JDBC
JDBC简述
先来段代码看看,诶诶诶,先别着急复制去Idea运行:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1、注册成功
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");//使用如果是mysql5.+版本可以不写这一句
//2、获取连接对象
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1?useSSL=false";//localhost 是mysql设置的主机 db1是自己新建的数据库名
String username = "root";//用户名(你自己的)
String password = "admin";//密码(你自己的)
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//3、定义SQL
String sql = "update tb_goods set title = '牛马' where id = 7";
//4、获取执行sql的对象
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
//5、执行sql
int count = stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
//6、处理结果
System.out.println(count);
//7、释放资源
stmt.close();
conn.close();
}
JDBC概念:
JDBC就是使用Java语言操作关系型数据库的一套API
运行代码
导包
IDEA新建工程(记得先设置好自己的SDK)
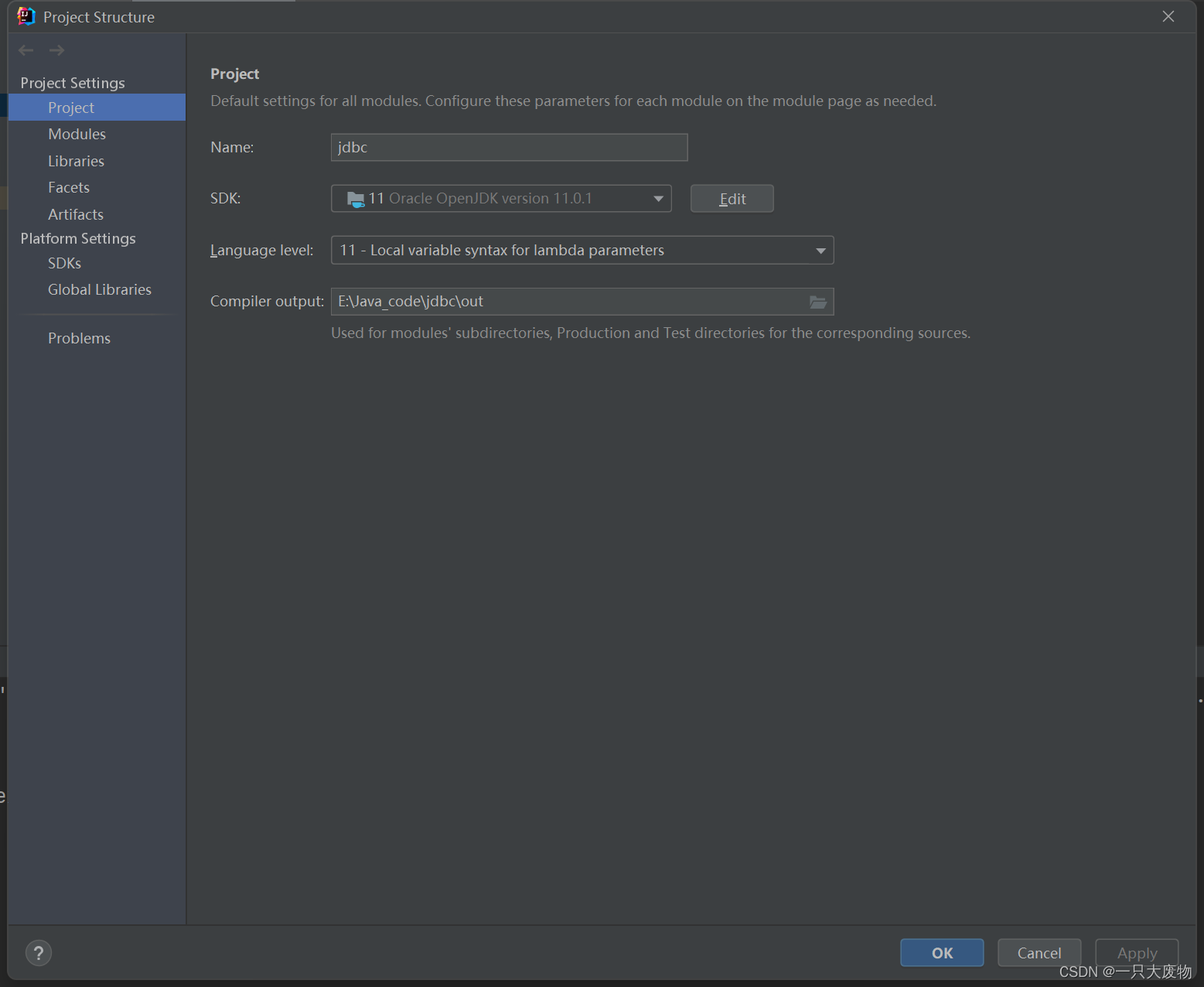
新建Modules,在新建的Modules目录下新建lib文件目录,后将下载好的jar包复制入jar包,我的版本是JDK11 使用了mysql-5.1.48,这里采用的是最基本的导包方法,后期使用到maven就不用这么麻烦
jar包上这儿下载去
mysql与数据库以及jdk各版本的匹配情况上这儿看
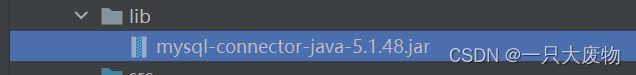
对准包右键点击Add as Li……
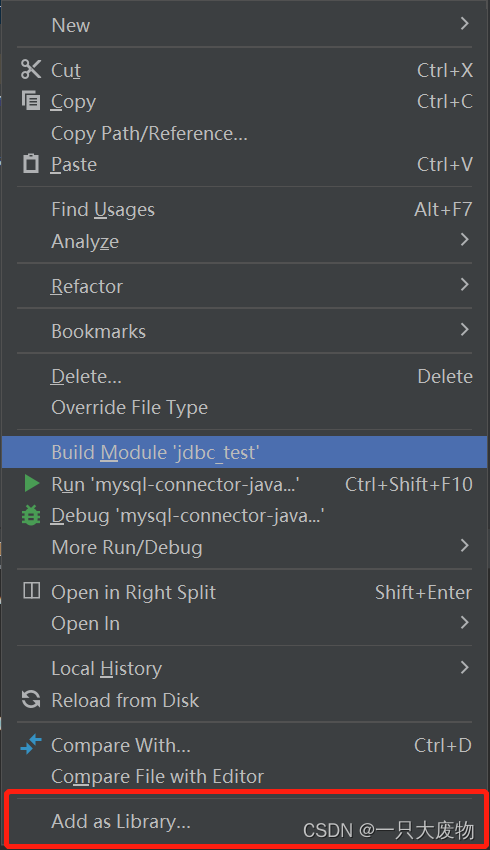
点击Module Library,直接OK就可以
接下去就新建类文件开始粘贴源码就可以运行自己的项目了
JDBC的API详解:
DriverManager(驱动管理类)
作用:
(较常用方法: getConnection(获取数据库连接Connetion对象)、registerDriver(注册驱动com.mysql.jdbc.Driver中使用了此方法))
- 注册驱动
- 获取数据库连接
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1?useSSL=false";
//如果连接的是本机且端口号也为3306可以简化书写为
String url = "jdbc:mysql:///db1?useSSL=false";
Connection(数据库连接对象)
作用:
- 获取执行SQL的对象
- 普通执行SQL对象:Statement createStatement()重点
- 预编译SQL的执行SQL对象:防止SQL注入PrepareStatement prepareStatement(sql)重点
- 执行存储过程的对象:CallableStatement prepareCall(sql)
防注入代码测试
public void testlogin() throws Exception {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1?useSSL=false";
String username = "root";
String password = "admin";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
String title = "'or '1' = '1";
double price = 4999.00;
String sql = "select * from tb_goods where title = '"+ title +"' and price = '" + price + "'";
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
if (rs.next()){
System.out.println("成功");
}else {
System.out.println("失败");
}
//7、释放资源
rs.close();
stmt.close();
conn.close();
}
如果出现在登录的功能,那么是不是意味着我只要把密码或者账号输入’or ‘1’ = '1,那我是不是就可以为所欲为了,直接登录都不要,注入!!注入!!!注入!!!!
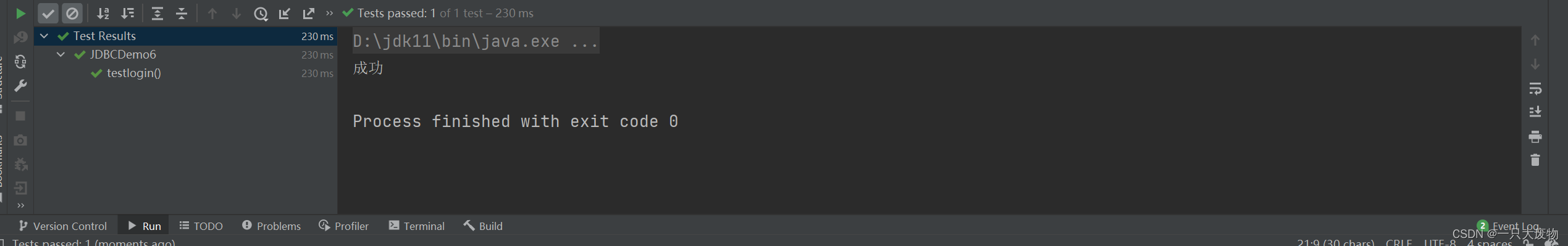
如何防止注入:
public void testPrepatedStatement() throws Exception {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1?useSSL=false";
String username = "root";
String password = "admin";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//SQL语句中的参数值,使用?占位符替代
String sql = "select * from tb_goods where title=? and id=?";
//通过Connection对象获取,并传入对应的sql语句,防注入
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//向?传入值
ps.setString(1, "手机");
ps.setInt(2, 2);
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()){
System.out.println(rs.getInt(1));
System.out.println(rs.getString(2));
System.out.println(rs.getDouble(3));
}
//7、释放资源
rs.close();
ps.close();
conn.close();
}
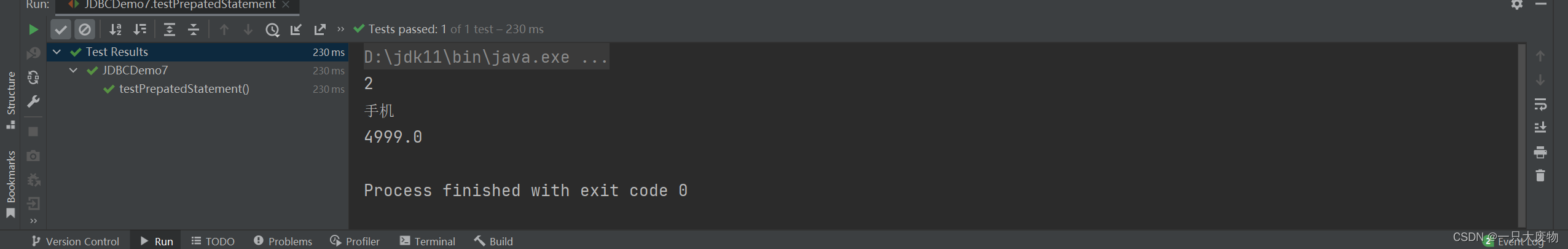
果然失败
下面会更加详细的介绍
- 管理事务
MySQL中:
# 开启事务
BEGIN;/START TRANSACTION;
# 提交事务
COMMIT;
# 回滚事务
ROLLBACK;
JDBC中:
//开启事务,true为自动提交事务;false为手动提交事务
setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit)
// 提交事务
commit()
//回滚事务
rollback();
试试:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1、注册成功
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2、获取连接对象
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1?useSSL=false";
String username = "root";
String password = "admin";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//3、定义SQL
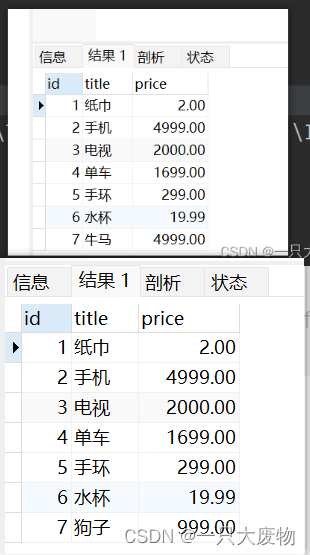
String sql1 = "update tb_goods set title = '狗子' where id = 7";
String sql2 = "update tb_goods set price = 4999.00 where id = 7";
//4、获取执行sql的对象
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
try {
//开启事务
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
//5、执行sql
int count1 = stmt.executeUpdate(sql1);
//6、处理结果
System.out.println(count1);
int i = 3/0;
//5、执行sql
int count2 = stmt.executeUpdate(sql2);
//6、处理结果
System.out.println(count2);
//提交事务
conn.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
//回滚事务
conn.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
}
//7、释放资源
stmt.close();
conn.close();
}
执行后数据库结果为:(由于误删所以截图就将就看吧)
Statement
作用:
- 执行SQL语句
-int executeUpdate():执行DML(对表中数据进行操作)、DDL(对数据库操作)
返回值:int(1)DML语句影响行数(2)DDL语句执行后,执行成功也可能返回0(后者少用)
-ReseultSet executeQuery(sql):执行DQL(对表中数据进行查询)语句
返回值:ResultSet
上代码:
@Test
public void testDML() throws Exception {
//1、注册成功
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2、获取连接对象
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1?useSSL=false";
String username = "root";
String password = "admin";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//3、定义SQL
String sql = "update tb_goods set title = '牛马' where id = 7";
//4、获取执行sql的对象
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
//5、执行sql
int count = stmt.executeUpdate(sql);//DML返回执行的影响行数
//6、处理结果
if(count > 0){
System.out.println("修改成功");
}else {
System.out.println("修改失败");
}
//7、释放资源
stmt.close();
conn.close();
}
@Test
public void testDDL() throws Exception {
//1、注册成功
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2、获取连接对象
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1?useSSL=false";
String username = "root";
String password = "admin";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//3、定义SQL
String sql = "drop DATABASE db2";
//4、获取执行sql的对象
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
//5、执行sql
int count = stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
//6、处理结果
System.out.println(count);//DDL可能返回0
//7、释放资源
stmt.close();
conn.close();
}
ResultSet(结果集对象)
作用:
-
封装了DQL查询语句的结果
ResultSet stmt.executeQuery(sql)//:执行DQL语句,返回ResultSet对象· 获取查询结果
boolean next():(1)将光标从当前位置向前移动一行(2)判断当前是否为有效行
返回值:
true:有效行,当前行有效数据
false:无效行,当前行没有数据xxx getXxx(参数):获取数据
xxx:数据类型;如:int getInt(参数);String getString(参数)
参数:
int:列的编号,从1开始
String:列的名称
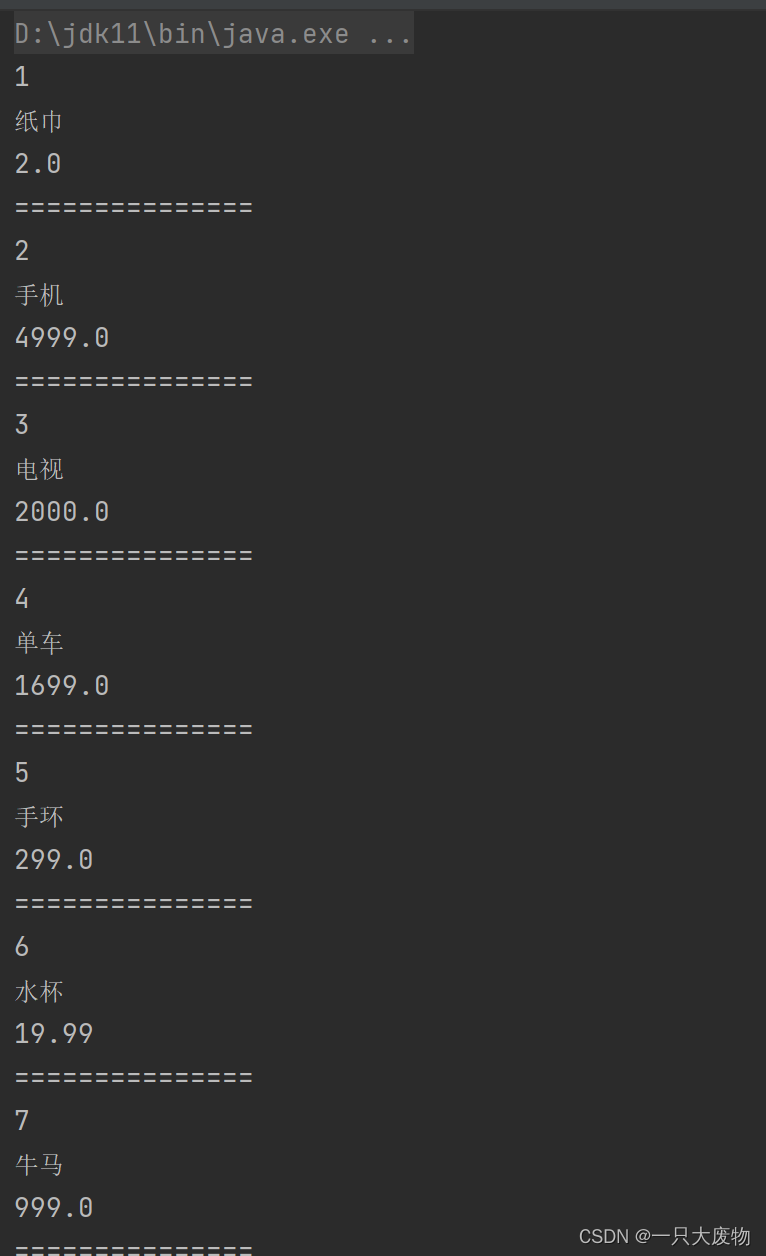
小小test一下
@Test
public void testDML() throws Exception {
//1、注册成功
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2、获取连接对象
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1?useSSL=false";
String username = "root";
String password = "admin";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//3、定义SQL
String sql = "select * from tb_goods";
//4、获取执行sql的对象
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
//5、执行sql
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
while(rs.next()){
int id = rs.getInt(1);
String title = rs.getString(2);
double price = rs.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id);
System.out.println(title);
System.out.println(price);
System.out.println("===============");
}
//7、释放资源
rs.close();
stmt.close();
conn.close();
}
PreparedStatement
-
作用:
预编译SQL语句并执行:预防SQL注入问题。 -
SQL注入
SQL注入是通过操作输入来修改事先定义好的SQL语句,用以达到执行代码对服务器进行攻击的方法。
看一个SQL注入的问题,就是字符串字段输入特殊的字段实现最终的成效果
@Test
public void testlogin() throws Exception {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1?useSSL=false";
String username = "root";
String password = "admin";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
String title = "手机";
double price = 4999.00;
String sql = "select * from tb_goods where title = '"+ title +"' and price = '" + price + "'";
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
if (rs.next()){
System.out.println("成功");
}else {
System.out.println("失败");
}
//7、释放资源
rs.close();
stmt.close();
conn.close();
}
/**
SQL注入的问题
* */
@Test
public void testlogin_Inject() throws Exception {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1?useSSL=false";
String username = "root";
String password = "admin";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
String title = "' or 'a' = 'a";
double price = 4999.00;
String sql = "select * from tb_goods where title = '"+ title +"' and price = '" + price + "'";
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
if (rs.next()){
System.out.println("成功");
}else {
System.out.println("失败");
}
//7、释放资源
rs.close();
stmt.close();
conn.close();
}
如何预防,来看看
-
获取PreparedStatement对象
//SQL语句中的参数值,使用?占位符替代 String sql = "select * from user where username=? and password=?"; //通过Connection对象获取,并传入对应的sql语句 PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql); -
设置参数值
PreparedStatement对象:setXxx(参数1,参数2):给?赋值
Xxx:数据类型;如setInt(参数1, 参数2)
参数1:?的位置编号,从1开始
参数2:?的值 -
执行SQL
//不需要再传递sql executeUpdate(); executeQuery();
看看代码:
@Test
public void testPrepatedStatement_Inject() throws Exception {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1?useSSL=false";
String username = "root";
String password = "admin";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//SQL语句中的参数值,使用?占位符替代
String sql = "select * from tb_goods where title=? and id=?";
//通过Connection对象获取,并传入对应的sql语句
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//向?传入值
ps.setString(1, "' or 'a' = 'a");
ps.setInt(2, 2);
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
if(rs.next()){
System.out.println("成功");
while (rs.next()) {
System.out.println(rs.getInt(1));
System.out.println(rs.getString(2));
System.out.println(rs.getDouble(3));
}
}else{
System.out.println("失败");
}
//7、释放资源
rs.close();
ps.close();
conn.close();
}
PreparedStatement原理
使用黑马的老师一张ppt来理解下

数据线程池
简介
数据连接池是个容器,负责分配,管理数据库连接(Connection)
好处:
- 资源重用
- 提升系统响应速度
- 避免数据库连接遗漏
Druid数据库连接池
使用步骤
-
导入jar包duid-1.1.12.jar
下载链接
粘贴到lib目录下
-
定义配置文件
driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1?useSSL=false&ServerPreStmts=true username=root password=admin # 初始化连接数量 initialSize=5 # 最大连接数 maxActive=10 # 最大等待时间 maxWait=3000 -
加载配置文件
Properties prop = new Properties(); prop.load(new FileInputStream("jdbc_demo/src/druid.properties")); -
获取数据库连接池对象
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(prop); -
获取连接
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
以下使用一个小案例来汇总一下数据库线程池的知识:
Goods.java
package com.test.pojo;
public class Goods {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private double price;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "goods{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}
GoodsTest.java
package com.test.example;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory;
import com.test.pojo.Goods;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Properties;
public class GoodsTest {
@Test
public void selectAll() throws Exception {
//加载配置文件
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.load(new FileInputStream("src/druid.properties"));
//创建连接对象
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(prop);
//创建数据库连接对象
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
//sql查询语句
String sql = "select * from tb_goods";
//定义sql的执行对象
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//执行sql语句
ResultSet rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
//定义List<Goods>进行存储
List<Goods> list = new ArrayList<>();
while (rs.next()) {
Goods goods = new Goods();
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String title = rs.getString("title");
double price = rs.getDouble("price");
goods.setId(id);
goods.setName(title);
goods.setPrice(price);
list.add(goods);
}
System.out.println(list);
pstmt.close();
rs.close();
conn.close();
}
@Test
public void testAll() throws Exception {
String goodsTitle = "鼠标";
double goodsPrice = 9.99;
//加载文件
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.load(new FileInputStream("src/druid.properties"));
//创建连接对象
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(prop);
//创建数据库连接对象
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into tb_goods(title, price) values (?,?);";
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//设置参数
pstmt.setString(1, goodsTitle);
pstmt.setDouble(2, goodsPrice);
int count = pstmt.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(count > 0);
prop.clone();
conn.close();
pstmt.close();
}
@Test
public void testUpdate() throws Exception {
String goodsTitle = "狗子";
int goodsId = 7;
//加载配置文件
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.load(new FileInputStream("src/druid.properties"));
//创建连接的对象
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(prop);
//创建数据库连接对象
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
String sql = "update tb_goods set title = ? where id = ?";
//执行sql语句
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, goodsTitle);
pstmt.setInt(2,goodsId);
int count = pstmt.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(count > 0);
prop.clone();
conn.close();
pstmt.close();
}
@Test
public void testDeleteById() throws Exception {
int goodsId = 9;
//加载配置文件
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.load(new FileInputStream("src/druid.properties"));
//创建连接的对象
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(prop);
//创建数据库连接对象
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
String sql = "delete from tb_goods where id=?";
//执行sql语句
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setInt(1,goodsId);
int count = pstmt.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(count > 0);
prop.clone();
conn.close();
pstmt.close();
}
}
当然这里也可以采用工具类或者是方法的方式来进行简化代码,由于是练习,就没有采取更加简洁的代码了,如果需要可以将每个方法中的如下方法进行提取: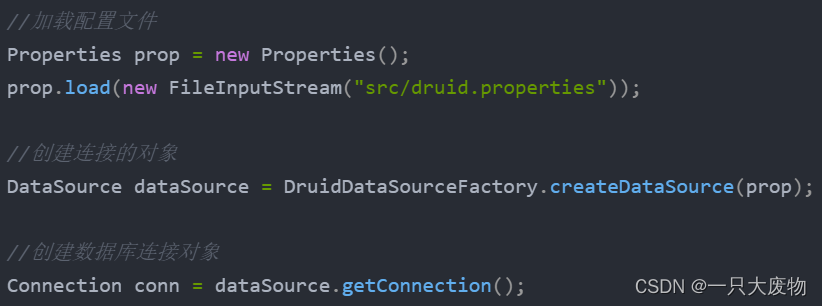
均可运行成功
druid.properties包路径出错的问题解决!
如果显示路径出错的话,你可以在本程序中进行输出当前程序路径,如果已经包含了当前项目名(module名)那就可以跟我一样写src/druid.properties即可,否则需将当前项目名(module名)添加,如:jdbc_demo/src/druid.properties
//路径可能会出错,有时需要添加(jdbc_demo)可以答应一下当前目录:
System.out.println(System.getProperty("user.dir"));
以上情况是我的输出当前文件,已经包含了本项目名






















 47
47











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








