标题:基于SUMO的动态路径规划对车辆通信的影响评估
ABSTRACT:
Simulations are the first approach used by the research community
to evaluate mobile ad hoc networks.(仿真是研究团体用来评估自组织网络的第一种方法)。
Particularly, vehicular ad hoc networks (V ANETs) are a singular type of mobile ad hoc networks
that raise technical challenges, for instance, in the context of vehic-ular mobility models. (特别是,车辆移动自组织网络(vanet)是一种单一类型的移动自组织网络,在车辆移动模型方面提出来技术挑战)
When assessing V ANETs, realistic vehicular models are essential to produce meaningful evaluation results. (在评估车辆模型时,真实的车辆模型对产生有意义的评估结果至关重要)
In this context, realistic vehicles’ mobility includes re-routing capabili-
ties that allow vehicles to re-compute their routes in front of specific
traffic conditions (e.g., traffic jams).(在这种情况下,现实车辆的移动性包括重新路由功能,允许车辆在特定的交通条件(如交通堵塞)面前重新计算自己的路线。)
In this paper, we provide a thorough analysis of the influence of enabling re-routing properties
on (i) the mobility of the vehicle and (ii) on the connections of the vehicular network. (在本文中,我们深入分析了启用重路由属性对(i)车辆的移动性和(ii)车辆网络连接的影响)
For this, we use the road traffic simulator SUMO to generate vehicular traces, and then we will analyze the connectivity of the vehicular network employing well-known graph metrics.(为此,我们使用道路交通模拟器SUMO生成车辆轨迹,然后我们将使用著名的图形度量来分析车辆网络的连通性。)
Our results provide insights about the behavior of the vehicle’s mobility and the nodes’ connectivity.我们的结果提供了有关车辆移动和节点连通性的见解。
1.INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, simulation is the first approach researchers follow to assess the performance of vehicular networks.(目前模拟是研究人员评估车辆网络性能的第一种方法)While the deployment of real test scenarios is infeasible in most cases (they arecomplex and costly), simulation techniques are commonly used tostudy vehicular network protocols and services for intelligent transportation systems (ITS).( 虽然真实测试场景部署在大多数情况下是不可行的(它们既复杂又昂贵)但仿真技术通常用于研究智能交通技术( intelligent transportation systems (ITS))的车辆网络协议和服务。) In the context of vehicular networks, the simulation of inter-vehicle communications typically involves the coupling of a network simulator (e.g., Veins, NS-3) and a realistic road traffic simulator (e.g., VISSIM, DRACULA, SUMO), including events detection (e.g., traffic jams, accidents), mobility models, realistic maps, and route planning capabilities.(在车辆网络的上下文中,车辆间通信模拟通常涉及网络模拟器(如:veins,NS-3)和真实的道路交通模拟器(如,VISSIM,DEACULA,SUMO)的耦合,包括 事件检测(如,交通堵塞,事故)、移动性模型、真实地图以及路径规划能力。)
A wide-spread road traffic simulator is Simulation of UrbanMObility (SUMO)【广泛使用的道路交通模拟器是城市交通模拟(SUMO)】 SUMO is an open-source space-continuous road traffic simulator commonly used for testing V ANETs and ITSservices.【SUMO是一个开源的空间连续的道路交通模拟器,通常适用于测试VANET和智能交通系统服务】 SUMO allows users to handle large road traffic networks.It includes components of the road network and vehicular demand
modeling (e.g., traffic lights, right-of-way rules, lane changing) and public transport and pedestrians. 【SUMO允许用户处理大型道路交通网络。它包括道路网络和车辆需求建模的组成部分(如交通灯、通行权规则、车道变换)以及公共交通和行人。】 Here, vehicles’ traces can be
defined manually or using tools included in the SUMO package(e.g., DUArouter, MArouter, OD2trips, Randomtrips)[【这里,可以手动或使用SUMO中包含的工具(例如:DUArouter, MArouter, OD2trips, Randomtrips)定义车辆的轨迹】
Most modern vehicles are equipped with real-time navigation services, allowing drivers to better use the available road capacity.【大多数现代车辆都配备了实时导航服务,使驾驶员能够更好地地利用现有的道路交通能力】Besides, drivers can be informed through the vehicular network about the road network’s events during their trips.【此外,驾车人士在行程中亦可透过车辆网络了解道路网络的情况。】In this context, most drivers are familiarized with the road network (urban environment) and, therefore, can decide to try an alternative path during their trips.【在这种情况下,大多数驾驶员熟悉道路交通网络(城市环境),因此,他们可以决定在出行期间尝试其他路径】This behavior is emulated in SUMO utilizing an additional feature, called re-routing device, with which vehicles may be equipped. If vehicles are equipped with a re-routing device, they can change their current routes, taking into account the road network’s current state. In this sense, SUMO includes capabilities for re-routing vehicles dynamically.【这种行为在SUMO中被模拟,利用了一个额外的功能 称之为重路由设备,车辆可能配备该设备。如果车辆配备了改道装置,则可以根据道路网络的当前状态更改当前路线。从这个意义上讲,SUMO包括动态地重新安排车辆路线的功能。】 This approach impacts the overall road traffic conditions (i.e., the road congestion level).Consequently, the data network connectivity in the V ANET is also affected by these vehicles’ re-routing scheme.【这种方法会影响整体道路交通状况(即道路拥堵水平)因此,vanet中的网络数据连接也会受到这些车辆重路由方案的影响】
Many researchers put their effort into the vehicular network model and the validation of results without considering the traffic state’s effect on the road network during the simulation.【在仿真过程中,许多研究人员没有考虑交通状态对道路网络的影响,而是致力于车辆网络模型和结果的验证】In this paper, we investigate the impact of enabling vehicles’ re-routing capabilities (i) over the vehicles’ mobility, and the effect (ii) on the connectivity of the vehicular network【在本文中,我们研究了启用车辆重路由功能(i)对车辆移动性的影响,以及(ii)对车辆网络连通性的影响。】Using the popular traffic simulator SUMO, we simulate the traffic mobility and the automatic vehicles’ re-routing property on a real map.【利用流行的交通仿真模拟器SUMO,我们在真实的地图上模拟了交通流动性和自动驾驶车辆的重路由特性】 Then to evaluate the inter-vehicle connectivity,we take advantage of theory concepts【为了 评估车辆间连通性方面,我们利用了图论的概念】First, we perform an offline analysis transforming the vehicular traces into snapshots at different simulation times to latter evaluate the network employing well-known graph metrics.【首先,我们进行离线分析,在不同的模拟时间将车辆轨迹转为快照,用已知的图形度量对网络进行评估】The remainder of the paper is organized as follows: Section 2, presents some related work【论文的其余部分组织如下:第2节,介绍了一些相关工作】In Section 3 the simulation environment is described, highlighting the automatic re-routing options.【第3节,描述了模拟环境,着重介绍了自动重路由的选项】In Section 4, we investigate the effect of vehicles’ re-routing on the vehicles’ mobility and the nodes’ connectivity.【第4节中,我们研究了车辆重路由对车辆移动性和节点的连通性的影响】Finally, in Section 5 conclusions and future perspectives are presented【最后,在第5节中给出了结论和未来展望】
2 RELATED WORK
Over the last few years, the vehicular networking community has proposed many proposals, applications, and services.【在过去几年中,车辆网络社区提出了许多建议、应用和服务。】One recurrent problem is to develop a reliable and usable mobility scenario to evaluate services for intelligent transportation systems (ITS).【一个经常出现的问题是开发一个可靠且可用的移动场景来评估智能交通系统(ITS)服务】In this context, several works present realistic simulation scenarios derived from real traffic statistics and mobility patterns.【在此背景下,有几项工作提出了从真实交通统计数据和移动模式下导出的真实模拟场景】
Regarding different scenarios available to the research community in [4], a realistic vehicular scenario is proposed called Luxembourg SUMO Traffic(LuST) scenario.关于[4]中研究团体可用的不同场景,提出了一种现实的车辆场景,称为 Luxembourg SUMO 交通(LuST)场景。Codecá. et al. built LuST from the road network of a real city imported from OpenStreetMaps (OSM) [10], including traffic demands and mobility patterns【Codecá.等人根据从OpenStreetMaps(OSM)[10]导入的真实城市道路网络构建了LuST,包括交通需求和流动模式】In that work, the authors use traffic statistics of Luxembourg city to calibrate the traffic demand.【在这项工作中,作者使用卢森堡市的交通统计数据来校准交通需求】Then, traffic demand was generated using the ACTIVITYGEN SUMO tool [11] based on the population and considering everyday trips (e.g., bus lines)【然后使用ACTIVITYGEN SUMO工具根据人口并考虑日常出行(如公交路线)生成交通需求】.The work includes an analysis of the impact of the traffic demand within 24 hours. Also, in [2], mixed traffic analysis of autonomous vehicles (AVs) and classic vehicles is presented.【这项工作包括分析24小时内交通需求的影响。此外,在[2]中,还介绍了自动驾驶车辆(AVS)和经典车辆的混合交通分析。】In that work, authors use linear approximations to calibrate and validate SUMO models based on real-traffic measurement data.【在此项工作中,作者使用线性近似来校准和验证基于真实交通测量数据的SUMO模型】Then, the effects of varying penetration rates of A Vs are analyzed in terms of traffic flow characteristics.【然后从交通流特性分析了自动驾驶车辆的不同渗透率的影响】
In contrast to previous works in [5], the Monaco SUMO Traffic (MoST) scenario includes a multimodal scenario that integrates vulnerable users intending to study advanced parking management solutions.【与[5]中以前的工作不同,摩纳哥SUMO交通(MoST)场景包括一个多模式场景,该场景集成了致力于研究高级停车管理解决方案的易受攻击用户。】It is based on synthetic activity-based mobility traces. The authors present mobility traces for pedestrians and motorbikes.【它是基于合成的基于活动的迁移轨迹。作者提出了行人和摩托车的移动轨迹。】Concerning the vehicular network connectivity analysis, in [6], authors propose a realistic capacity analysis for V ANETs through graph theory concepts【关于车辆网络的连通性分析,在[6]中,作者通过图论的概念提出了一个实际的V ANETs容量分析】The proposed network model is constructed utilizing a Euclidean planar graph and an interference relationship graph.【利用欧几里得平面图和干涉关系图构造网络模型。】First, the authors modeled urban area structures as grid-based structures using a Euclidean graph, where vertices represent points in the plane, and the Euclidean distance between those points means the edges. Then, the interference relationship graph shows the interference relationship between every two units abstracted from the Euclidean planar graph.【首先,作者使用欧式图将城市区域结构建模为基于网格的结构,其中定点表示平面上的点,这些点的欧氏距离表示边。然后干涉关系图显示了从欧几里得平面图中抽象出来每两个单元之间的干涉关系】
In addition to the considerations typically used in the literature (real maps, real traffic demand), we consider the effect of enabling dynamic vehicle routing.【除了文献中常用的考虑因素(真实地图、真实交通需求)外,我们还考虑了启用动态车辆路径的影响。】On the one hand, we claim that by allowing vehicles’ re-routing capabilities, the congestion levels of the scenario’s vehicular traffic are significantly affected. On the other hand, the effect of vehicles’ dynamic route planning modifies the vehicular network behavior.【一方面,我们认为通过允许车辆重路由的能力,会显著影响场景中车辆交通的拥堵水平。另一方面,车辆动态路径规划的影响改变了车辆网络行为。】
3 SIMULATION ENVIRONMENT
In this section, we describe the methodology steps followed to generate both theroad network and the traffic demand; see the flowchart depicted in Fig. 1.【在本节中,我们将描述产生道路网络和交通需求所遵循的方法步骤;参见图1所示的流程图。】
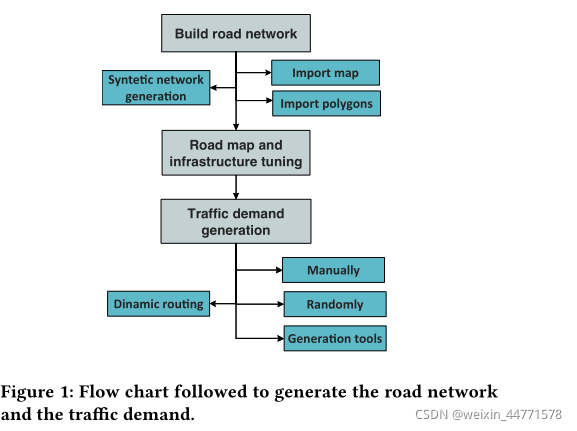
By road network, we refer to the traffic-related part of a map, including roads (edges), traffic lights, intersections,and the logic between elements. 【路网,指的是地图中与交通相关的部分,包括道路(边)、交通灯、十字路口以及元素之间的逻辑。】 By traffic demand, we mean the number of vehicles circulating in the road network at a given time of day (e.g., peak hours, off-peak hours).【交通需求,指在一天中某一特定时段(如高峰时段、非高峰时段)在道路网络内流动的车辆数目。】The first step is to build a road network.【第一步是构造一个路网】 By using SUMO built-in tools, two methods can be followed: (i) create a synthetic network (e.g., a grid network), or (ii) generate a realistic network based on real maps. 【通过使用SUMO内置工具,可以遵循两种方法:(i)创建一个合成网络(例如网格网络),或(ii)基于真实地图生成一个真实的网络。】 Here, OSM excels other repositories because it is free and presents an excellent real-world representation.【在这里,OSM优于其他存储库,因为它是免费的,并提供了良好的现实世界表示。】To generate the road network, SUMO provides several tools [17]. In this work, we have used the following:【为了生成路网,SUMO提供了以下几个工具,在此项工作中,我们使用了以下几点】
Netconvert: It takes digital map files from different sources (e.g., OSM, VISSIM, MATsim) and converts them into one road network file readable by SUMO, called .net file. It provides a full set of processing options for map conversion. A complete list of options is available in [16]. Common options to characterize urban environment maps, arere move-edges.by-vclass, remove-edges.isolated, no-turnarounds, and geometry.remove, as it was detailed in a previous work [20].【它从不同的来源(如OSM, VISSIM, MATsim)获取数字地图文件,并将它们转换成一个由SUMO可读的公路网络文件,称为.net文件。它为映射转换提供了一套完整的处理选项。[16]中提供了完整的选项列表。描述城市环境地图的常用方法是move-edges.by-vclass, remove-edges.isolated, no-turnarounds, and geometry.remove,这在之前的工作[20]中有详细说明。】
Polyconvert: It allows us to import geometrical shapes (polygons) from different sources (e.g., OSM). It is particularly important when evaluating vehicular networks operating in suburban and urban environments. Due to the presence of buildings (i.e., polygons), radio transmissions are heavily impacted by signal shadowing effects in this environment.【Polyconvert:它允许我们从不同来源(如OSM)导入几何形状(多边形)。当评估在郊区和城市环境中运行的车辆网络时,这一点尤为重要。由于建筑物(即多边形)的存在,在这种环境中,无线电传输受到信号阴影效应的严重影响。】
Once the road network has been defined, to further modify or debug network properties (e.g., roads’ length, traffic lights, intersections logic), the SUMO package includes a useful graphical tool:【一旦道路网络被定义,为了进一步修改或调试网络属性(例如,道路长度,交通灯,十字路口逻辑),SUMO包包括一个有用的图形工具: 】
Netedit: It is a visual network editor that allows us to edit/create all available network properties and infrastructure in the network (e.g., bus stops, traffic light cycles).【Netedit:这是一个可视化的网络编辑器,允许我们编辑/创建网络中所有可用的网络属性和基础设施(例如,公交车站,交通灯循环)。】
Then, the traffic demand generation, see Fig. 1, refers to the definition of the vehicles circulating on the road network during the simulation.【由此,交通需求生成如图1所示,即为仿真过程中在路网上行驶的车辆定义。】 In SUMO, each vehicle is defined by a vehicle type that describes the vehicle’s physical properties (e.g., size, gas/electric fueled), a route the vehicle shall take, and the vehicle itself.【在SUMO中,每辆车都由描述车辆物理特性(如尺寸、汽油/电动燃料)的车辆类型、车辆应走的路线以及车辆本身来定义。】A single route can be assigned to a single-vehicle (e.g., trips, routes) or several vehicles (e.g., flows of vehicles) 【一条路线可以分配给一辆车(如行程、路线),也可以分配给多辆车(如车流)】At this point, routes can be defined in three different ways,【此时,可以通过三种不同的方式来定义路由】(i) manually specify all the components of the route (i.e., set of edges), (ii) generate routes randomly, or (iii) use the SUMO generation tools.【(i)手动指定路线的所有组成部分(即边集),(ii)随机生成路线,或(iii)使用SUMO生成工具。】In this work, we use (ii) to randomly create routes for the road network. For this, the following tools are used:【在本实验中,我们使用(ii)为路网随机创建路线。为此,需要使用以下工具:】
DUARouter: It computes the shortest path between a vehicle’s origin and destination in terms of trip time or trip length. Different demand definitions, such as trips or flows, can be used as input of the script. Several routing algorithms can be configured to find a new vehicle’s route (e.g., Astar, Dijkstra, etc.). By default,duarouter uses the Dijkstra algorithm [15].【DUARouter:它计算车辆从出发地到目的地的最短路径,以行驶时间或行驶长度为单位。不同的需求定义(如行程或流量)可以用作脚本的输入。可以配置几种路由算法来查找新车辆的路线(例如,Astar, Dijkstra等)。默认情况下,duarouter使用Dijkstra算法[15]。】
RandomTrips.py: This script allows us to quickly generate a set of random trips on a given road network, which is required as an input parameter for the script [19].【RandomTrips.py:该脚本允许我们在给定的道路网络上快速生成一组随机出行,这是脚本[19]所需的输入参数。】By default, the source and destination of the route are selected randomly.【默认情况下,路由的源和目的是随机选择的。】As the destination point is randomly selected, it may not be reachable from the origin point.【由于目标点是随机选取的,从原点可能无法到达】The option−r automatically calls duarouter[15] tool to discard disconnected trips.【选项 -r 自动调用duarouter 工具来摒弃断开连接的线路】
Finally, vehicles’ routes are composed of a set of edges. Then, vehicles are denoted by the combination of a vehicle type and a given route.【最后,车辆路径由一组边缘组成。然后,通过车辆类型和给定路线的组合来表示车辆。】By default, in SUMO, each vehicle will circulate along the edges of its corresponding path.【默认情况下,在SUM O中,每辆车将沿着其相应路径的边缘循环。】Following this approach, some realistic route events (e.g., traffic jams) during the simulation will not be tackled.【按照这种方法,模拟过程中的一些真实路线事件(如交通堵塞)将不会得到解决。】That is, if a road becomes congested, vehicles do not modify their routes as it would be desirable in a realistic scenario.【也就是说,如果道路变得拥挤,车辆不会像在现实场景中那样修改其路线。】Dynamic route planning can be enabled in SUMO to cope with these situations.【可以在SUMO中启用动态路线规划来应对这些情况。】Here, vehicles can modify their routes during the simulation [12], which reflects what would happen in reality. In the following section, re-routing configurations are detailed.【在这里,车辆可以在模拟过程中修改其路线[12],这反映了实际情况。在下一节中,将详细介绍重配置。】
3.1 Dynamic route planning
Nowadays, most modern vehicles are equipped with real-time navigation services, allowing drivers to plan their routes before and during their trip.【如今,大多数现代车辆都配备了实时导航服务,允许驾驶员在出行前和途中规划路线。】Vehicles need to change their routes during their trips dynamically to provide a realistic mobility pattern.【车辆在行驶过程中需要动态改变路线,以提供真实的移动模式。】In SUMO, each vehicle can be equipped with a re-routing device allowing vehicles to change their routes during their trips dynamically.【在SUMO中,每辆车都可以装配一个改道装置,允许车辆在行驶过程中动态改变路线】A device refers to a container for data and functionality that enable vehicles to interact with their environment【设备是指数据和功能性的容器,使得车辆能够与其环境进行交互】
This re-routing approach works by giving vehicles the ability to re-compute their routes periodically (i.e., re-routing is triggered by the vehicle).【这种重路由方法的工作原理是让车辆能够定期重新计算其路线(即,重路由由车辆触发)。】For this, some or all the vehicles in the simulation can be equipped with a re-routing device [14].【为此,模拟中部分或全部的车辆可配备路由装置】By default, the percentage of vehicles that have a re-routing device is set to 0.【默认情况下,具有重路由的车辆百分比设置为0】Four main steps are considered to configure vehicles’ re-routing:【配置车辆重路由需要下列4个主要步骤】
Step 1: Before the simulation initializes, each vehicle has assigned a vehicle type and a route, as it is detailed in Section 3. Also, the percentage of vehicles equipped with a re-routing device is defined.【步骤1:在模拟初始化之前,每辆车都分配了一个车辆类型和路线,详见第3节。此外,还定义了配备改道装置的车辆百分比。】Step 2: Once the simulation starts, conditions along the road network are updated following a fixed time interval of t(seconds). 【步骤2:一旦模拟开始,沿道路网络的条件将按照以下固定时间间隔进行更新:t(秒)。】For this, SUMO assigns a weight to each edge in the network. The evolution of the edges’ weights during simulation is computed as an estimation of the travel time (time required to traverse an edge). The travel time is estimated by calculating the mean speed on the road and then dividing the road length by that speed【为此,SUMO为网络中的每条边指定一个权重。在模拟过程中,边权重的演变计算为行程时间(穿过边所需的时间)的估计。通过计算道路上的平均速度,然后将道路长度除以该速度来估计行驶时间】Step 3: Vehicles equipped with a re-routing device re-apply the optimal path computation following the r(seconds) re-routing interval.【步骤3:配备重路由装置的车辆在以下步骤后重新应用最佳路径计算:r(秒)重新路由间隔。】r refers to the interval time elapsed between consecutive re-routing events【t指连续重新路由事件之间经过的间隔时间。】If the travel time on the new route is shorter than on the current one, the vehicle changes the route accordingly.【如果新路线上的行驶时间短于当前路线上的行驶时间,车辆将相应地更改路线。】Step 4: At this time, to select the fastest path for the current vehicle, SUMO uses the vehicle’s current position, destination’s position, and current status in the road network (updated at t time). If the new path results faster than the current one, the vehicle updates its route. The fastest path is computed using theDUARouter tool, which is commented in Section 3.【步骤4:此时,为了选择当前车辆的最快路径,SUMO使用车辆的当前位置、目的地位置和道路网络中的当前状态(更新于t时间)。如果新路径比当前路径更快,车辆将更新其路线。最快的路径是使用UARUTER工具计算的,该工具在第3节中有注释。】
In the next section, we first take the mobility traces generated in Section 3, and then we vary the parameters associated with the vehicles’ re-routing. The goal is to analyze the mobility pattern’s impact and on the nodes’ connectivity (vehicular network).【在下一节中,我们首先获取第3节中生成的移动轨迹,然后改变与车辆重新路由相关的参数。目的是分析移动模式对节点连通性(车辆网络)的影响。】
4 RESULTS ANALYSIS
We divide the analysis into two parts. First, we study the impact of automatic routing on traffic mobility employing trip statistics. Here, we consider fundamental mobility metrics (trip time and distance) and the number of route changes performed by vehicles during the simulation.【我们将分析分为两个部分,首先,我们利用出行统计数据对交通流动性的影响,在这里,我们考虑基本的移动性度量(行程时间和距离)和车辆在模拟过程中执行的路线变化的数量。】We then study the impact of automatic routing in the vehicular communication network by using graph theory concepts. For this, we evaluate the communication between nodes utilizing well-known graph metrics【然后,我们利用图论的概念研究了车辆通信网络中自动路由的影响。为此,我们利用众所周知的图度量来评估节点之间的通信】
4.1 Simulation settings
In this work, we use a realistic scenario, shown in Fig. 2, to carry out the simulations.【在这项工作中,我们使用图2所示的真实场景来进行模拟。】It corresponds to Gracia’s district and its surroundings in the city of Barcelona, Spain, with an area of 7 km2.【它对应于西班牙巴塞罗那市的格拉西亚区及其周边地区,面积为7平方公里。】The road network has been generated using a real map imported from OSM [10] through the use of theNetconvert SUMO tool, described in Section 3.【道路网是使用第3节所述的NetConvert Sumo工具从OSM[10]导入的真实地图生成的】Also, roads’ speed information has been imported from OSM;【此外,还从osm导入了道路速度信息】see the colors bar in Fig. 2. Exclusive lanes for the tram, rail, electric rail, bicycles, and pedestrians have been removed from the road network, as part of the road map tuning process, according to Fig. 1【请参见图2中的颜色栏。根据图1,作为路线图调整过程的一部分,有轨电车、铁路、电动铁路、自行车和行人专用车道已从道路网中移除】Besides, buildings information has been generated by using thePolyconvert tool described in Section 3. Also, the area of study has been tuned using the Netedit tool (i.e., roads were set within the area of study)【此外,利用第3节所述的PolyConverte工具生成建筑物信息。此外,使用NetEdit工具对研究区域进行了调整(即,在研究区域内设置了道路)】
Once the road network has been defined, we generated mobility traces.【一旦定义了路网,我们就生成了移动轨迹。】We consider data related to real traffic demand in the district of Gracia, according to Barcelona’s City Hall [1].【根据巴塞罗那市政厅的数据,我们考虑宇格拉西亚地区实际交通需求有关数据】The traffic demand refers to the mean number of vehicles per hour that circulate on a working day.【交通需求是指在一个工作日内每小时循环的平均车辆数量。】. For this area, in rush hours, there are around 17500vehicles/hour【在这个地区,高峰时间大约有17500辆车/小时】In Table 1, we have derived the number of vehicles for 40%, 70%, and 100% of the maximum real traffic demand;【在表1中,我们得出了最大实际交通需求的40%、70%和100%的车辆数量;】henceforth low, medium, and high vehicular traffic demand, respectively.【此后,车辆交通需求分别为低、中、高】We have generated vehicles for three hours for each traffic demand through the use of the RandomTrips.py tool in combination with the DUARouter tool, described in Section 3.【如第3节所述,我们通过RandomTrips.py工具和DUARouter 工具的使用,为每个交通需求生成了三个小时的车辆】

4.2 Traffic mobility analysis
SUMO provides several statistics [18] from simulations. We consider fundamental traffic measures: (i) the trip time, defined as the minimum time required for the vehicle to travel from origin to destination; (ii) the trip length, defined as the total length from origin to destination; and (iii) the number of route changes each vehicle performs【SUMO提供了一些统计数据,我们考虑基本交通措施:(i)出行时间,定义为车辆从出发地到目的地所需要的最小时间 (ii)行程长度:定义为从起点到目的地的总长度,(iii)每辆车执行的路线变更次数】Note that the a vehicle will update its route if it finds a new path to the destination faster than the current one, as detailed in Section 3.1.【注意,如果车辆发现到达目的地的新路径比当前路径快,则车辆将更新其路线,如第3节所述。1.】
Trip time: Fig. 3 shows the improvement in the travel time by enabling re-routing capabilities.【行程时间:图3显示了通过启用重路由功能来改善行程时间。 】The most significant improvement can be observed for the "R - 1 min" case with the 40% of the traffic demand, see Fig. 3(a).【在40%的交通需求下,“R-1分钟”情况下可以观察到最显著的改善,见图3(a)。】By the end of the fourth hour, vehicles require 50 minutes less to complete their trips compared to the NR case.【到第四个小时结束时,与NR情况相比,车辆完成行程所需时间减少50分钟】. In the NR case, vehicles select the shortest path to destination without considering the current traffic state (number of vehicles in streets).【在NR情况下,车辆选择到达目的地的最短路径,而不考虑当前的交通状态(街道上的车辆数量)。】Therefore, at a specific time (minute 50 in Fig. 3(a) ), when new vehicles enter the simulation, they will continue using already congested streets.【因此,在特定时间(图3(a)中的50分钟),当新车辆进入模拟时,它们将继续使用已经拥挤的街道。】This implies that the mean trip time and the number of vehicles running in the simulation increases【这意味着平均行车时间和模拟中运行的车辆数量增加】Before this time point, re-route actions are only triggered by spurious congestion situations, leading to slightly higher trip times than NR.【在此时间点之前,只有在虚假拥堵情况下才会触发改道行动,导致出行时间略高于 NR。】The lower trip time by using rerouting when streets are continuously congested is because vehicles have updated information concerning the overall traffic conditions about the road map to make better decisions.【当街道持续拥堵时,通过改道减少出行时间是因为车辆更新了有关路线图总体交通状况的信息,以便做出更好的决策。】Moreover, in the low traffic scenario, vehicles find alternative routes keeping mean trip time constant (steady situation).【此外,在低交通量情况下,车辆会找到保持平均出行时间恒定(稳定情况)的备选路线。】
We can see that as the re-routing interval increases, vehicles make worse decisions, especially under high traffic demands (rush hours), see Fig. 3(c)【我们可以看到,随着改道间隔的增加,车辆会做出更糟糕的决策,特别是在交通需求高的情况下(高峰时间),见图3(c)】Further, by increasing the traffic demand in the scenario, the level of congestion increases consequently.【此外,通过增加场景中的交通需求,拥堵水平也随之增加。】We can see this behavior in Fig. 3(c) with 100% of the traffic demand.【我们可以在图3(c)中看到这种行为,流量需求为100%】On the one hand, the NR case produces the highest trip times because it is more probable for a vehicle to get stuck in a congested situation.【一方面,NR情况产生的行程时间最高,因为车辆在拥挤情况下更容易卡住。】On the other hand, the improvement in terms of trip time due to vehicles’ re-routing is less significant since roads in the road network begin to be blocked【另一方面,由于道路网络中的道路开始堵塞,车辆改道导致的出行时间改善不太明显】
Trip length: In Fig. 4, the NR case (no vehicle can re-route its trip) produces the shortest trip lengths under the different traffic demands, even though vehicles take more time to complete their travels, as we see in Fig. 3.【旅程长度:在图4中,NR情况(没有车辆可以重路由其行程)在不同的交通需求下产生最短的行程长度,即使车辆需要更多的时间来完成其行程,如图3所示。】This is because, by default, SUMO looks for the fastest path from origin to destination, but without considering the presence of other vehicles in the map.【这是因为,在默认情况下,SUMO会寻找从起点到到终点的最快路径,但不考虑路径中是否存在其他车辆】Alternatively, in the R cases analysed, vehicles consider current traffic conditions to re-compute new optimal routes with respect to the travel time.【另外,在被分析R案例中,车辆会考虑当前的交通条件来从新计算相对于行驶时间的新的最优路线】Each time a vehicle re-routes, it is because the new route takes less time than the current route (which suffers some level of congestion).【每次车辆改道,都是因为新路线比当前路线花费的时间少(当前路线存在一定程度的拥堵)。】Notice that the new route will be longer but with fewer cars on it.【注意到,新路线将更长,但车更少】On the one hand, a vehicle that can re-route every 6 min will select longer paths in low-traffic conditions than the initial route planned. On the other hand, for Medium and High traffic, as the re-route interval increases, vehicles find a lower number of better routes than for the case r=1 min (see Fig. 5) and therefore, the average trip length decreases【一方面,每6分钟可重路由的车辆将在低交通量的条件下选择比初始条件下规划更长的路径。另一方面,对于中等和高交通量,随着改道间隔的增加,车辆找到的更好的路线数量低于实际情况r=1分钟(见图5),因此,平均行程长度减小】
Route changes: Fig. 5 shows the mean number of route changes that vehicles perform per kilometer. As it is expected, the "R - 1 min" case produced more route changes.【路线变更:图5显示了车辆每公里执行的路线变更的平均数量。正如所料,“R-1分钟”的情况产生了更多的路线变化。】We can see that the effect of varying the re-routing interval is more significant under medium and high traffic conditions.【我们可以看到,在中流量和高流量条件下,改变重路由间隔的效果更为显著。】Mainly, under a high traffic demand, using a re-route interval of 1 minute (R - 1 min), it doubles the number of route changes when compared to the "R - 3 min" case, and four times compared to the "R - 6 min" case.【主要是在高交通需求下,使用1分钟(R-1分钟)的改道间隔,与“R-3分钟”情况相比,改道次数增加一倍,与“R-6分钟”情况相比增加四倍。】
We can conclude that re-routing capability modifies the mobility pattern making vehicle distribution more spread as vehicles choose different routes not congested (i.e., with the minimum number of vehicles).【我们可以得出结论,当车辆选择不拥挤的不同路线(即车辆数量最少)时,重路由能力会改变移动模式,使车辆分布更加分散。】Therefore, re-routing reduces the overall vehicles’ trip time.【因此,改道减少了车辆的总出行时间。】However, re-routing may introduce unrealistic mobility behavior during the simulation【 然而,在仿真的过程中,重路由可能会已你如不切实际的移动行为】For instance, Fig. 4 and Fig. 5 show that for the "R - 1 min" case, in a route of 2.2 km, vehicles would change their routes in average about 32 times (i.e., 16 re-routes/km).【例如,从图4和图5中可以看出,在“R - 1 min”情况下,在2.2 km的路线中,车辆平均会改变路线32次(即每km 16次改道)。】This is because roads along the map are congested (rush hour), so vehicles modify their routes very often. In real life, drivers would not change their routes so often (e.g., each minute), just when they are involved in a severe traffic jam【这是因为地图上的道路都很拥挤(高峰期),所以车辆经常修改路线。在现实生活中,司机不会仅仅在遇到严重交通堵塞的时候,就这么频繁地改变路线(比如每分钟)。】
4.3 Impact of vehicle re-routing capacity on vehicle network connectivity
To provide an idea of the impact of vehicle re-routing capacity in the connectivity of vehicular networks, we take advantage of graph theory concepts.【为了了解车辆改道能力对车辆网络连通性的影响,我们利用了图论的概念。】First, we visually evaluate nodes’ connectivity through the adjacency matrix obtained by enabling vehicles’ rerouting.【首先,我们通过允许车辆改道得到的邻接矩阵直观地评估节点的连通性。】Then, through the use of well-know graph metrics [8], we intend to provide valuable insight into vehicular network behavior.【然后,通过使用众所周知的图指标[8],我们打算提供有价值的洞察车辆网络行为。】To this end, we consider the vehicular network settings summarized in Table 2【为此,我们考虑了表2中总结的车载网络设置。】
First, we assume all vehicles in the scenario are equipped with an IEEE 802.11p network card and have defined a transmission power of 23 dBm.【首先,我们假设场景中的所有车辆都配备了IEEE 802.11p网卡,并定义了23dbm的传输功率。】Thus, the communication range will be approximately 400m.【因此,通信距离约为400米。】We also consider the building attenuation model proposed in [9] to model the non-line of sight (NLOS) condition to generate the building information, as it is described in Section 3.【我们还考虑了[9]中提出的建筑衰减模型,以模拟非视线(NLOS)条件来生成建筑信息,如第3节所述。】The first step to analyze the network is to convert vehicular traces in network snapshots at different simulation times.【分析网络的第一步是转换不同仿真时间的网络快照中的车辆轨迹】Then, the nodes’ connectivity can be represented as a graph G where V(G) refers to the set of vertices(nodes) of the graph, and E(G) is the set ofedges of the graph.【然后,节点的连通性可以表示为一个图G,其中V(G)为图的顶点(节点)集,E(G)为图的边缘集。】An edge is added between two nodes (i,j) in case those nodes reach each other (i.e., reception power > -82 dBm).【如果两个节点(i,j)相互到达(即接收功率> -82 dBm),则在两个节点(i,j)之间增加一条边。】The network is represented by the adjacency matrix (Ai,j), where each entry corresponds to the weight of the edge (EW(i,j))【网络由邻接矩阵(Ai,j)表示,其中每一项对应着边的权值(EW(i,j))】This weight of the edge corresponds to the signal strength in the link between two nodes, as follows:【该边的权值对应于两个节点之间链路的信号强度,如下所示:】

In Fig. 6, we depict the nodes’ connectivity by means of the adjacency matrix.【在图6中,我们用邻接矩阵来描述节点的连通性。】To obtain the edges’ weight of the graph, we have added the signal strength each time that two nodes are in contact during the period of study【为了得到图的变的权值,我们在研究期间郑佳丽两个节点每次接触时的信号强度】We take into account the 250 nodes with the highest signal strength. The connection intensity varies from light-red (few nodes are connected) to very dark-red (many nodes are connected), depending on the node’s edge weights.【我们考虑了250个信号强度最高的节点。连接强度从浅红色(连接的节点很少)到深红色(连接的节点很多)不等,这取决于节点的边权值。】We evaluate two cases considering low (off-peak hours) and high (peak hours) traffic demands.【我们评估了两种情况,考虑低(非高峰时间)和高(高峰时间)的交通需求。】In the figure ,R cases mean that all vehicles in the simulation can perform route changes during their trips, where as NR cases mean that no re-routing is allowed. We use below the terms vehicle and node interchangeably.【在图中,R情况表示模拟中的所有车辆在行驶过程中都可以改变路线,NR情况表示不允许重路由。下面我们可以将术语vehicle和node互换使用。】

Fig. 6(a) shows that under a low traffic demand, the NR case obtains a set of nodes that are highly interconnected (there are few white spaces), while the R case represents a sparser nodes’ connectivity【从图6(a)可以看出,在低流量需求下,NR情形得到的是一组高度互连的节点(空白部分较少),而R情形则表示节点的连通性较稀疏】The reason is that in case R vehicles are allowed to choose alternative routes to avoid congested roads. Also, vehicles move faster, reducing connectivity opportunities.【原因是,R类车辆被允许选择其他路线,以避免道路拥挤。此外,车辆移动速度更快,减少了连接机会。】This way, we can notice how the re-routing capacity of vehicles affects negatively the vehicular network connectivity under low traffic demands.【通过这种方式,我们可以注意到在低流量需求下,车辆重路由能力如何对网络连接产生负面影响】
In contrast, under high traffic demands, see Fig. 6(b), the R case shows a large amount of connected nodes with high intensity.【相反,在高流量需求下,参见图6(b),R案例显示了大量高强度的连接节点。】The reason is that as the traffic demand increases, the probability of a vehicle to be in a traffic jam increases too.【原因是,随着交通需求的增加,车辆发生交通堵塞的概率也随之增加。】 In such a case, vehicles would move slowly (with higher trip times, see Fig. 3(c)) so that nodes increase their connectivity opportunities.【在这种情况下,车辆将缓慢移动(具有较高的行程时间,见图3(c)),以便节点增加其连接机会。】However, for very high traffic demands traffic jams are unavoidable, which could also lead to a congested vehicular network with a high packet collision probability.【然而,对于非常高的交通需求,交通堵塞是不可避免的,这也可能导致具有高数据包冲突概率的拥挤的车辆网络。】
In the rest of this section, we analyze the nodes’ connectivity in terms of well-known graph metrics to characterize vehicular networks. For this, we define two scenarios called Average, and Summary, as follows:【在本节的其余部分,我们将根据的图指标来分析节点的连通性,以描述车辆网络。为此,我们定义了两个场景,分别是average和Summary,如下所示:】
A verage graph: We construct a graph Gt for every snapshot. Then, we average the metrics computed for each graph separately.【平均图:我们为每个快照构建一个图Gt。然后,我们分别计算每个图的度量值的平均值。】We generate a network graph every 30s, where the edges’ weight is the strength of the signal.【我们每30秒生成一个网络图,其中边的权重就是信号的强度。】Recall that an edge of the graph links two vertices(vehicles) are in the transmission range of each other. This metric provides an idea of the behavior of the vehicular network at a specific moment.【回想一下,图的一条边将两个顶点(车辆)链接在彼此的传动范围内。该指标提供了特定时刻车辆网络行为的概念】
Summary graph: We construct a single summary graph G considering all the samples during a period.【摘要图:我们构建了一个单一的摘要图G,其中考虑了一段时间内的所有样本。】 In case two nodes were in the transmission range of each other (at least once during the simulation), we draw an edge between them.【如果两个节点在彼此的传输范围内(在模拟过程中至少有一次),我们将在它们之间绘制一条边。】Weights of edges are obtained by adding the signal strength each time two nodes are in contact【每次两个节点接触时,通过增加信号强度来获得边的权重】This metric gives an idea of how often two nodes coincide during the studied period【该度量给出了在研究期间两个节点重合的频率。】
Edge percentage(EP): The EP is defined in the range [0, 1], where EP=0 means no connectivity between nodes and EP=1 means full connectivity between nodes.【边缘百分比(EP):EP在范围[0,1]中定义,其中EP=0表示节点之间无连接,EP=1表示节点之间完全连接。】 The EP is defined as
![]() Here,E is the number of edges and N the total number of vertices (nodes) of G.【其中,E为G的边数,N为G的顶点(节点)总数。】Fig. 7 shows the average and summary graphs detailed above . Regarding the average graph, all re-routing cases produce a similar behavior.【关于平均图,所有的重路由方案都会产生类似的行为。】The ED is low, just 1,3% of vehicles are (directly) connected under sparse scenario (Low traffic);【ED较低,在稀疏场景(低交通量)下,只有1,3%的车辆(直接)连接;】furthermore, this index halves under high traffic condition.【此外,该指数在高流量条件下减半。】This effect is more notable when re-routing is allowed, since vehicles can modify their planned routes to avoid congested streets so they will find less vehicles in the new routes.【当允许改道时,这种影响更为显著,因为车辆可以修改其计划的路线,以避免拥挤的街道,从而在新路线中发现更少的车辆】 Regarding thesummary graph, in case of low traffic demand by enabling re-routing capabilities (Rcases) nodes’ connectivity between nodes is highly affected (negatively) compared to the NR case (no re-routing is allowed)【从摘要图中可以看出,通过启用重路由功能(情况R)实现低流量需求的情况下,与NR情况相比(不允许重路由),节点之间的连接受到高度影响(负面)】This is because during the studied period, vehicles select new routes with low congestion levels so that vehicles are sparsely distributed and consequently the EP decreases.【这是因为在研究期间,车辆选择拥堵程度较低的新路线,因此车辆分布稀疏,因此EP降低。】In contrast, with high traffic demand, the EP values increase (to a higher value than the NR case), meaning that it is possible to establish more connections between nodes compared to the NR case (no re-routing is allowed).【相反,在高流量需求下,EP值增加(比NR情况高),这意味着与NR情况相比,可以在节点之间建立更多的连接(不允许重新路由)。】The reason is that vehicles looking for a new route will try to look for a faster route, but also with a lot of traffic.【原因是,寻找新路线的车辆会尝试寻找更快的路线,但也会有大量的交通。】The results of thesummary graph correspond with observed behavior with the adjacency matrices in Fig. 6. 摘要图的结果和图6中邻接矩阵所观察的结果一致 That is, the re-routing capacity of vehicles negatively affects
Here,E is the number of edges and N the total number of vertices (nodes) of G.【其中,E为G的边数,N为G的顶点(节点)总数。】Fig. 7 shows the average and summary graphs detailed above . Regarding the average graph, all re-routing cases produce a similar behavior.【关于平均图,所有的重路由方案都会产生类似的行为。】The ED is low, just 1,3% of vehicles are (directly) connected under sparse scenario (Low traffic);【ED较低,在稀疏场景(低交通量)下,只有1,3%的车辆(直接)连接;】furthermore, this index halves under high traffic condition.【此外,该指数在高流量条件下减半。】This effect is more notable when re-routing is allowed, since vehicles can modify their planned routes to avoid congested streets so they will find less vehicles in the new routes.【当允许改道时,这种影响更为显著,因为车辆可以修改其计划的路线,以避免拥挤的街道,从而在新路线中发现更少的车辆】 Regarding thesummary graph, in case of low traffic demand by enabling re-routing capabilities (Rcases) nodes’ connectivity between nodes is highly affected (negatively) compared to the NR case (no re-routing is allowed)【从摘要图中可以看出,通过启用重路由功能(情况R)实现低流量需求的情况下,与NR情况相比(不允许重路由),节点之间的连接受到高度影响(负面)】This is because during the studied period, vehicles select new routes with low congestion levels so that vehicles are sparsely distributed and consequently the EP decreases.【这是因为在研究期间,车辆选择拥堵程度较低的新路线,因此车辆分布稀疏,因此EP降低。】In contrast, with high traffic demand, the EP values increase (to a higher value than the NR case), meaning that it is possible to establish more connections between nodes compared to the NR case (no re-routing is allowed).【相反,在高流量需求下,EP值增加(比NR情况高),这意味着与NR情况相比,可以在节点之间建立更多的连接(不允许重新路由)。】The reason is that vehicles looking for a new route will try to look for a faster route, but also with a lot of traffic.【原因是,寻找新路线的车辆会尝试寻找更快的路线,但也会有大量的交通。】The results of thesummary graph correspond with observed behavior with the adjacency matrices in Fig. 6. 摘要图的结果和图6中邻接矩阵所观察的结果一致 That is, the re-routing capacity of vehicles negatively affects
the vehicular network connectivity under low traffic demands.【也就是说,在低的交通需求之下,车辆的重新路由能力会对车辆网络连通性产生负面影响。】
Transitivity(T): The transitivity of a graph is defined as the ratio oftrianglesin the graph (i.e., a→b,b→c,c→a), compared to the total number of connected triples(i.e.,a→b,b→c).【传递性(T):图的传递性定义为图中三角形的比率(即a→b、 b→c、 c→a) ,与连接的三元组的总数(即→b、 b→c) 。】 T indicates the proportion of nodes that have adjacent nodes interconnected. It is defined in the range [0, 1], where T=1 if the network contains all possible edges (full connectivity).【T表示相邻节点互连的节点比例。它在范围[0,1]中定义,其中,如果网络包含所有可能的边(完全连接),则T=1。】In opportunistic networks, transitivity can be interpreted as the chances that two nodes that communicate directly (a→b)can also communicate back by using only two additional hops (b→c,c→a).【在机会性的网络中,传递性可以解释为两个直接通信的节点(a→b) 也可以只使用两个额外的跃点(b→c、 c→a) 。】In Fig. 8, the higher associated transitivity takes place with NR under low and medium traffic【在图8中,在低流量和中等流量下,NR具有较高的关联传递性】We can conclude that by enabling re-routing capabilities, less back-up triangle paths will be generated.【我们可以得出结论,通过启用重路由功能,将生成较少的备用三角形路径。】This is due to the fact that dynamic route planning diminishes congestion levels throughout the road map.【这是因为动态路线规划降低了整个路线图的拥堵程度。】In this case, vehicles move faster (see, Fig. 3), so that it is less probable that back-up triangles can be generated.【在此情况下,车辆移动更快,因此这样就不太可能生成后备三角形。】

Diameter(D): The diameter of a graph G is the length of the longest shortest path (obtained in terms of the number of hops) between any two graph vertices (nodes) i and j in G【直径(D):图G的直径是图G中任意两个顶点(节点)i和j之间的最长最短路径的长度(以跳数计算)】This way, D reflects the largest number of vertices which must be traversed in order to travel from one vertex to another (paths which backtrack, detour or loop are not considered).【这样,D就反映了从一个顶点到另一个顶点所必须经过的最大顶点数(不考虑回溯、绕行或循环的路径)。】Regarding the average scenario in Fig. 9, we can see that as the traffic demand increases, diameter values for R-cases (re-routing is allowed) also increase【对于图9中的平均情景,我们可以看到,随着交通需求的增加,r 情形(允许重路由)的直径值也会增加。】In the context of vehicular communications, a long diameter value means that distant nodes could be reached using a suitable routing protocol.【在车载通信环境中,长直径值意味着可以使用合适的路由协议到达遥远的节点。】This result agrees to the one obtained for the edge percentage, see Fig. 7.【该结果与边缘百分比的计算结果一致,如图7所示 】A low EP value means that more hops are needed to reach distant nodes.【低EP值意味着需要更多的跳数才能到达远处的节点。】Regarding the summary case, we can see that for low traffic density, as the re-routing interval decreases (i.e., re-routing events occurs more often), the diameter increases.【对于summary case,我们可以看到,对于低流量密度,随着重路由间隔的减小(即重路由事件发生的频率增加),直径增大。】 Particularly, in the "R - 1 min" case, vehicles cover more areas of the map (vehicles are spread distributed), so that vehicles will require more hops to connect to distant vehicles.【特别是在“R - 1分钟”的情况下,车辆覆盖了更多的地图区域(车辆是分散分布的),因此车辆需要更多的跳数来连接到远处的车辆。】In case of medium and high traffic demands, no significant difference is produced for the three re-routing intervals considered.【在中等和高的流量需求之下,所考虑到三种路由间隔没有显著差异。】
Mean node’s degree: The degree of a node i is defined as deg(i)= |N(i)|, where N(i) is the number of neighbors of that node.【平均节点度:节点i的度定义为deg(i)= |N(i)|,其中N(i)为该节点的邻居数。】In Fig. 10, as it is expected when the traffic demand increases the average nodes’ degree increases as well (i.e., nodes have a higher number of neighbors).【在图10中,正如预期的那样,当交通需求增加时,平均节点度也会增加(即 节点有更多的相邻节点)】Focusing on the averag ecase, we can see that while the NR case obtains higher node degree values when traffic demand is low and medium, with high traffic demand all cases behave similarly.【从平均情况可以看出,在交通需求较低和中等时,NR情况的节点度值较高,而在交通需求较高时,所有情况的行为相似。】Regarding the summary case, re-routing options produce higher values for medium and high traffic demands.【从概要图上可以看出,重路由选项对于中等和高流量交通需求会产生更高的价值】It means that nodes will have more options to forward packets under high traffic demands for all cases.【这意味着节点在所有情况下的高交通需求下会有更多的选择来转发数据包】However, very high traffic demands can lead to congested roads (traffic jams) and also to congested vehicular network.【然而,非常高的交通需求会导致道路拥挤(交通堵塞),也会导致车载网络拥挤】
Betweenness centrality: It measures the number of shortest paths that go through a particular node.【中间中心性:它度量通过特定节点的最短路径的数量】This metric shows if there are nodes that often become intermediate nodes between other nodes in the network.【这个度量显示了是否有节点经常成为网络中其他节点之间的中间节点】We use the signal strength (i.e., edges’ weight) to compute the shortest paths. In Fig. 11, a high value shows that a set of nodes arises repetitively in the shortest path creation.【我们使用信号强度(即边的权值)来计算最短路径。在图11中,高的值表示在最短路径创建过程中重复出现了一组节点。】We can see that the NR option (no re-routing is allowed) reaches higher values for medium and high traffic demands.【我们可以看到,对于中等和高流量需求,NR选项(不允许重路由)的值更高。】This is because vehicles mainly follow the same routes in their trips (computed in an empty road map) so that it produces similar intermediate nodes【这是因为车辆在行驶过程中主要是遵循相同的路线(在空的路线图中计算),因此会产生类似的中间节点】On the other hand, among the "R cases" (re-routing is allowed), there is not a significant difference, since vehicles choose different routes based on traffic conditions.【另一方面,在允许重路由的“R模式”中,差异不显著,因为车辆会根据交通情况选择不同的路线。】It is important to notice that the centrality score accounts for the disproportion of the metric (in this case betweenness) among nodes of the graph.【需要注意的是,中心性得分说明了图中节点之间的度量(在本例中是介于度量之间)的不比例。】In this regard, medium traffic load leads to the highest disproportion in the score of nodes. However, the average betweenness value of a node in high traffic is higher than in the medium traffic case.【因此,中等流量负载导致的节点评分不均衡比例最高。但是高流量情况下节点的平均间值高于中等流量情况下节点的平均间值。】

Number of Communities: This metric shows the tendency of a graph with nodes densely connected among each other, but sparsely connected to other communities.【群体数量:这个指标显示了节点之间紧密连接,但与其他群体稀疏连接的图的趋势。】This metric is useful to infer how clusters are formed when routing protocols based on cluste rapproach work.【当基于集群方法的路由协议工作时,此度量有助于推断集群是如何形成的。】To detect the communities, we use the algorithm proposed in [3] for every graph. In Fig. 12, we can see that a higher number of clusters are obtained for "R cases", especially when vehicles are more sparsely distributed.【为了检测通信,我们对每个图使用[3]中提出的算法。从图12中我们可以看出,“R case”的聚类数更高,尤其是车辆分布更稀疏的情况下。】As it is expected, the number of clusters decreases as the traffic demand increases since more often vehicles encounter each other during the simulation.【正如所预期的那样,由于在模拟过程中车辆相遇的频率增加,集群的数量随着交通需求的增加而减少】
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this work, we have studied the impact of enabling dynamic route planning in vehicular simulations, from two points of view:【在本工作中,我们从两个角度研究了使能动态路径规划在车辆仿真中的影响:】(i) how re-routing in vehicles, which is interesting to have more realistic simulations, affect the vehicle’s mobility; and (ii) how re-routing affect the nodes’ connectivity in the vehicular network.
On the one hand, the first analysis shows that re-routing capabilities modifies the shape of the vehicular traffic in the roads, minimizing traffic congestion levels and making vehicles’ distribution more spread in the roads.【一方面,第一个分析表明,改道能力改变了道路上车辆交通的形状,使交通拥挤程度最小化,使车辆分布在道路上更加分散。】In real life, drivers use re-routing to look for faster paths till destination and also to be able to avoid congested roads.【在现实生活中,司机使用改道来寻找更快的路径直到目的地,也能够避免拥堵的道路。】Effectively, by allowing re-routing in our sim-ulations we have measured lower vehicles’ trip time.【有效地,通过在我们的模拟中允许重新路由,我们测量了更低的车辆行驶时间。】Moreover, enabling re-routing capabilities helps to avoid unrealistic situations like congestion under low-traffic load due to the SUMO’s default configuration of static routes.【此外,启用重路由功能有助于避免由于SUMO默认配置静态路由而导致的低流量负载下的拥塞等不切实际的情况。】Moreover, enabling re-routing capabilities helps to avoid unrealistic situations like congestion under low-traffic load due to the SUMO’s default configuration of static routes.【此外,启用重路由功能有助于避免由于SUMO默认配置静态路由而导致的低流量负载下的拥塞等不切实际的情况。】Therefore, considering re-routing is essential to produce meaningful evaluation results when assessing ITS services.【因此,在评估ITS服务时,考虑重路由对于产生有意义的评价结果至关重要。】On the other hand, we have analyzed the nodes’ connectivity by using well-known graph metrics for network analysis.【另一方面,我们使用已知的网络分析图度量来分析节点的连通性。】Results show that by enabling re-routing capabilities, vehicular network connectivity is highly impacted specially in case of low traffic demands (off-peak hours).【结果表明,通过启用重路由功能,车辆的连通性将会受到很大影响,特别是在低交通需求(非高峰时段)的情况下】At the same time, it improves the connectivity of the vehicular network under high traffic demands (peak hours)【同时,在高交通需求(高峰时段),会提高车载网络的连通性。】Concluding, SUMO vehicular traces with re-routing capabilities would significantly modify the simulation results obtained when we assess the performance of services, such as traffic reporting and accident warnings.【综上所述,当我们评估服务性能(如交通报告和事故警告时),具有重路由的SUMO车辆将显著修改得到的仿真结果。】This fact has paramount importance to obtain realistic simulation results。【这一事实对于获得真是的仿真结果非常重要】
Allowing re-routing in vehicular scenarios is of paramount importance to attain realistic simulations.【允许在车辆场景中重新路由对于实现真实的仿真是至关重要的】For instance, varying too often, the re-routing frequency may generate too many route changes, which may introduce anomalies during the simulation (i.e., unrealistic behavior).【例如,变化太频繁,重路由频率可能会产生太多的路由更改,这可能会在仿真期间引入异常(即不现实的行为)。】In a future work, we will test a more granular set of R values and of traffic update intervals. Also, we will use different traffic demand generators.【在未来的工作中,我们将测试一组更细粒度的R值和流量更新间隔。此外,我们将使用不同的交通需求生成器。】Additionally, we will assess a more extensive map area, including accidents during the simulation, to analyze the impact of vehicles re-routing their trips to avoid the area around the accident. 【此外,我们将评估更广泛的图区域,包括仿真过程中的事故,以分析车辆重路由对避免周围区域的事故的影响】




















 1115
1115











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








