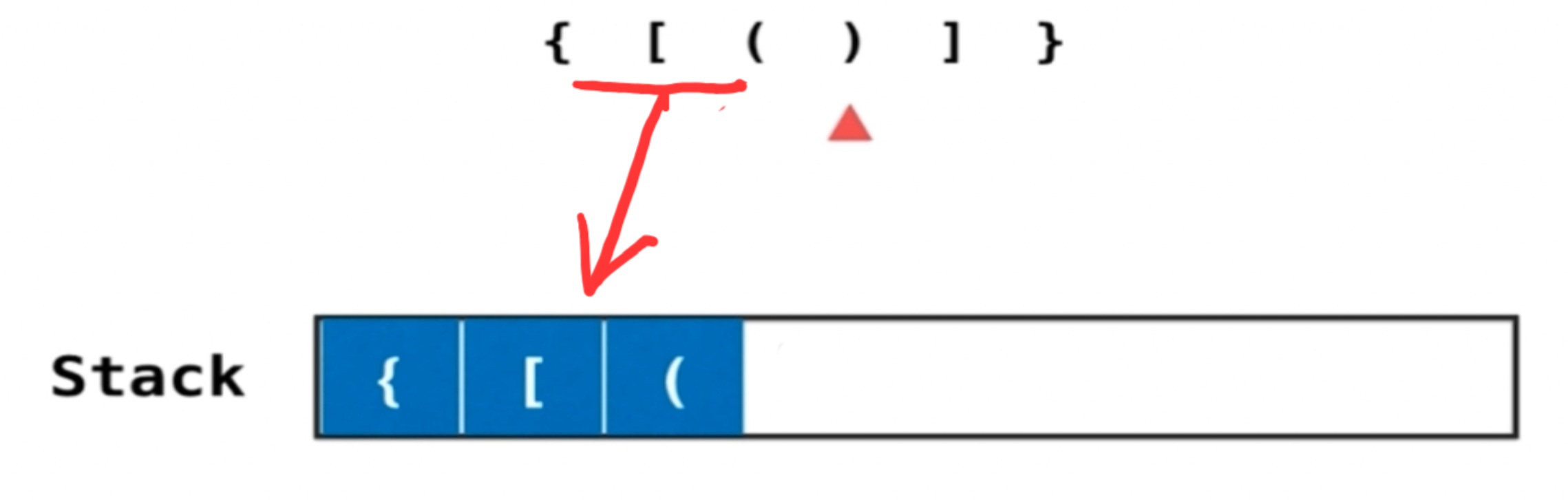
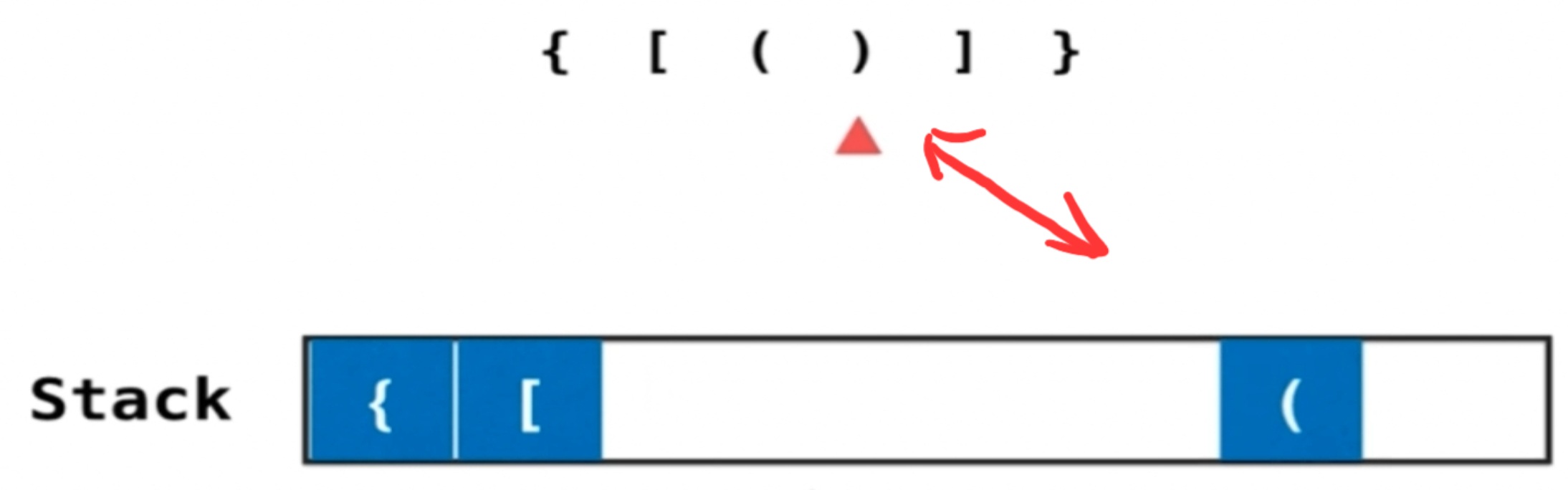
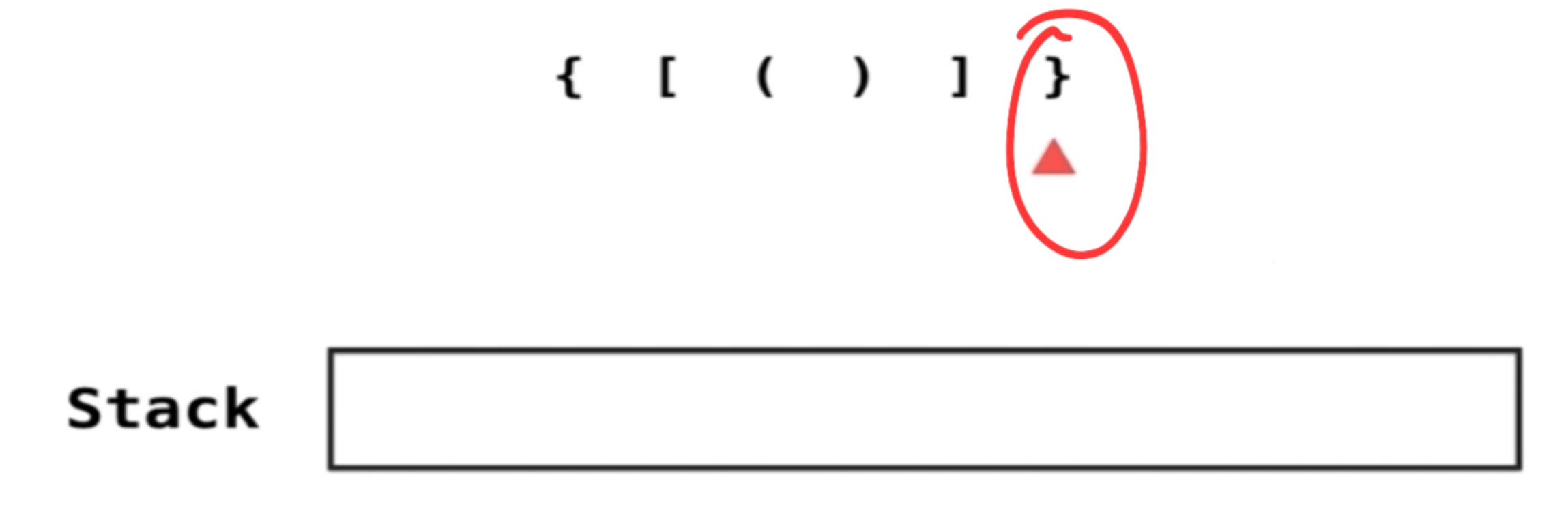
一:利用栈进行括号匹配
很简单:
遇到左括号就进栈,遇到右括号就将当前栈顶元素出栈,如果最后遍历完字符串栈为空就说明匹配了
bool isValid(string s) { stack<char> sta; for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){ if((s[i]=='(')||(s[i]=='{')||(s[i]=='[')) sta.push(s[i]); else{ //如果栈此时无元素,直接return if(sta.size()==0) return false; char aux=sta.top(); sta.pop(); if(s[i]==')'){ if(aux!='(') return false; } else if(s[i]=='}'){ if(aux!='{') return false; } else{ assert(s[i]==']'); if(aux!='[') return false; } } } if(sta.empty()) return true; return false; }不难,但是有几点细节
- 在匹配时候,判断一下栈是否为空。栈空一定不符合要求。(左括号少)
- 在结尾时候,依然判断一下栈是否为空。(左括号多)
char match; if(s[i]==')'){ match='('; } else if(s[i]=='}'){ match='{'; } else{ assert(s[i]==']'); match='['; } if(aux!=match) return false;可以这样写,使代码更简洁
if(aux==match) continue;
else return false;
bool isValid(string s) { stack<char> sta; for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){ if((s[i]=='(')||(s[i]=='{')||(s[i]=='[')) sta.push(s[i]); else{ //如果栈此时无元素,直接return if(sta.size()==0) return false; char aux=sta.top(); sta.pop(); if(s[i]==')'){ if(aux=='(') continue; else return false; } else if(s[i]=='}'){ if(aux=='{') continue; else return false; } else{ assert(s[i]==']'); if(aux=='[') continue; else return false; } } } if(sta.empty()) return true; return false; }
| 注意------栈对于解决嵌套问题很有帮助 |
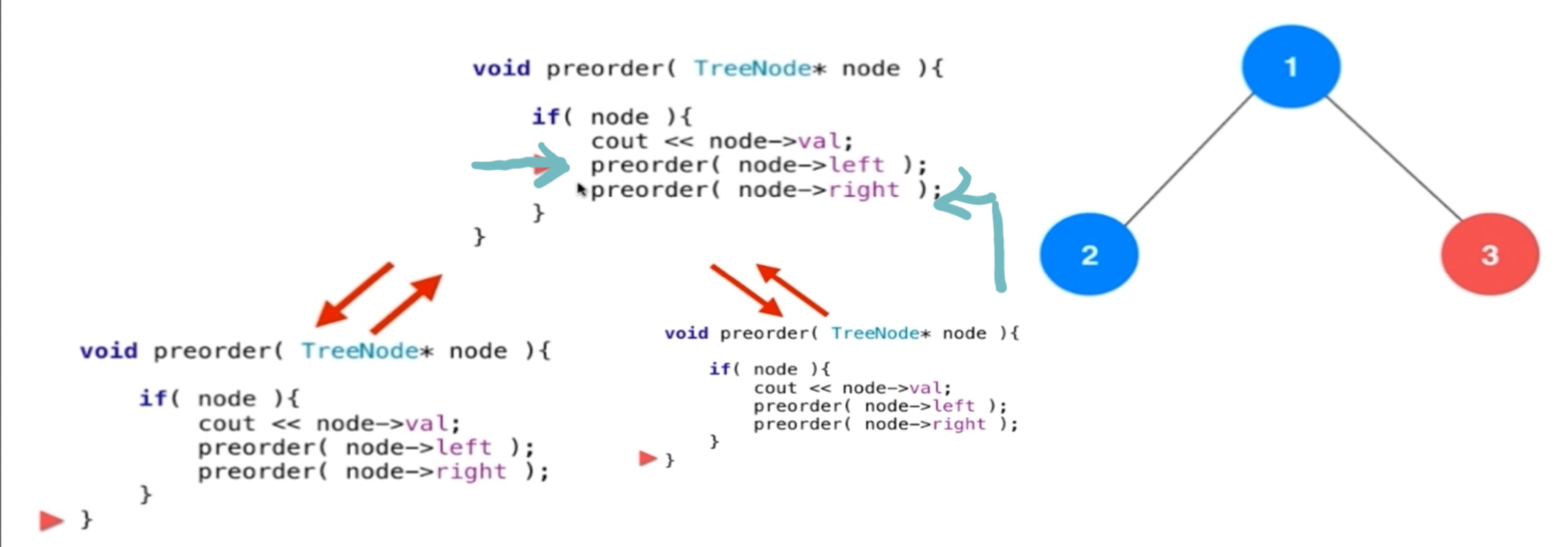
二:栈和递归的紧密关系
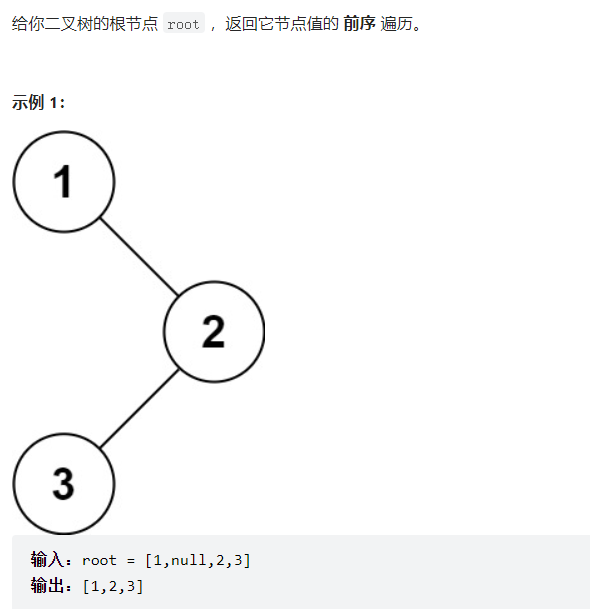
二叉树的前序遍历-----递归过程
其实就相当于不断执行子函数,然后暂停运行自己的所在程序,直至子程序运行结束,继续执行自己所在程序.
树的前序遍历------站实现
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) { //定义返回结果 vector<int> res; if(root==NULL) return res; //定义栈 stack<TreeNode*> sta; sta.push(root); //结果 while(!sta.empty()){ TreeNode* tmp=sta.top(); sta.pop(); res.push_back(tmp->val); //注意栈的后进先出 if(tmp->right) sta.push(tmp->right); if(tmp->left) sta.push(tmp->left); } return res; }
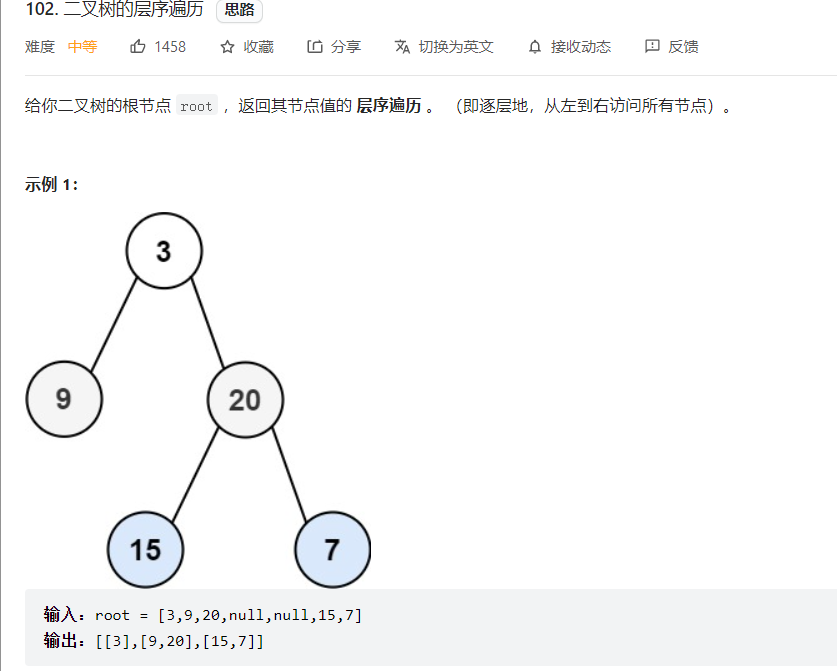
三:层次遍历-----分清每一层元素
代码:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) { //定义返回值--[[],..,[]] vector<vector<int>> res; if(root==NULL) return res; //队列用pair存放:元素+对应层数 queue<pair<TreeNode*,int>> que; que.push(make_pair(root,0)); //判断 while(!que.empty()){ //定义变量接收队列元素 TreeNode* tmp=que.front().first; int level=que.front().second; que.pop(); //存入res if(level==res.size()){//判断层数和res中【..】个数 res.push_back(vector<int>()); } res[level].push_back(tmp->val); if(tmp->left) que.push(make_pair(tmp->left,level+1)); if(tmp->right) que.push(make_pair(tmp->right,level+1)); } return res; }不难就是因为记录信息多了需要注意细节:
queue<pair<TreeNode*,int>> que;----注意队列的存放元素
que.push(make_pair(root,0));-----这里的0对应的是【。。】中的【】排序
TreeNode* tmp=que.front().first;------注意两个变量对应
int level=que.front().second;
res.push_back(vector<int>());-----初始化的是大【】中的小【】
res[level].push_back(tmp->val);-----给小【】存元素
注意几个忽视点:
if(root==NULL) return res;--------判断根节点不为空
if(level==res.size())------比较level和res中小括号的对应
四:C++的优先队列
#include<iostream> #include<queue> #include<ctime> using namespace std; int main(){ srand(time(NULL));//生成随机种子 priority_queue<int> p; for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ int n=rand()%100; p.push(n);//入队 } while(!p.empty()){ cout<<p.top()<<" "; p.pop(); } return 0; }
结论-----c++默认的优先级队列是大顶堆
这个就是最小堆的定义:
传入三个参数-----堆中数据类型,堆的底层数据实现类型,可以理解--孩子比自己greater
#include<iostream> #include<queue> #include<ctime> using namespace std; int main(){ srand(time(NULL));//生成随机种子 priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>> p; priority_queue<int,vector<int>,less<int>> q; for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ int n=rand()%100; p.push(n);//入队 q.push(n); } while(!p.empty()){ cout<<p.top()<<" "; p.pop(); } cout<<endl; while(!q.empty()){ cout<<q.top()<<" "; q.pop(); } return 0; }
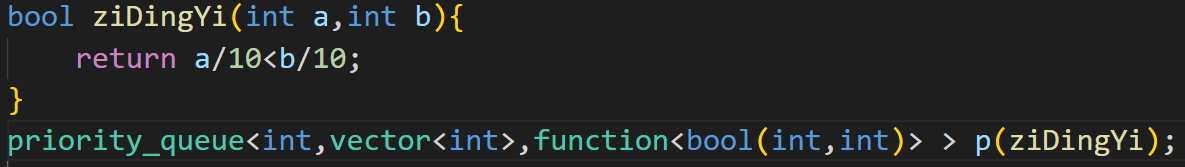
传入自定义函数的写法
首先头文件:#include<functional>
自己的写的函数:
bool mycmp(int a,int b){return a%10 < b%10 }
然后传入:function<bool(int,int)>
变量: p(mycmp);
五:Top K Frequent Elememt
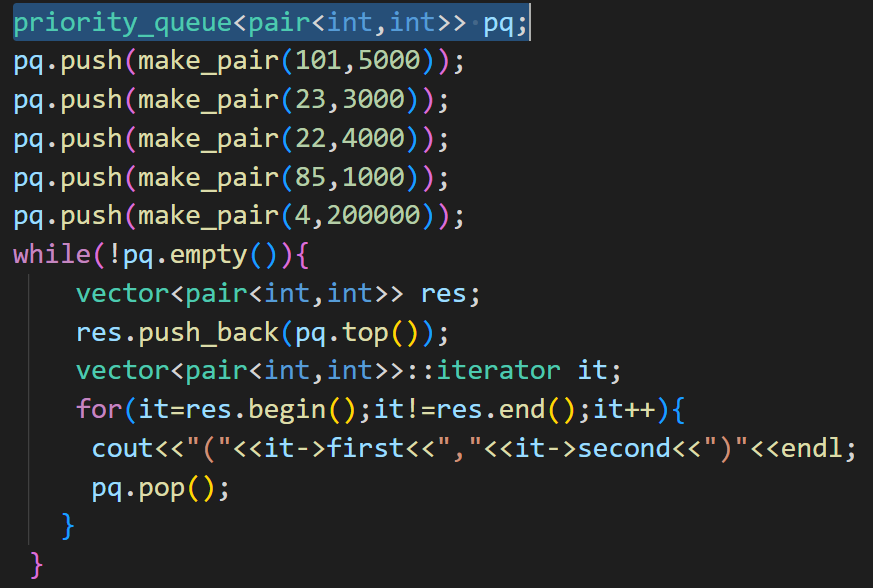
首先分析----存pair对的优先级队列
结论---------存放pair对的有限队列,默认对第一个元素进行排序
法一:
vector<int> topKFrequent(vector<int>& nums, int k) { //该题要输出频次最高的元素,也就是说:频次和元素两个都很重要 //查找表用map:k---元素,v---频次 //队列(大顶堆less):排序v,所以:pair<频次,元素> map<int,int> record; priority_queue<pair<int,int>> pq; //遍历数组更新查找表 for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++) record[nums[i]]++; //遍历查找表,把所有元素进队列 map<int,int>::iterator it; for(it=record.begin();it!=record.end();it++){ pq.push(make_pair(it->second,it->first));//先频次,后元素 } //输出要求的的前k个结果 vector<int> res; for(int i=0;i<k;i++){ res.push_back(pq.top().second);//元素 pq.pop(); } return res; }思想很简单粗暴:
- 遍历一下查找表,得到k-v对(map[k]=v),这里:k是元素值,v是频次
- 然后建立一个最大堆,这里因为要排序频次,输出元素,注意pair<频次,元素>
- 然后输出前k个就是所求的。
当然可以优化,因为题目要求输出前k个,那我们在堆中只存k个。这时候因为要淘汰频率低的,所以选用小顶堆。
class Solution { public: vector<int> topKFrequent(vector<int>& nums, int k) { //查找表用map:k---元素,v---频次 //队列(小顶堆greater):排序v,所以:pair<频次,元素> map<int,int> record; priority_queue<pair<int,int>,vector<pair<int,int>>,greater<pair<int,int>>>pq; //遍历数组更新查找表 for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++) record[nums[i]]++; //遍历查找表,把所有元素进队列 map<int,int>::iterator it; for(it=record.begin();it!=record.end();it++){ if(pq.size()==k){ if(it->second>pq.top().first){ pq.pop(); pq.push(make_pair(it->second,it->first));//先频次,后元素 } } else{ pq.push(make_pair(it->second,it->first)); } } //输出要求的的前k个结果 vector<int> res; while(!pq.empty()){ res.push_back(pq.top().second); pq.pop(); } return res; } };priority_queue< pair<int,int>,vector<pair<int,int>>,greater<pair<int,int>> > pq;
pair<int,int>
vector<pair<int,int>>
greater<pair<int,int>>

























 325
325











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








