JZ4 重建二叉树
递归
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Solution {
public TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int [] pre,int [] in) {
//数组长度为0的时候要处理
if(pre.length == 0){
return null;
}
int rootVal = pre[0];
//数组长度仅为1的时候就要处理
if(pre.length == 1){
return new TreeNode(rootVal);
}
//我们先找到root所在的位置,确定好前序和中序中左子树和右子树序列的范围
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
int rootIndex = 0;
for(int i=0;i<in.length;i++){
if(rootVal == in[i]){
rootIndex = i;
break;
}
}
//递归,假设root的左右子树都已经构建完毕,那么只要将左右子树安到root左右即可
//这里注意Arrays.copyOfRange(int[],start,end)是[)的区间
root.left = reConstructBinaryTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(pre,1,rootIndex+1),Arrays.copyOfRange(in,0,rootIndex));
root.right = reConstructBinaryTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(pre,rootIndex+1,pre.length),Arrays.copyOfRange(in,rootIndex+1,in.length));
return root;
}
}
更简便
import java.util.*;
/**
* Definition for binary tree
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int [] pre,int [] in) {
if(pre.length == 0||in.length == 0){
return null;
}
//新建一个TreeNode
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(pre[0]);
//对中序数组进行输入边界的遍历
for(int i = 0; i < in.length; i++){
if(pre[0] == in[i]){//i就是根节点位置
//重构左子树,注意边界条件
//root. left = BinaryTree(左子树的前序数组,左子树的中序数组)
node.left = reConstructBinaryTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(pre, 1, i+1), Arrays.copyOfRange(in, 0, i));
//重构右子树,注意边界条件
//root. right = BinaryTree(右子树的前序数组,右子树的中序数组)
node.right = reConstructBinaryTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(pre, i+1, pre.length), Arrays.copyOfRange(in, i+1,in.length));
}
}
return node;
}
}
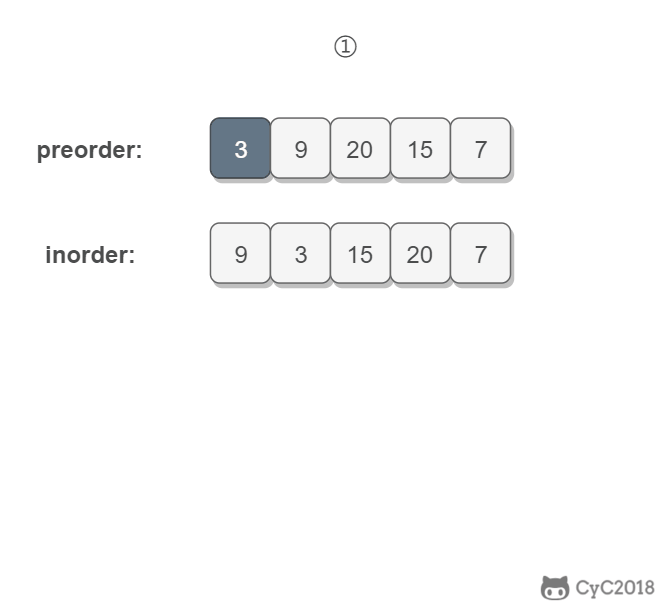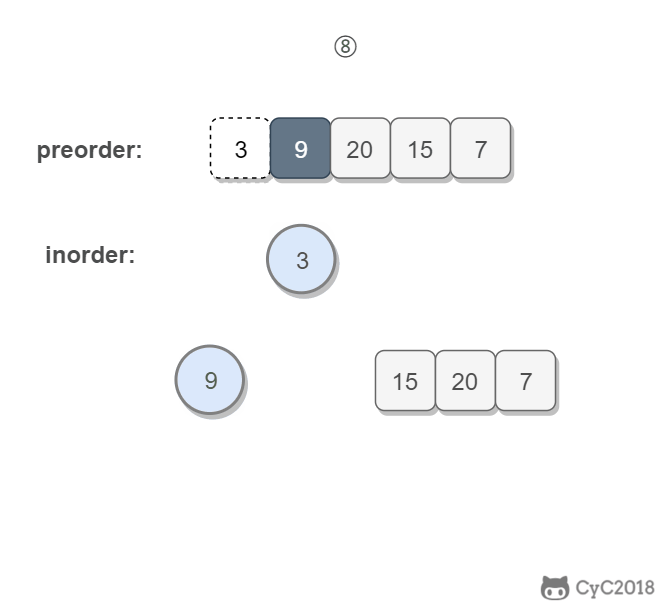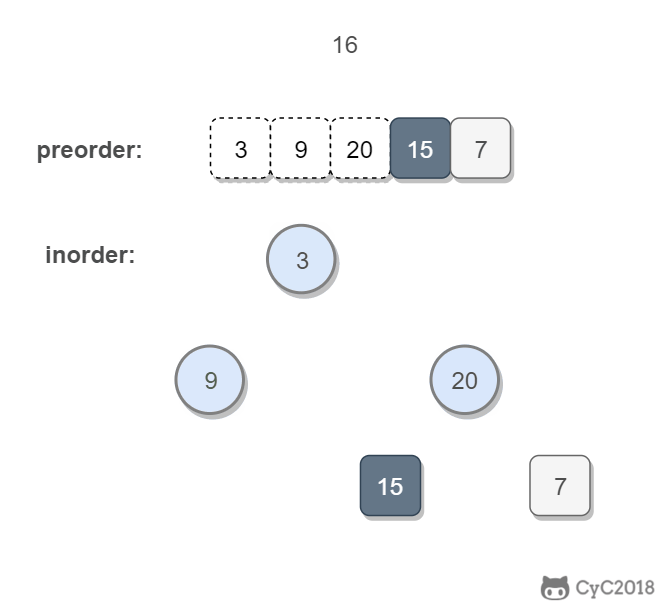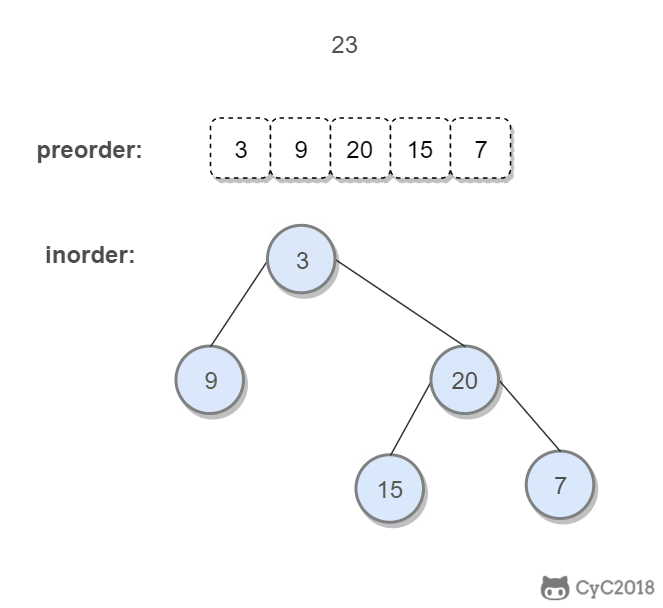
思路:
中序遍历的左右子树是由根节点获得:根节点左边是左子树,右边是右子树。
前序遍历的左右子树由 中序遍历的左右子树长度获得:中序遍历左子树长度为x,前序遍历的左子树就是根到x
所以只要找到中序遍历数组根节点的位置index
步骤:
- 构建一个找根的index的函数
- 写递归表达式
- 写归出口
JZ26 二叉搜索树与双向链表
代码
public class Solution {
TreeNode pre = null;//用一个全局变量去保存前一个节点
TreeNode root = null;
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode pRootOfTree) {
if (pRootOfTree==null)
return null;
Convert(pRootOfTree.left);
if (root==null){
root=pRootOfTree;
}
if (pre!= null){//和前一个节点创建关系
pRootOfTree.left=pre;
pre.right=pRootOfTree;
}
pre=pRootOfTree;//移动到下一节点
Convert(pRootOfTree.right);
return root;
}
}
JZ57 二叉树的下一个结点
代码
public class Solution {
TreeLinkNode GetNext(TreeLinkNode node)
{
if(node==null) return null;
if(node.right!=null){ //如果有右子树,则找右子树的最左节点
node = node.right;
while(node.left!=null) node = node.left;
return node;
}
while(node.next!=null){ //没右子树,则找父亲结点
if(node.next.left==node) return node.next;
node = node.next;
}
return null; //退到了根节点仍没找到,则返回null
}
}
分析
以该二叉树为例,中序遍历为:{D,B,H,E,I,A,F,C,G}

仔细观察,可以把中序下一结点归为几种类型:
-
有右子树,下一结点是右子树中的最左结点,例如 B,下一结点是 H
-
无右子树,且结点是该结点父结点的左子树,则下一结点是该结点的父结点,例如 H,下一结点是 E
-
无右子树,且结点是该结点父结点的右子树,则我们一直沿着父结点追朔,直到找到某个结点是其父结点的左子树,如果存在这样的结点,那么这个结点的父结点就是我们要找的下一结点。例如 I,下一结点是 A;例如 G,并没有符合情况的结点,所以 G 没有下一结点
JZ60 把二叉树打印成多行(套路)
队列
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > Print(TreeNode pRoot) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> res=new ArrayList<>();
if(pRoot==null)
return res;
Queue<TreeNode> q=new LinkedList<>();
q.add(pRoot);
while(!q.isEmpty()){
int size=q.size();
ArrayList<Integer> temp=new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
TreeNode node=q.poll();
temp.add(node.val);
if(node.left!=null)q.add(node.left);
if(node.right!=null)q.add(node.right);
}
res.add(temp);
}
return res;
}
}
思路:
- 创建数组链表 res,创建队列,加入根节点
- 循环队列(当队列不为空时)
先求队列的size,每次循环都会创建一个temp 的数组链表,
2.1 for循环q,把队列分别弹出node,加入temp,同时,加入加入下一层的节点(相当于一层一层弹出 ,一层的数量就是size) - for循环结束后把temp加入res
递归
//用递归做的
public class Solution {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > Print(TreeNode pRoot) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
depth(pRoot, 1, list);
return list;
}
private void depth(TreeNode root, int depth, ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> list) {
if(root == null) return;
if(depth > list.size())
list.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
list.get(depth -1).add(root.val);
depth(root.left, depth + 1, list);
depth(root.right, depth + 1, list);
}
}
思路:
利用递归的方法进行先序遍历,传递深度,递归深入一层扩容一层数组,先序遍历又保证了同层节点按从左到右入数组。
if(depth > list.size()) list.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());保证里面的ArrayList的个数正确。
list.get(depth -1).add(root.val); 保证了节点位置正确。
JZ58 对称的二叉树
递归
boolean isSymmetrical(TreeNode pRoot) {
if (pRoot == null)
return true;
return isSymmetrical(pRoot.left, pRoot.right);
}
boolean isSymmetrical(TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2) {
if (t1 == null && t2 == null)
return true;
if (t1 == null || t2 == null)
return false;
if (t1.val != t2.val)
return false;
return isSymmetrical(t1.left, t2.right) && isSymmetrical(t1.right, t2.left);
}
t1 指针和 t2指针一开始都指向这棵树的根,随后 t1 右移时,t2 左移,t1 左移时,t2右移。每次检查当前 t1 和 t2节点的值是否相等,如果相等再判断左右子树是否对称。
思路:
return isSymmetrical(t1.left, t2.right) && isSymmetrical(t1.right, t2.left);
不能判断某一节点的左右是不是一样
需要判断左节点的左节点和右节点的右节点
例如:
{8,6,6,5,7,7,5}
5和7是不一样的,但是是镜像
较难
JZ17 树的子结构
代码分析(递归)
public class Solution {
public boolean HasSubtree(TreeNode root1,TreeNode root2) {
if(root1 == null) return false;
if(root2 == null) return false;
return help(root1,root2) || HasSubtree(root1.left,root2) || HasSubtree(root1.right,root2);
}
public boolean help(TreeNode root1,TreeNode root2){
if(root2 == null) return true;
if(root1 == null ) return false;
return root1.val==root2.val&&help(root1.left,root2.left) && help(root1.right,root2.right);
}
}
分析


JZ23 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
递归
public class Solution {
public boolean VerifySquenceOfBST(int [] sequence) {
if(sequence.length == 0)
return false;
return helper(sequence, 0, sequence.length - 1);
}
boolean helper(int[] postorder, int left, int right) {
//如果left==right,就一个节点不需要判断了,如果left>right说明没有节点,
//也不用再看了,否则就要继续往下判断
if (left >= right)
return true;
int mid = left;//创建指针找出右子树,数组中第一个大于root的值 ,mid是右子树,mid后的也是右子树,
int root = postorder[right];
while (postorder[mid] < root)
mid++;
int temp = mid;//创建右子树的指针,为了判断后面的值是不是都大于root
while (temp < right) {
if (postorder[temp++] < root)
return false;//右子树一定比root大,不然就false
}
//然后对左右子节点进行递归调用
return helper(postorder, left, mid - 1) && helper(postorder, mid, right - 1);
}
}
分析
二叉搜索树的特点是左子树的值<根节点<右子树的值。而后续遍历的顺序是:
左子节点→右子节点→根节点;
步骤:
- 找出右子树,数组中第一个大于root的值
- 右子树后面的都大于root
- 再递归判断
栈
public boolean verifyPostorder(int[] postorder) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int parent = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
//注意for循环是倒叙遍历的
for (int i = postorder.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
int cur = postorder[i];
//当如果前节点小于栈顶元素,说明栈顶元素和当前值构成了倒叙,
//说明当前节点是前面某个节点的左子节点,我们要找到他的父节点
while (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() > cur)
parent = stack.pop();
//只要遇到了某一个左子节点,才会执行上面的代码,才会更
//新parent的值,否则parent就是一个非常大的值,也就
//是说如果一直没有遇到左子节点,那么右子节点可以非常大
if (cur > parent)
return false;
//入栈
stack.add(cur);
}
return true;
}
JZ24 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
解法一(递归回溯)
public class Solution {
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> FindPath(TreeNode root,int target) {
//终止条件
if (root == null || root.val > target) return list;
//添加进path
path.add(root.val);
//修正target
target -= root.val;
if (target == 0 && root.left == null && root.right == null) {
list.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(path));
}
//递归
FindPath(root.left, target);
FindPath(root.right, target);
//回溯
path.remove(path.size()-1);
return list;
}
}
解法二(遍历)
JZ61 序列化二叉树
解法一(递归)
public int index = -1;
String Serialize(TreeNode root) {
//序列化主要就是通过将这颗树以一种方式进行顺序化。我们就将这颗二叉树进行先序遍历,得到
//访问这颗二叉树的一个访问顺序
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
if(root == null){
sb.append("#,");
return sb.toString();
}
sb.append(root.val+",");
sb.append(Serialize(root.left));
sb.append(Serialize(root.right));
return sb.toString();
}
TreeNode Deserialize(String str) {
//反序列化二叉树则是需要将一个二叉树组成的字符创进行反序列化,然后得到这个
//字符串表示的二叉树
index ++;
int length = str.length();
if(index >= length){
return null;
}
String[] strr = str.split(",");
TreeNode node = null;
while(!strr[index].equals("#")){
node = new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(strr[index]));
node.left = Deserialize(str);
node.right = Deserialize(str);
}
return node;
}
解法二(队列)
String Serialize(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return "[]";
//序列化为"[1,2,3,null,null,4,5]"
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder("[");
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode t = q.poll();
if (t != null) {
res.append(t.val + ",");
q.add(t.left);
q.add(t.right);
} else
res.append("null,");
}
res.append("]");
return res.toString();
}
TreeNode Deserialize(String str) {
if (str.equals("[]")) return null;
String[] vals = str.substring(1, str.length() - 1).split(",");
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(vals[0]));
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(root);
int i = 1;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = q.poll();
if (!vals[i].equals("null")) {
node.left = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(vals[i]));
q.add(node.left);
}
i++;
if (!vals[i].equals("null")) {
node.right = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(vals[i]));
q.add(node.right);
}
i++;
}
return root;
}






















 3850
3850











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








