相关文章:
1. 通过网格搜索完善模型
在本文中,我们将为决策树模型拟合一些样本数据。 这个初始模型会过拟合。 然后,我们将使用网格搜索为这个模型找到更好的参数,以减少过拟合。
首先,导入所需要的库:
%matplotlib inline
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
1.1 数据导入
首先定义一个函数用于读取 csv 数据并进行可视化:
def load_pts(csv_name):
data = np.asarray(pd.read_csv(csv_name, header=None))
X = data[:,0:2]
y = data[:,2]
plt.scatter(X[np.argwhere(y==0).flatten(),0], X[np.argwhere(y==0).flatten(),1],s = 50, color = 'blue', edgecolor = 'k')
plt.scatter(X[np.argwhere(y==1).flatten(),0], X[np.argwhere(y==1).flatten(),1],s = 50, color = 'red', edgecolor = 'k')
plt.xlim(-2.05,2.05)
plt.ylim(-2.05,2.05)
plt.grid(False)
plt.tick_params(
axis='x',
which='both',
bottom='off',
top='off')
return X,y
X, y = load_pts('Data/data.csv')
plt.show()
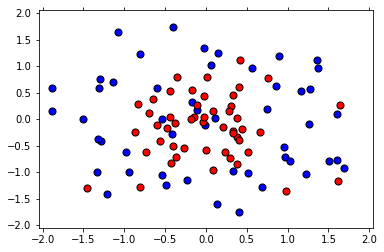
1.2 拆分数据为训练集和测试集
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import f1_score, make_scorer
#Fixing a random seed
import random
random.seed(42)
# Split the data into training and testing sets
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
1.3 拟合决策树模型
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
# Define the model (with default hyperparameters)
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=42)
# Fit the model
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Make predictions
train_predictions = clf.predict(X_train)
test_predictions = clf.predict(X_test)
现在我们来可视化模型,并测试 f1_score,首先定义可视化函数:
def plot_model(X, y, clf):
# 绘制两类点的散点图
plt.scatter(X[np.argwhere(y==0).flatten(),0],X[np.argwhere(y==0).flatten(),1],s = 50, color = 'blue', edgecolor = 'k')
plt.scatter(X[np.argwhere(y==1).flatten(),0],X[np.argwhere(y==1).flatten(),1],s = 50, color = 'red', edgecolor = 'k')
# 图形设置
plt.xlim(-2.05,2.05)
plt.ylim(-2.05,2.05)
plt.grid(False)
plt.tick_params(
axis='x',
which='both',
bottom='off',
top='off')
# 利用 np.meshgrid(r,r) 生成一个平面对于的横纵坐标
r = np.linspace(-2.1,2.1,300)
s,t = np.meshgrid(r,r)
# 将坐标转换为与决策树的训练集相同格式
s = np.reshape(s,(np.size(s),1))
t = np.reshape(t,(np.size(t),1))
h = np.concatenate((s,t),1)
# 对平面上的每一个点进行预测类别
z = clf.predict(h)
# 将横纵坐标及对应类别转换为矩阵形式
s = s.reshape((np.size(r),np.size(r)))
t = t.reshape((np.size(r),np.size(r)))
z = z.reshape((np.size(r),np.size(r)))
# 利用 plt.contourf 绘制不同等高面
plt.contourf(s,t,z,colors = ['blue','red'],alpha = 0.2,levels = range(-1,2))
# 绘制等高面边缘
if len(np.unique(z)) > 1:
plt.contour(s,t,z,colors = 'k', linewidths = 2)
plt.show()
plot_model(X, y, clf)
print('The Training F1 Score is', f1_score(train_predictions, y_train))
print('The Testing F1 Score is', f1_score(test_predictions, y_test))
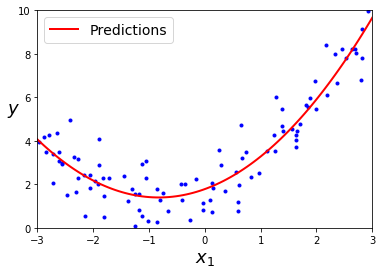
The Training F1 Score is 1.0
The Testing F1 Score is 0.7000000000000001
训练集得分为 1 ,而测试集得分为 0.7,可以看出当前模型有些过拟合,下面我们通过网络搜索来优化参数。
1.4 使用网络搜索完善模型
现在,我们将执行以下步骤:
1.首先,定义一些参数来执行网格搜索:max_depth, min_samples_leaf, 和 min_samples_split。
2.使用f1_score,为模型制作记分器。
3.使用参数和记分器,在分类器上执行网格搜索。
4.将数据拟合到新的分类器中。
5.绘制模型并找到 f1_score。
6.如果模型不太好,则更改参数的范围并再次拟合。
from sklearn.metrics import make_scorer
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=42)
# 生成参数列表
parameters = {'max_depth':[2,4,6,8,10],'min_samples_leaf':[2,4,6,8,10], 'min_samples_split':[2,4,6,8,10]}
# 定义计分器
scorer = make_scorer(f1_score)
# 生成网络搜索器
grid_obj = GridSearchCV(clf, parameters, scoring=scorer)
# 拟合网络搜索器
grid_fit = grid_obj.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 获得最佳决策树模型
best_clf = grid_fit.best_estimator_
# 对最佳模型进行拟合
best_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 对测试集和训练集进行预测
best_train_predictions = best_clf.predict(X_train)
best_test_predictions = best_clf.predict(X_test)
# 计算测试集得分和训练集得分
print('The training F1 Score is', f1_score(best_train_predictions, y_train))
print('The testing F1 Score is', f1_score(best_test_predictions, y_test))
# 模型可视化
plot_model(X, y, best_clf)
# 查看最佳模型的参数设置
best_clf
The training F1 Score is 0.8148148148148148
The testing F1 Score is 0.8
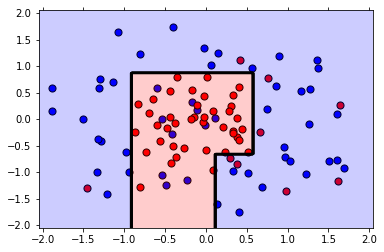
DecisionTreeClassifier(class_weight=None, criterion='gini', max_depth=4,
max_features=None, max_leaf_nodes=None,
min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None,
min_samples_leaf=2, min_samples_split=2,
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, presort=False,
random_state=42, splitter='best')
由此可以看出,最佳参数为:
max_depth=4
min_samples_leaf=2
min_samples_split=2
且相对于第一个图,边界更为简单,这意味着它不太可能过拟合。
1.5 交叉验证可视化
首先看一下不同参数下的信息:
results = pd.DataFrame(grid_obj.cv_results_)
results.T
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | ... | 115 | 116 | 117 | 118 | 119 | 120 | 121 | 122 | 123 | 124 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mean_fit_time | 0.000536919 | 0.000609636 | 0.00067091 | 0.0005006 | 0.000532627 | 0.000538429 | 0.00162276 | 0.000725031 | 0.000346661 | 0.000960668 | ... | 0.000691652 | 0.000363668 | 0.00054733 | 0.000414769 | 0.000365416 | 0.000314713 | 0.000483354 | 0.000389099 | 0.000378688 | 0.000585318 |
| std_fit_time | 7.36079e-05 | 0.000217965 | 0.000120917 | 7.64067e-05 | 0.000118579 | 0.000201879 | 0.00125017 | 0.000257437 | 2.95338e-05 | 0.000841452 | ... | 0.00027542 | 3.20732e-05 | 0.000166427 | 5.31612e-05 | 2.22742e-05 | 5.03509e-06 | 0.000156771 | 0.000113168 | 6.09452e-05 | 0.000168713 |
| mean_score_time | 0.00124542 | 0.00209157 | 0.0011754 | 0.00118478 | 0.00127451 | 0.00132982 | 0.00173569 | 0.00158167 | 0.000804345 | 0.00165256 | ... | 0.00107495 | 0.000776132 | 0.0010496 | 0.00107972 | 0.000799974 | 0.000889381 | 0.00097998 | 0.000957966 | 0.00082167 | 0.00108504 |
| std_score_time | 0.000460223 | 0.00131765 | 0.000217313 | 0.000175357 | 0.000274129 | 0.000684221 | 0.00012585 | 0.000531796 | 2.83336e-05 | 0.00103978 | ... | 0.000327278 | 1.61637e-05 | 0.000181963 | 0.000226213 | 3.18651e-05 | 0.00015253 | 0.000282182 | 0.00014771 | 5.40954e-05 | 0.00015636 |
| param_max_depth | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | ... | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| param_min_samples_leaf | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | ... | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| param_min_samples_split | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | ... | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 |
| params | {'max_depth': 2, 'min_samples_leaf': 2, 'min_s... | {'max_depth': 2, 'min_samples_leaf': 2, 'min_s... | {'max_depth': 2, 'min_samples_leaf': 2, 'min_s... | {'max_depth': 2, 'min_samples_leaf': 2, 'min_s... | {'max_depth': 2, 'min_samples_leaf': 2, 'min_s... | {'max_depth': 2, 'min_samples_leaf': 4, 'min_s... | {'max_depth': 2, 'min_samples_leaf': 4, 'min_s... | {'max_depth': 2, 'min_samples_leaf': 4, 'min_s... | {'max_depth': 2, 'min_samples_leaf': 4, 'min_s... | {'max_depth': 2, 'min_samples_leaf': 4, 'min_s... | ... | {'max_depth': 10, 'min_samples_leaf': 8, 'min_... | {'max_depth': 10, 'min_samples_leaf': 8, 'min_... | {'max_depth': 10, 'min_samples_leaf': 8, 'min_... | {'max_depth': 10, 'min_samples_leaf': 8, 'min_... | {'max_depth': 10, 'min_samples_leaf': 8, 'min_... | {'max_depth': 10, 'min_samples_leaf': 10, 'min... | {'max_depth': 10, 'min_samples_leaf': 10, 'min... | {'max_depth': 10, 'min_samples_leaf': 10, 'min... | {'max_depth': 10, 'min_samples_leaf': 10, 'min... | {'max_depth': 10, 'min_samples_leaf': 10, 'min... |
| split0_test_score | 0.642857 | 0.642857 | 0.642857 | 0.642857 | 0.642857 | 0.642857 | 0.642857 | 0.642857 | 0.642857 | 0.642857 | ... | 0.642857 | 0.642857 | 0.642857 | 0.642857 | 0.642857 | 0.642857 | 0.642857 | 0.642857 | 0.642857 | 0.642857 |
| split1_test_score | 0.764706 | 0.764706 | 0.764706 | 0.764706 | 0.764706 | 0.764706 | 0.764706 | 0.764706 | 0.764706 | 0.764706 | ... | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| split2_test_score | 0.709677 | 0.709677 | 0.709677 | 0.709677 | 0.709677 | 0.709677 | 0.709677 | 0.709677 | 0.709677 | 0.709677 | ... | 0.714286 | 0.714286 | 0.714286 | 0.714286 | 0.714286 | 0.666667 | 0.666667 | 0.666667 | 0.666667 | 0.666667 |
| mean_test_score | 0.705698 | 0.705698 | 0.705698 | 0.705698 | 0.705698 | 0.705698 | 0.705698 | 0.705698 | 0.705698 | 0.705698 | ... | 0.617857 | 0.617857 | 0.617857 | 0.617857 | 0.617857 | 0.602381 | 0.602381 | 0.602381 | 0.602381 | 0.602381 |
| std_test_score | 0.0501306 | 0.0501306 | 0.0501306 | 0.0501306 | 0.0501306 | 0.0501306 | 0.0501306 | 0.0501306 | 0.0501306 | 0.0501306 | ... | 0.0889995 | 0.0889995 | 0.0889995 | 0.0889995 | 0.0889995 | 0.0737135 | 0.0737135 | 0.0737135 | 0.0737135 | 0.0737135 |
| rank_test_score | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | ... | 42 | 42 | 42 | 42 | 42 | 62 | 62 | 62 | 62 | 62 |
14 rows × 125 columns
接着我们来看一下在不同的最大深度(max_depth)下,每片叶子的最小样本数(min_samples_leaf)和每次分裂的最小样本数(min_samples_split)对决策树模型的泛化性能的影响。
首先定义一个函数来绘制不同最大深度下的热力图(需安装 mglearn):
def hotmap(max_depth, results):
fliter = results[results['param_max_depth']==max_depth]
scores = np.array(fliter['mean_test_score']).reshape(5, 5)
mglearn.tools.heatmap(scores, xlabel='min_samples_split', xticklabels=parameters['min_samples_split'],
ylabel='min_samples_leaf', yticklabels=parameters['min_samples_leaf'], cmap="viridis")
绘制到子图中:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 20))
plt
for i in [1,2,3,4,5]:
plt.subplot(1,5,i, title='max_depth={}'.format(2*i))
hotmap(2*i, results)
从图中可以看出,每次分裂的最小样本数(min_samples_split)对模型几乎没有影响,而随着最大深度(max_depth)的增加,模型得分逐渐降低。
1.5 总结
通过使用网格搜索,我们将 F1 分数从 0.7 提高到 0.8(同时我们失去了一些训练分数,但这没问题)。 另外,如果你看绘制的图,第二个模型的边界更为简单,这意味着它不太可能过拟合。
























 2981
2981











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








