一、设备树的配置
1.进入设备树目录查看设备树文件,本实验用的是百问网100ask_imx6ull的开发板。
book@jay:~$ cd 100ask_imx6ull-sdk/Linux-4.9.88/arch/arm/boot/dts/
2.更改100ask_imx6ull-14x14.dts文件,往根节点中添加led子节点的信息
100ask_led1 {
compatible = "100ask,leddrv";
gpios = <&gpio5 3 0>;//第三个值为0表示高电平点亮LED灯
default-state = "off";//表示默认情况下LED灯是熄灭的
};注意

新插入的子节点一定要写在model和compatible这两个属性后面,否则后面编译.dtb文件会报错!
3.返回源码目录生成dtb文件

4.将生成的dtb文件拷贝到开发板的网络文件系统
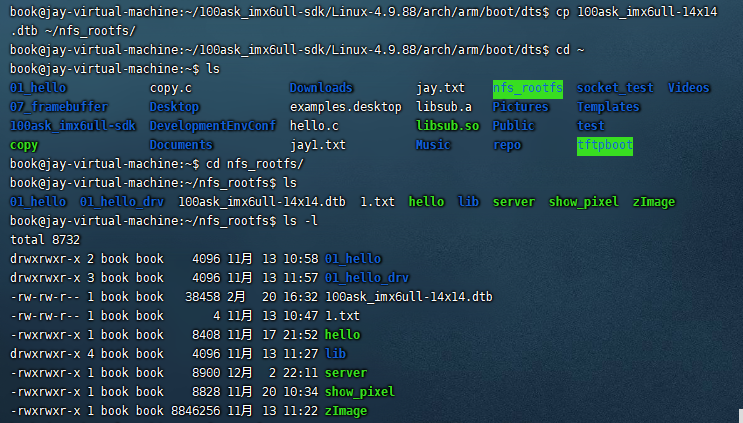
5.将dtb文件拷贝到开发板的/boot目录下重新启动开发板

二、重新启动后查看设备信息
1.查看创建出的平台设备
进入/sys/bus/platform/devices/目录可以查看根据设备树生成的平台设备

2.查看节点
进入/sys/firmware/devicetree/base目录查看生成的节点

三、编写、编译驱动程序
1.编写程序
//dtsled.c 驱动程序
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/major.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
#include <linux/stat.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/kmod.h>
#include <linux/gfp.h>
#include <linux/gpio/consumer.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/of_gpio.h>
#include <linux/of_irq.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/irq.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/fcntl.h>
#include <linux/timer.h>
#include <linux/workqueue.h>
#include <asm/current.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/timex.h>
int major=0;//主设备号
static struct class *led_class;//创建一个LED设备类
static struct gpio_desc *led_gpio;//创建一个指向LED的gpio的结构体
static ssize_t led_read (struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *off)
{
return 0;
}
static int led_open (struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
gpiod_direction_output(led_gpio, 0);
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
/*
* @description : 向设备写数据
* @param - file : 设备文件,表示打开的文件描述符
* @param - buf : 要写给设备写入的数据
* @param - size : 要写入的数据长度
* @param - off : 相对于文件首地址的偏移
* @return : 写入的字节数,如果为负值,表示写入失败
*/
static ssize_t led_write (struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *off)
{
char val;
int err;
err = copy_from_user(&val, buf, 1);
gpiod_set_value(led_gpio, val);
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return 1;
}
/* 设备操作函数 基本操作函数:读、写、打开设备、关闭设备*/
static struct file_operations led_ops={
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = led_open,
.read = led_read,
.write = led_write,
};
static int led_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
/*1.获取硬件信息*/
led_gpio=gpiod_get(&pdev->dev, NULL, 0);
if (IS_ERR(led_gpio)) {
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
}
/*2.创建设备节点*/
device_create(led_class,NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "100askled");
return 0;
}
static int led_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
gpiod_put(led_gpio);
return 0;
}
static const struct of_device_id my_led[] = {
{ .compatible = "100ask,leddrv" },
{}//需要多加一个{}。否则就会报:struct of_device_id is not terminated with a NULL entry!的错误。
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of,my_led);
static struct platform_driver led={
.driver = {
.name = "led",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.of_match_table = of_match_ptr(my_led),
},
.probe = led_probe,
.remove = led_remove,
};
static int __init led_init(void)
{
int err;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
/*确定主设备号*/
major=register_chrdev(major, "myled", &led_ops);
/*创建类*/
led_class=class_create(THIS_MODULE, "led");
if (IS_ERR(led_class)) {
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
unregister_chrdev(major, "myled");
return PTR_ERR(led_class);
}
err=platform_driver_register(&led);
return 0;
}
static void __exit led_exit(void)
{
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
device_destroy(led_class, MKDEV(major, 0));
class_destroy(led_class);
unregister_chrdev(major, "myled");
platform_driver_unregister(&led);
}
module_init(led_init);
module_exit(led_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");//ledtest.c 测试程序
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
/*
* ./ledtest /dev/100ask_led0 on
* ./ledtest /dev/100ask_led0 off
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd;
char status;
/* 1. 判断参数 */
if (argc != 3)
{
printf("Usage: %s <dev> <on | off>\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
/* 2. 打开文件 */
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR);
if (fd == -1)
{
printf("can not open file %s\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
/* 3. 写文件 */
if (0 == strcmp(argv[2], "on"))
{
status = 1;
write(fd, &status, 1);
}
else
{
status = 0;
write(fd, &status, 1);
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}# 1. 使用不同的开发板内核时, 一定要修改KERN_DIR
# 2. KERN_DIR中的内核要事先配置、编译, 为了能编译内核, 要先设置下列环境变量:
# 2.1 ARCH, 比如: export ARCH=arm64
# 2.2 CROSS_COMPILE, 比如: export CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu-
# 2.3 PATH, 比如: export PATH=$PATH:/home/book/100ask_roc-rk3399-pc/ToolChain-6.3.1/gcc-linaro-6.3.1-2017.05-x86_64_aarch64-linux-gnu/bin
# 注意: 不同的开发板不同的编译器上述3个环境变量不一定相同,
# 请参考各开发板的高级用户使用手册
KERN_DIR = /home/book/100ask_imx6ull-sdk/Linux-4.9.88
all:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules
$(CROSS_COMPILE)gcc -o ledtest ledtest.c
clean:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules clean
rm -rf modules.order
rm -f ledtest
# 参考内核源码drivers/char/ipmi/Makefile
# 要想把a.c, b.c编译成ab.ko, 可以这样指定:
# ab-y := a.o b.o
# obj-m += ab.o
obj-m += dtsled.o将驱动程序、测试程序和Makefile放在同一个文件夹里,如下:

2.编译led驱动
编译驱动前,要确保虚拟机上的Linux内核版本与开发板上的内核版本一致。
将上面的06_dtsled文件夹上传到虚拟机上,并进入到此文件夹。执行“make”命令就可以编译,编译完成后会生成 dtsled.ko 、ledtest 两个文件。
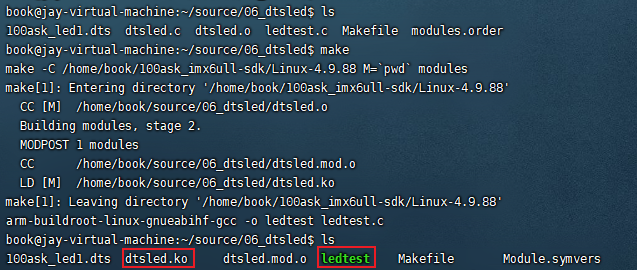
此时,把这两个文件拷贝到 Ubuntu上的nfs 目录下备用:
cp 100ask_led.ko ledtest ~/nfs_rootfs 3.在开发板上安装驱动模块
在开发板串口终端上执行如下命令,即可安装相应的驱动模块。
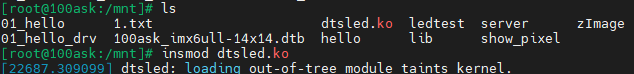
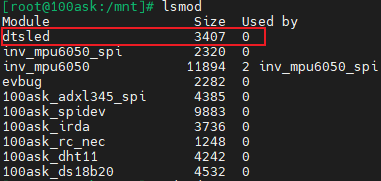
安装完成后可以执行 lsmod 命令来查看是否安装成功。
4.执行测试程序
驱动模块安装成功后,就可以使用测试程序来控制 led 灯的状态,如下图所示,操作 led 灯时可同时观察开发板串口旁的灯是否有亮灭的变化。

























 340
340

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








