Q1: A Plus Abs B
源码:
from operator import add, sub
def a_plus_abs_b(a, b):
"""Return a+abs(b), but without calling abs.
>>> a_plus_abs_b(2, 3)
5
>>> a_plus_abs_b(2, -3)
5
"""
if b < 0:
f = _____
else:
f = _____
return f(a, b)
实现一个函数,返回 a + b的绝对值,但不使用 abs 函数。
from operator import add, sub
def a_plus_abs_b(a, b):
"""Return a+abs(b), but without calling abs.
>>> a_plus_abs_b(2, 3)
5
>>> a_plus_abs_b(2, -3)
5
"""
if b < 0:
f = sub
else:
f = add
return f(a, b)
使用python3 ok -q a_plus_abs_b命令,测试结果如下:

结果正确。
Q2: Two of Three
源码:
def two_of_three(a, b, c):
"""Return x*x + y*y, where x and y are the two largest members of the
positive numbers a, b, and c.
>>> two_of_three(1, 2, 3)
13
>>> two_of_three(5, 3, 1)
34
>>> two_of_three(10, 2, 8)
164
>>> two_of_three(5, 5, 5)
50
"""
return _____
实现一个从初始值为a,b,c中选择最大的两个数字x,y,返回值为xx + yy
的函数。
def two_of_three(a, b, c):
"""Return x*x + y*y, where x and y are the two largest members of the
positive numbers a, b, and c.
>>> two_of_three(1, 2, 3)
13
>>> two_of_three(5, 3, 1)
34
>>> two_of_three(10, 2, 8)
164
>>> two_of_three(5, 5, 5)
50
"""
return a*a + b*b + c*c - pow(min(a, b, c), 2)
使用命令python3 ok -q two_of_three测试代码如下:

运行结果正确。
Q3: Largest Factor
源码:
def largest_factor(n):
"""Return the largest factor of n that is smaller than n.
>>> largest_factor(15) # factors are 1, 3, 5
5
>>> largest_factor(80) # factors are 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 10, 16, 20, 40
40
>>> largest_factor(13) # factor is 1 since 13 is prime
1
"""
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
实现一个能找到比 n 小的最大的因子的函数。
def largest_factor(n):
"""Return the largest factor of n that is smaller than n.
>>> largest_factor(15) # factors are 1, 3, 5
5
>>> largest_factor(80) # factors are 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 10, 16, 20, 40
40
>>> largest_factor(13) # factor is 1 since 13 is prime
1
"""
cnt = n
while cnt > 0:
cnt = cnt - 1
if n % cnt == 0:
print(cnt)
break
使用命令:python3 ok -q largest_factor获得测试结果如下:

运行结果正确。
Q4: If Function vs Statement
源码:
def if_function(condition, true_result, false_result):
"""Return true_result if condition is a true value, and
false_result otherwise.
>>> if_function(True, 2, 3)
2
>>> if_function(False, 2, 3)
3
>>> if_function(3==2, 3+2, 3-2)
1
>>> if_function(3>2, 3+2, 3-2)
5
"""
if condition:
return true_result
else:
return false_result
实现一个与if语句功能相同的函数。(当分别输入with_if_function和with_if_statement 时,其中一个返回1,但是另外一个不是)
def with_if_statement():
"""
>>> with_if_statement()
1
"""
if c():
return t()
else:
return f()
def with_if_function():
return if_function(c(), t(), f())
def c():
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
def t():
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
def f():
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
我的答案:
def if_function(condition, true_result, false_result):
"""Return true_result if condition is a true value, and
false_result otherwise.
>>> if_function(True, 2, 3)
2
>>> if_function(False, 2, 3)
3
>>> if_function(3==2, 3+2, 3-2)
1
>>> if_function(3>2, 3+2, 3-2)
5
"""
if condition:
return true_result
else:
return false_result
def with_if_statement():
"""
>>> with_if_statement()
1
"""
if c():
return t()
else:
return f()
def with_if_function():
return if_function(c(), t(), f())
def c():
return 1
def t():
print(1)
def f():
print(0)
运行结果如下:
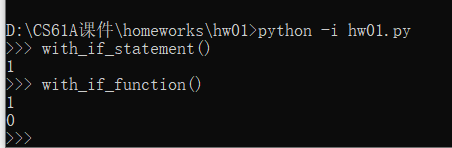
Q5: Hailstone
源码:
def hailstone(n):
"""Print the hailstone sequence starting at n and return its
length.
>>> a = hailstone(10)
10
5
16
8
4
2
1
>>> a
7
"""
"*** YOUR CODE HERE ***"
实现一个打印从 n 开始的冰雹序列并返回其长度的函数。
def hailstone(n):
"""Print the hailstone sequence starting at n and return its
length.
>>> a = hailstone(10)
10
5
16
8
4
2
1
>>> a
7
"""
cnt = 1
print(n)
while n != 1:
if n % 2:
n = n * 3 + 1
print(int(n))
cnt = cnt + 1
else:
n = n / 2
print(int(n))
cnt = cnt + 1
return cnt
使用命令:python ok -q hailstone运行结果如下:

结果正确。























 790
790











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










