Unit 3
Part 1
1. Does the following network represent a star topology?
True
2. Does the following network represent a line topology?
True
3. Does the following network represent a ring topology?
True
4. Does the following network represent a star topology?
False
5. Does the following network represent a star topology?
True
6. Does the following network represent a bus topology?
True
7. Does the following network represent a wireless topology?
False
8. Does the following network represent an ad-hoc topology?
False
9. Does the following network represent a star topology?
False
10. Does the following network represent a full mesh topology?
False
11. Does the following network represent a star topology?
True
12. Does the following network represent an ad-hoc topology?
True
13. Does the following network represent a line topology?
False
- Does the following network represent a ring topology?
False
Part 2
16. Does the following hybrid network topology contain an ad-hoc subnetwork?
True
17. Does the following hybrid network topology contain a ring subnetwork?
True
18. Does the following hybrid network topology contain a line subnetwork?
True
19. Does the following hybrid network topology contain a line subnetwork?
True
20. Does the following hybrid network topology contain a full mesh subnetwork?
False
21. Does the following hybrid network topology contain a star subnetwork?
True
22. Does the following hybrid network topology contain a tree subnetwork?
True
23. Does the following hybrid network topology contain a bus subnetwork?
True
24. Does the following hybrid network topology contain a tree subnetwork?
True
25. Does the following hybrid network topology contain an ad-hoc subnetwork?
True
26. Does the following hybrid network topology contain a ring subnetwork?
True
27. Does the following hybrid network topology contain a bus subnetwork?
False
28. Does the following hybrid network topology contain a tree subnetwork?
False
29. Does the following hybrid network topology contain a tree subnetwork?
True
30. Does the following hybrid network topology contain a line subnetwork?
True
31. Does the following hybrid network topology contain an ad-hoc subnetwork?
True
32. Does the following hybrid network topology contain a line subnetwork?
False
33. Does the following hybrid network topology contain a wireless subnetwork?
False
34. Does the following hybrid network topology contain an ad-hoc subnetwork?
False
35. Does the following hybrid network topology contain a wireless subnetwork?
False
Part 3
1. What is the port number why it is important?
What is the port number?
The so-called port is like a house number. The client can find the corresponding server through the IP address, but the server has many ports. Each application corresponds to a port number. Through the port number similar to the house number, the client Only the client can actually access the server. In order to distinguish the ports, each port is numbered, which is the port number
why it is important?
Port numbers can be used for different programs on the same host
2. What are the well-known port numbers for the most popular protocols? You can make a table to list the most known port numbers.
| Port number | function |
| 22 | SSH remote connection |
| 23 | TELNET remote login |
| 53 | DNS domain name resolution |
| 80 | HTTP communication |
| 443 | HTTPS encrypted hypertext transfer |
3. What is the difference between TCP and UDP protocols?
1) TCP is connection-based, while UDP is connectionless;
2) Requirements for system resources: more TCP (TCP has 20-byte packets), less UDP (UDP only has 8 bytes);
3) UDP program structure is relatively simple;
4) TCP is a byte stream mode, while UDP is a data packet mode;
- TCP guarantees data correctness, security and reliability, and guarantees data order, while UDP may lose packets, and UDP does not guarantee data order.
4. Suppose a 10-Mbps Ethernet hub (repeater) is replaced by a 10-Mbps switch, in an
environment where all traffic is between a single server and N “clients.” Because all
traffic must still traverse the server–switch link, nominally there is no improvement in
bandwidth. (a) Would you expect any improvement in bandwidth? If so, why? (b) What other advantages and drawbacks might a switch offer versus a hub?
- Hub is bandwidth shared, switch are bandwidth independent. If you use a switch, the bandwidth of each machine is 10 M, and if you use a hub, the bandwidth of each machine is 10/N M.
- The hub adopts a bus topology, and each node shares a bus for communication. The transmission and reception of data packets use the CSMA/CD protocol, which must be unidirectional at the same time and can only be maintained in half-duplex mode. Two ports cannot send and receive data at the same time, and when two ports communicate, the other ports work differently. When two ports on the switch communicate, the channels between them are independent of each other, enabling full-duplex communication. Both ports send and receive data at the same time.
5. What aspect of IP addresses makes it necessary to have one address per network
interface, rather than just one per host?
- Limited resources
- When setting up a large and medium-sized local area network, it can satisfy the interconnection of lower-level devices and the communication of devices at the same level.
6. What are the source and destination IP addresses in the ARP request and ARP reply
packet?
“It depends”.
If the sending host does not have an existing ARP entry for the destination IP it is attempting to send communicate with, then the ARP request is sent as a local broadcast, which means the destination address is 255.255.255.255, but sourced from the hosts’s own IP. If a host that has the requested IP address is on the network, it will reply to the ARP with the requestor’s destination IP in the ARP reply and its own IP is the source.
ARP requests are also sent by the transmitting host at an interval before the expiration of the ARP cache timeout, in order to reset the timer on the cache entry and avoid having to stop transmissions to re-discover the destination MAC address. These requests are sent directly to the end host’s IP, not broadcast.
There is also a type of ARP message called a “Gratuitous ARP” which is simply an ARP reply message that is sent preemptively as a broadcast in order to update the ARP caches on other hosts on the broadcast domain. These are often used by devices implementing a failover protocol such as VRRP, where the ownership of an IP address can move between devices. Without that, end hosts would not be able to reach the IP on the new device until their own ARP caches timed out.
- Having ARP table entries time out after 10 to 15 minutes is an attempt at a reasonable compromise. Describe the problems that can occur if the timeout value is too small or too large.
If the timeout time is too short, the traffic of ARP request and response packets will be too frequent, and if the timeout time is too long, the host after replacing the network card will be unable to communicate with other hosts on the network.
8. What is the difference between IP address and MAC address? Why there are two
methods of addressing in computer networks?
1) The nature of the address is different
MAC addresses are physical addresses and IP addresses are logical addresses. MAC address is immutable, IP address can be changed.
2) Variability
The MAC address is unique, and the MAC address of each hardware is fixed when it leaves the factory; the IP address is not unique. Therefore, many application software are developed around the MAC address.
3) Different working levels
Layer 2 forwards data frames based on MAC addresses, and Layer 3 forwards packets based on IP addresses. Layer 2 switches forward data based on the MAC address table, and routers forward data based on the routing table (IP address).
4) Length definition
The MAC address is the address carried on the Ethernet network card, and the length is 48 bits. The current mainstream IP address is 32 bits long. IP addresses and MAC addresses are linked together by the ARP protocol.
5) The distribution is based on different
IP address assignment is based on network topology and MAC address assignment is based on manufacturer.
The role of the network layer ip address is different from the problem solved by the mac address of the data link layer. The network layer ip address solves the problem of cross-network transmission, while the mac address of the data link layer solves the problem of the local area network (more To be precise, it is the problem of Ethernet) transmission
9.What is the subnet mask? And how can it improve the performance?
What is the subnet mask?
A subnet mask determines which parts of the IP address are network and host identifiers. It is a 32-bit number that distinguishes each octet in the IP address.
And how can it improve the performance?
The subnet mask allows network traffic to understand IP addresses by splitting them into the network and host addresses.
10. Define a network that would be suitable for
A. Client-Server architecture.
B. Peer-to-Peer architecture.
You can use the same idea of representing the network from Parts 1 & 2, and you can
either draw a diagram for the network or describe the breaking down links between any
two devices using text. For the client-server, your network should connect client
devices node1, node2, node3, laptop4, laptop5, and laptop6 to one or more servers over
an internet network. You can add as many other devices (switches, routers, nodes,
access points, busses, etc.) to the network as you wish, using the same naming scheme
as in the previous parts.
For the peer-to-peer, you can add as many other devices (switches, routers, nodes,
access points, busses, etc.) to the network as you wish, using the same naming scheme
as in the previous parts.
Unit 4
1.
- IP header
# 0x0000: a454 31c3 bc86 7ad0 b284 0f1f 8847 0000
# 0x0010: 03e7 4500
a454 31c3
a:version number
4:Header length, 4*4 bytes = 16 bytes
54:Service type
31c3:Total IP packet length=12739 bytes
bc86 7ad0
bc86:package unique identifier
7ad0:111 1 0101 1010 000
111:000 0 0000 0000 0000, 1+no segment+have subsequent segments
1 0101 1010 000:slice offset
b284 0f1f
b2:survival time
84:protocol, 0x84=132, SCTP Stream Control Transmission Protocol
0f1f:header checksum
8847 0000 03e7 4500
8847 0000:source IP, 136.71.0.0
03e7 4500:destination IP, 3.231.69.0
0038 0000 4000 3406 0000 b3d5 ..E..8..@.4.....
# 0x0020: 400e 4c63 32ab f448 7f80 5e80 63cf 33e3 @.Lc2..H..^.c.3.
# 0x0030: 8544 5082 d4d0 0000 000a 3215 35da c68a .DP.......2.5...
# 0x0040: 3a79 f2fb 9d9d 12e1 8cd1 :y........
Unit 5
1.Taking TCP as an example, In TCP connection, flags are used to indicate a particular state of connection or to provide some additional useful information like troubleshooting purposes or to handle a control of a particular connection. Most commonly used flags are “SYN”, “ACK ” and “FIN”. Each flag corresponds to 1 bit information.
No, it will waste unnecessary resources
2.Affect communication reliability
Payload is a variable-length field. Its minimum size is governed by a requirement for a minimum frame transmission of 64 octets.[d] With header and FCS taken into account, the minimum payload is 42 octets when an 802.1Q tag is present[e] and 46 octets when absent. When the actual payload is less than the minimum, padding octets are added accordingly. IEEE standards specify a maximum payload of 1500 octets. Non-standard jumbo frames allow for larger payloads on networks built to support them.
3.Payload is a variable-length field. Its minimum size is governed by a requirement for a minimum frame transmission of 64 octets.With header and FCS taken into account, the minimum payload is 42 octets when an 802.1Q tag is present and 46 octets when absent. When the actual payload is less than the minimum, padding octets are added accordingly. IEEE standards specify a maximum payload of 1500 octets. Non-standard jumbo frames allow for larger payloads on networks built to support them.
4.AODV routing algorithm
5.The packet will circle endlessly, in both the M => B2 => L => B1 and M => B1 => L => B2 directions.
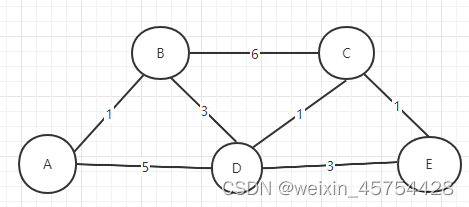
6.As can be seen from the figure, B1 has the smallest ID, while B3 and B7 are designated bridges. It can be seen from the spanning tree algorithm that the two ports of the B5 bridge, the upper left port of the B2 bridge, and the lower port of the B6 bridge are not selected. The answer is pictured
7.When fragmenting, only the upper layer data is fragmented, and the original IP header does not need to be fragmented, so the length of the data to be fragmented is only 5200-20=5180
The specific process is as follows:
1) First calculate the length of the IP payload in the largest IP packet = MTU-IP header length = 1500-20= 1480 bytes.
2) Then divide 5180 bytes into 4 pieces according to the length of 1480 bytes, 5180= 1480+1480+1480+74.
3) In the end, the sender will add IP headers to the 4 fragments, and then send them to form 4 IP packets. The lengths of the 4 IP packets are 1500 bytes, 1500 bytes, 1500 bytes and 94bytes respectively.
8.
1) Class A address
The representation range of class A addresses is: 0.0.0.0~127.255.255.255, and the default netmask is: 255.0.0.0; class A addresses are allocated to large-scale networks. A class A network uses the first group of numbers to represent the address of the network itself, and the last three groups of numbers as the addresses of the hosts connected to the network. Assigned to large networks with a large number of hosts (direct individual users) and a small number of local area networks. For example, IBM's network.
2) Class B address
The representation range of class B addresses is: 128.0.0.0~191.255.255.255, and the default network mask is: 255.255.0.0; class B addresses are assigned to general medium-sized networks. Class B networks use the first and second sets of numbers to represent the address of the network, and the last two sets of numbers represent the host addresses on the network.
3) Class C address
The representation range of class C addresses is: 192.0.0.0~223.255.255.255, and the default netmask is: 255.255.255.0; class C addresses are assigned to small networks, such as general local area networks and campus networks, and the number of hosts that can be connected is the least , use the user to be divided into several network segments for management. Class C networks use the first three sets of numbers to represent the address of the network, and the last set of numbers as the host address on the network.
9.The mobile network environment is becoming more and more complex, making it difficult to apply routing algorithms to the mobile network environment.
10.
1) IPv6 uses a smaller routing table. It makes routers forward packets faster
2) IPv6 adds enhanced multicast support and convection control, which is very beneficial for multimedia applications and quality of service (QoS) control
3) IPv6 adds support for automatic configuration. This is an improvement and extension of the DHCP protocol, which makes the management of the network (especially the local area network) more convenient and fast.
4) IPv6 has higher security. Users can encrypt data at the network layer and verify IP messages, which greatly enhances the security of the network
5) IPv6 has better capacity expansion capability. IPv6 allows the protocol to be extended when new technologies or applications require it
6) IPv6 has a better header format. IPv6 uses a new header format that simplifies and speeds up the routing process and improves efficiency.






















 627
627











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








