Integer i = null;
PreparedStatement ps=null;
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/school?characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai", "root", "1234");
ps = conn.prepareStatement("update student set student_name=?,student_gender=?,birthday=?,address=?,grade_id=?,student_card=? where student_id=?");
//给占位符赋值
ps.setString(1,student.getStudentName());
ps.setString(2,student.getStudentGender());
//参数需要的java.sql.Date 实例化此对象需要的long的数据
//student.getBirthday()得到的是java.util.Date类型数据
ps.setDate(3,new java.sql.Date(student.getBirthday().getTime()));
ps.setString(4,student.getAddress());
ps.setInt(5,student.getGradeId());
ps.setString(6,student.getStudentCard());
ps.setInt(7,student.getStudentId());
i = ps.executeUpdate();//更新的语句
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if (ps != null) {
ps.close();
}
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return i;
}
5.5 删除
public Integer deleteStudentById(Integer studentId){
Connection conn=null;
Integer i = null;
PreparedStatement ps=null;
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/school?characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai", "root", "1234");
ps = conn.prepareStatement("delete from student where student_id=?");
ps.setInt(1,studentId);
i = ps.executeUpdate();//更新的语句
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if (ps != null) {
ps.close();
}
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return i;
}
5.6模糊查询
public List<Student> findStudentLikeName(String LikeName){
Connection conn=null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs=null;
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
try {
conn= DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/school?characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=UTC",
"root", "1234");
ps=conn.prepareStatement("select * from student where student_name like ?");
ps.setString(1,LikeName);
rs = ps.executeQuery();
while(rs.next()){
Student student = new Student();
student.setStudentId(rs.getInt("student_id"));
student.setStudentName(rs.getString("student_name"));
student.setStudentGender(rs.getString("student_gender"));
student.setBirthday(rs.getDate("birthday"));
student.setAddress(rs.getString("address"));
student.setGradeId(rs.getInt("grade_id"));
student.setStudentCard(rs.getString("student_card"));
list.add(student);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if (rs != null) {
rs.close();
}
if (ps != null) {
ps.close();
}
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return list;
}
5.7 分页
public List<Student> findStudentByPage(Integer index){
Connection conn=null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs=null;
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();
try {
conn= DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/school?characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=UTC",
"root", "1234");
ps=conn.prepareStatement("select * from student limit ?,2");
ps.setInt(1,index);
rs = ps.executeQuery();
while(rs.next()){
Student student = new Student();
student.setStudentId(rs.getInt("student_id"));
student.setStudentName(rs.getString("student_name"));
student.setStudentGender(rs.getString("student_gender"));
student.setBirthday(rs.getDate("birthday"));
student.setAddress(rs.getString("address"));
student.setGradeId(rs.getInt("grade_id"));
student.setStudentCard(rs.getString("student_card"));
list.add(student);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if (rs != null) {
rs.close();
}
if (ps != null) {
ps.close();
}
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return list;
}
数据库连接池和事务
1.原生的JDBC存在的问题
频繁的创建和销毁链接
读取数据比较繁琐
异常在持久化层处理
2.DBCP数据库连接池
下载教程:
https://www.cnblogs.com/seansheep/p/12894208.html
apache jar包下载地址:
https://commons.apache.org/proper/
commons-beanutils-1.9.1.jar下载:https://nowjava.com/jar/path/commons-beanutils/commons-beanutils/1.9.1.html
mysql-connector jar下载:
https://blog.csdn.net/T_Y_F_/article/details/125194749
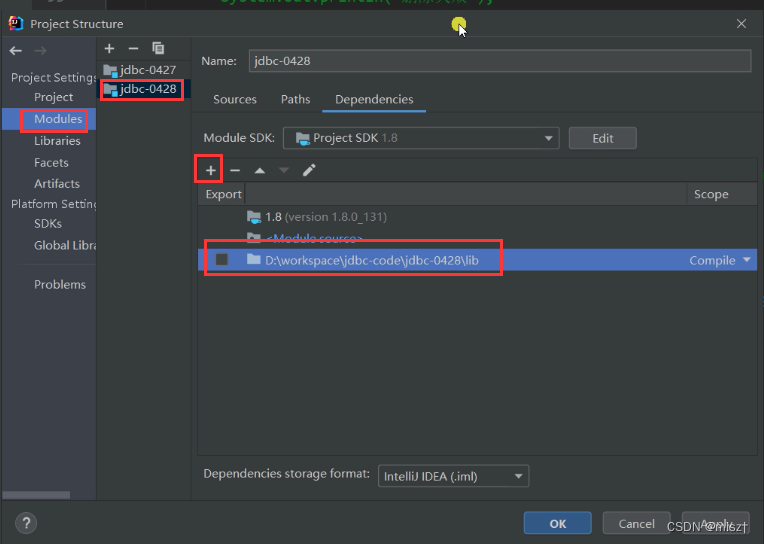
2.1 导入依赖
2.2查看DBCP常见的属性
| 属性名 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| driverClassName | 数据库驱动类名 | |
| url | 数据库地址 | |
| username | 数据库用户名 | |
| password | 数据库密码 | |
| initialSize | 0 | 连接池初始化生成的连接数 |
| minIdle | 0 | 连接池中保持的最小空闲连接数(如果不足则补上) |
| maxIdle | 8 | 连接池中保持的最大空闲连接数。超过了的释放 |
| maxActive | 8 | 链接池中支持最大活动连接数 |
| maxWait | -1 | 当连接池中没有空闲连接时的最大等待时间(毫秒) |
| testOnBorrow | true | 借出链接的时候是否校验,默认校验,建议设置false |
| testOnReturn | false | 归还链接的时候是否校验。默认不校验 |
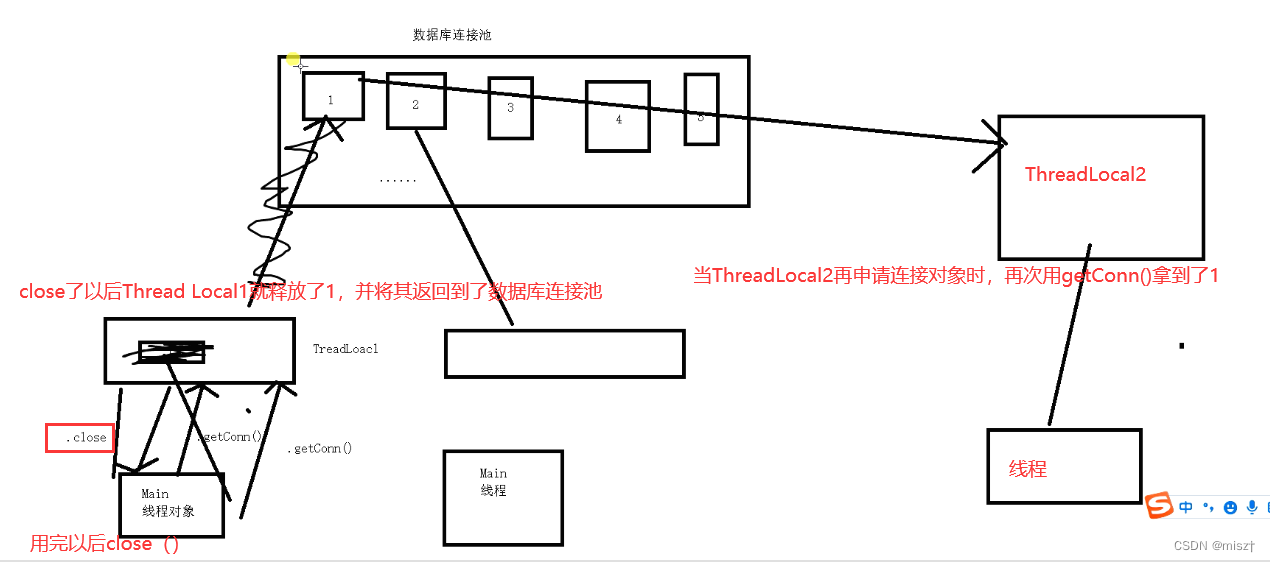
2.3 ThreadLocal
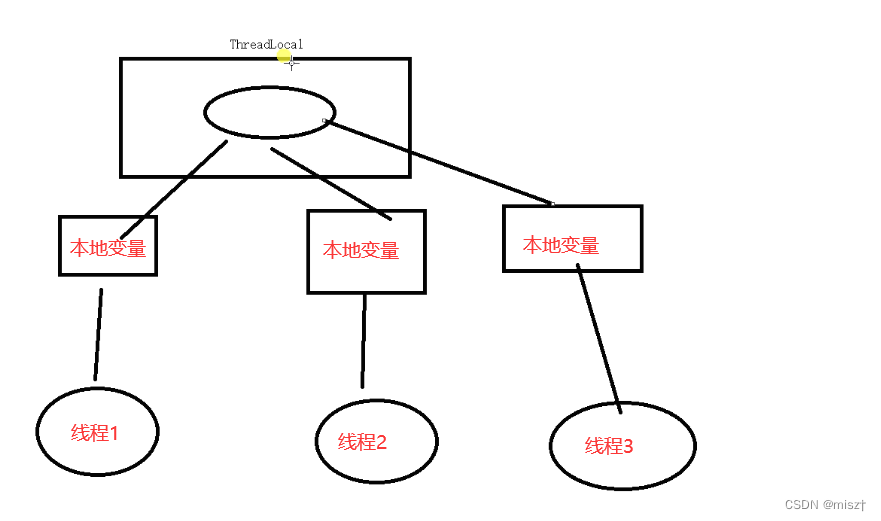
多线程访问同一个共享变量的时候会出现并发问题。特别是多个线程对一个变量进行写入操作的时候,为了解决这个问题一般程序员都对共享变量操作的时候都会添加额外的同步操作。上述操作可以解决线程的安全。但是效率会降低。为了完美解决上述存在的问题,可以使用ThreadLocal。
ThreadLocal是JDK提供的。它是提供线程本地变量,如果创建了一个ThreadLocal变量,那么访问这个变量的线程就会变成一个副本。在实际多线程开发中操作的都是本地内存中的副本变量,从而解决线程安全问题。
package com.sxj.util;
import org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource;
import org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSourceFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Properties;
// 工具类
public class ConnUtil {
创建链接
// public void getConn() {
// Properties properties = new Properties();
// InputStream inputStream = ConnUtil.class.getResourceAsStream("/mysql.properties");
// try {
// properties.load(inputStream);
// DataSource dataSource = BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
// Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
// } catch (Exception e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
BasicDataSource basicDataSource = new BasicDataSource();
// protected boolean testOnBorrow = true; //借出
// protected boolean testOnReturn = false; //归还
BasicDataSourceFactory dataSource = new BasicDataSourceFactory();
//----------------------------------------------------------------------
private static ThreadLocal<Connection> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal();
private static DataSource dataSource;
//在静 态块中对资源文件进行加载并且创建数据源对象
static {
try {
Properties properties = new Properties();
InputStream inputStream = ConnUtil.class.getResourceAsStream("/mysql.properties");
properties.load(inputStream);
//使用资源创建数据源对象
dataSource = BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//获取数据库连接对象
public static Connection getConn() throws SQLException {
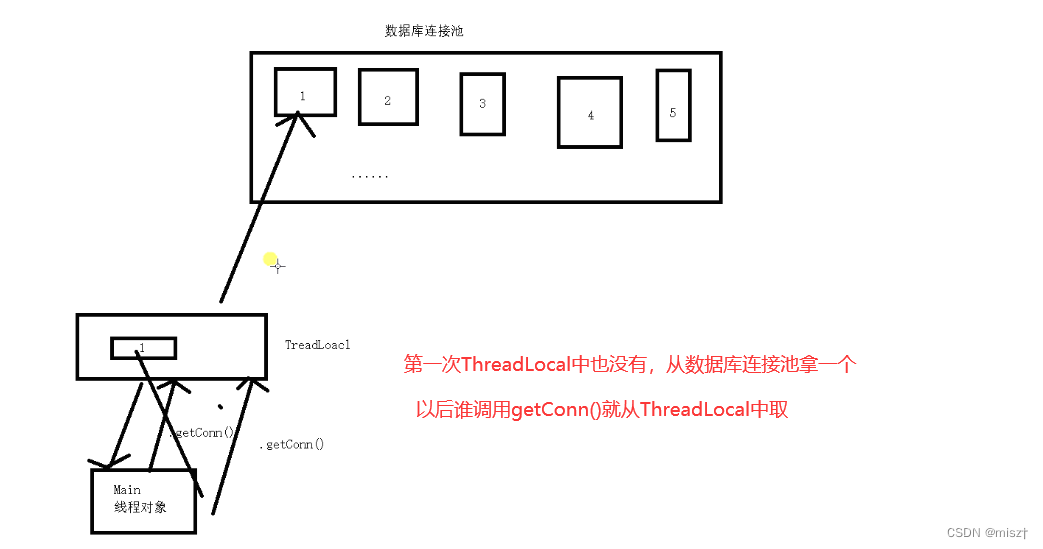
Connection connection = threadLocal.get();//除了第一次,接下来每一次都是从theadLocal获取副本
// 抛出异常,谁调用getConn()谁处理异常
if (connection==null || connection.isClosed()){
connection=dataSource.getConnection();
threadLocal.set(connection);
}
return connection;
}
//关闭数据库连接对象
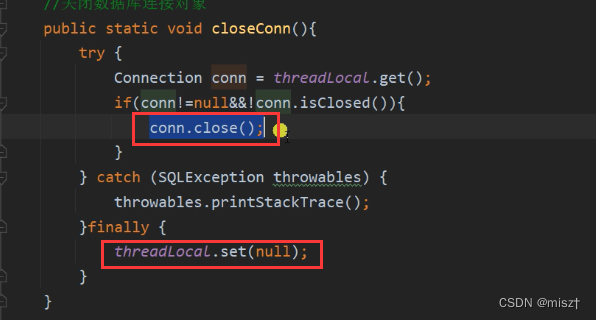
public static void closeConn(){
Connection connection = threadLocal.get();
try {
if (connection!=null && !connection.isClosed()){//不为空且没有关流
connection.close();//手动关闭
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
threadLocal.set(null);//set将值设为null
}
}
}
多表联查
ConnUtil.java
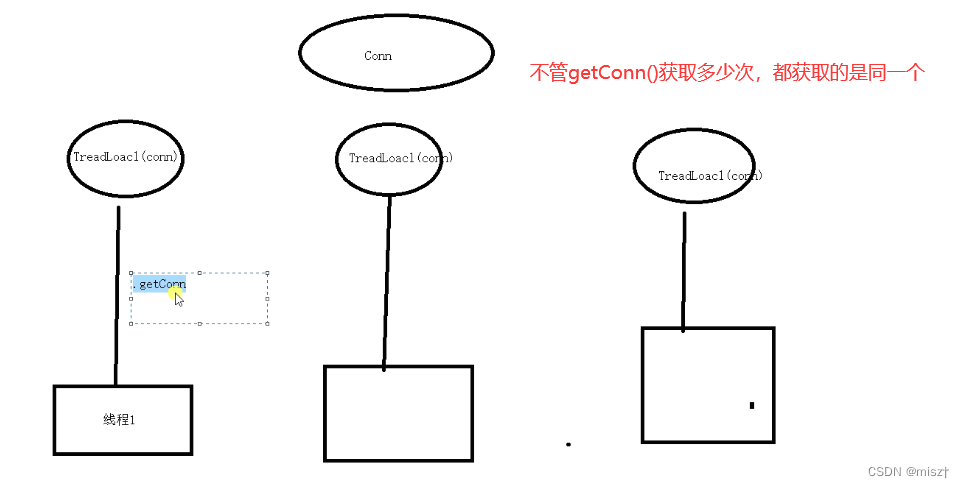
并发的时候,每一个线程得到的是从连接池中获取的连接对象,接下俩此线程不管申请多少个连接,都是同一个连接
package com.sxj.util;
import org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource;
import org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSourceFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Properties;
// 工具类
public class ConnUtil {
private static ThreadLocal<Connection> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal();
private static DataSource dataSource;
//在静态块中对资源文件进行加载并且创建数据源对象
static {
InputStream inputStream =null;
try {
Properties properties = new Properties();
inputStream = ConnUtil.class.getResourceAsStream("/mysql.properties");
// System.out.println(inputStream);
properties.load(inputStream);
// // 获取属性值
// String driverClassName = properties.getProperty("driverClassName");
// String url = properties.getProperty("url");
// String username = properties.getProperty("username");
// String password = properties.getProperty("password");
// System.out.println("driverClassName="+driverClassName+",url="+url+",username="+username+",password="+password);
//使用资源创建数据源对象
dataSource = BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);//真正的数据库连接池
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
// 关闭输入流
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//获取数据库连接对象
public static Connection getConn() throws SQLException {
Connection connection = threadLocal.get();//除了第一次,接下来每一次都是从theadLocal获取副本
// 抛出异常,谁调用getConn()谁处理异常
if (connection == null || connection.isClosed()) {
connection = dataSource.getConnection();//从数据库连接池中获取一个连接
threadLocal.set(connection);
}
return connection;
}
//关闭数据库连接对象
public static void closeConn() {
try {
Connection connection = threadLocal.get();
if (connection != null && !connection.isClosed()) {//不为空且没有关流
connection.close();//手动关闭
}
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {
threadLocal.set(null);//set将值设为null
}
}
}
package com.sxj.entity.pojo;
import com.sxj.entity.Grade;
import com.sxj.entity.Student;
public class StudentAndGrade {
private Student student;
private Grade grade;
public StudentAndGrade() {
}
public StudentAndGrade(Student student, Grade grade) {
this.student = student;
this.grade = grade;
}
public Student getStudent() {
return student;
}
public void setStudent(Student student) {
this.student = student;
}
public Grade getGrade() {
return grade;
}
public void setGrade(Grade grade) {
this.grade = grade;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "StudentAndGrade{" +
"student=" + student +
", grade=" + grade +
'}';
}
}
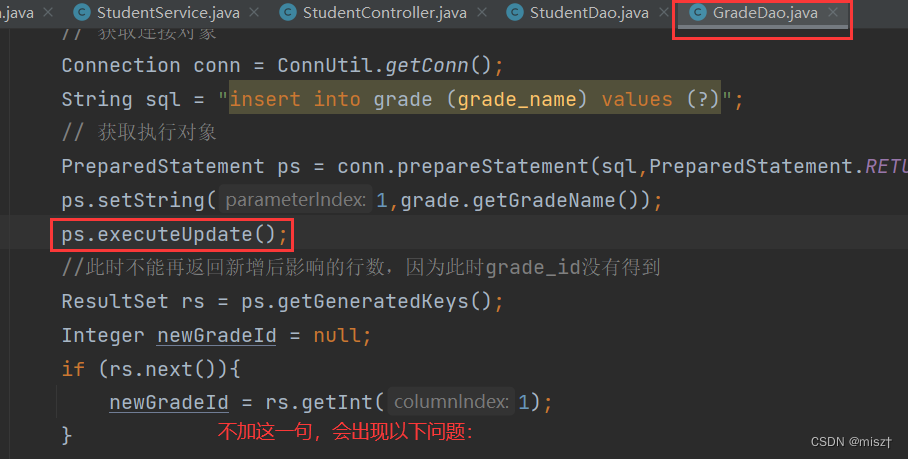
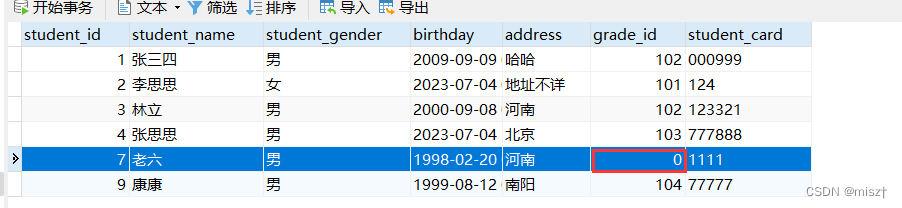
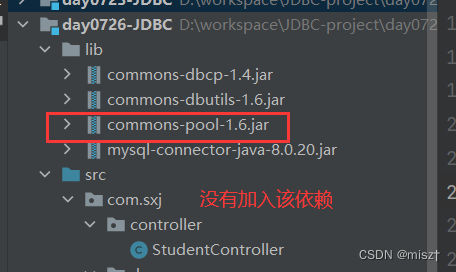
报错:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError:
Could not initialize class com.sxj.util.ConnUtil
原因:


























 812
812











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










