一、为什么会使用子查询
虽然可以通过连接查询来实现多表查询数据记录,但不建议使用,因为连接查询的性能很差,为什么呢?我们来进行分析,例如 我们要查询部门表dept 和雇员表employee中的数据记录,一般可能会写成:
SELECT * FROM Course c1,Scroe c2
WHERE c1.c_id=c2.c_id;
对于这条SQL语句,在数据库执行的时候,会先对两个表进行笛卡尔积操作,然后再选取符合条件 t1.deptno=t2.deptno的数据记录。由于笛卡尔积时是将两个表中的记录数做乘积生成新的记录,如果当两个表中的数据记录都比较多时,进行乘积操作时性能将会很差,甚至造成死机。为了解决该问题,我们可以使用子查询来实现多表查询。
二、什么是子查询
子查询,就是在一个查询中嵌套了其他若干查询,即在一个SELECT查询语句的FROM或WHERE字句中包含另一个SELECT查询语句,在这种嵌套的查询语句中,外层的SELECT查询语句称为主查询,WHERE或FROM中的查询语句称为子查询,也叫嵌套查询。通过子查询可以实现多表查询,子查询经常出现在WHERE或FROM字句中。
- WHERE子句中的子查询:该位置处的子查询一般返回单行单列,多行单列,单行多列数据。就是返回能够作为WHERE子句查询条件的值。(
子查询返回的值作为主查询的查询条件) - FROM子句中的子查询:该位置处的子查询一般返回多行多列数据,相当于是返回一张临时表,符合FROM子句后面是表的规则,就是通过这种方式来实现多表查询的。
三、子查询的具体使用+实例
1、WHERE子句后使用子查询
a.返回结果为单行单列的子查询(就是有一个查询字段一个取值的情况)
案例:
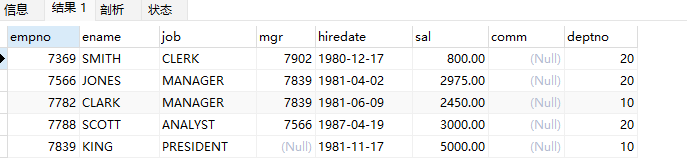
//查询部门编号小于3的员工信息
SELECT * from emp
WHERE deptno < (
SELECT deptno from dept where dname=3
)
b.返回结果为单行多列的子查询(就是有多个查询字段)
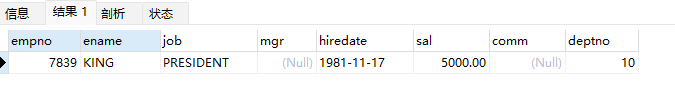
//查询部门编号小于3的部门编号并且薪水高于3000的员工记录
SELECT * from emp
WHERE deptno < (
SELECT deptno from dept where dname=3
)AND sal>3000
c.返回结果为单列多行的子查询(就是一个查询字段,有多个值的情况)
对于这种情况,在WHERE子句中就可以使用IN,ANY,ALL,EXISTS等关键字。
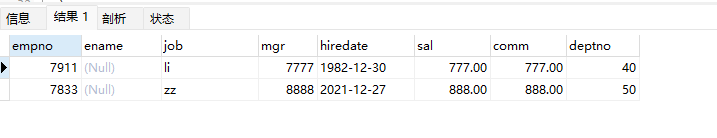
//查询部门编号不在dept表中的员工信息
SELECT * from emp
WHERE deptno not in (
SELECT deptno from dept
)
输出结果
2、FROM子句后使用子查询
FROM子句后的子查询返回的结果为多行多列的数据记录,就类似一个虚拟的表,可以使用该种方式实现多表查询。
先在navicat中新建五张表并填入数据
drop table if exists Course;
drop table if exists Score;
drop table if exists Student;
drop table if exists Teach;
drop table if exists Teacher;
/* Table: Course */
create table Course
(
c_id varchar(10) not null,
c_name varchar(100),
primary key (c_id)
);
/* Table: Score */
create table Score
(
s_id varchar(20) not null,
c_id varchar(10) not null,
s_score decimal(5,2),
primary key (s_id, c_id)
);
/* Table: Student */
create table Student
(
s_id varchar(20) not null,
s_name varchar(50),
s_gender varchar(2),
s_birthday date,
primary key (s_id)
);
/* Table: Teach */
create table Teach
(
t_id varchar(20) not null,
c_id varchar(10) not null,
primary key (t_id, c_id)
);
/* Table: Teacher */
create table Teacher
(
t_id varchar(20) not null,
t_name varchar(50),
primary key (t_id)
);
alter table Score add constraint FK_Score foreign key (s_id)
references Student (s_id) on delete restrict on update restrict;
alter table Score add constraint FK_Score2 foreign key (c_id)
references Course (c_id) on delete restrict on update restrict;
alter table Teach add constraint FK_Teach foreign key (t_id)
references Teacher (t_id) on delete restrict on update restrict;
alter table Teach add constraint FK_Teach2 foreign key (c_id)
references Course (c_id) on delete restrict on update restrict;
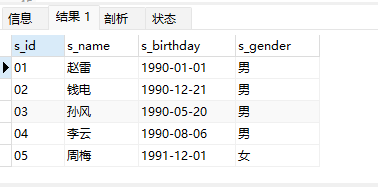
insert into Student values('01' , '赵雷' , '1990-01-01' , '男');
insert into Student values('02' , '钱电' , '1990-12-21' , '男');
insert into Student values('03' , '孙风' , '1990-05-20' , '男');
insert into Student values('04' , '李云' , '1990-08-06' , '男');
insert into Student values('05' , '周梅' , '1991-12-01' , '女');
insert into Student values('06' , '吴兰' , '1992-03-01' , '女');
insert into Student values('07' , '郑竹' , '1989-07-01' , '女');
insert into Student values('08' , '王菊' , '1990-01-20' , '女');
insert into Course values('01' , '语文');
insert into Course values('02' , '数学');
insert into Course values('03' , '英语');
insert into teacher values('01' , '张三');
insert into teacher values('02' , '李四');
insert into teacher values('03' , '王五');
insert into teach values('01' , '01');
insert into teach values('01' , '02');
insert into teach values('02' , '03');
insert into teach values('03' , '05');
insert into teach values('03' , '04');
insert into Score values('01' , '01' , 80);
insert into Score values('01' , '02' , 90);
insert into Score values('01' , '03' , 99);
insert into Score values('02' , '01' , 70);
insert into Score values('02' , '02' , 60);
insert into Score values('02' , '03' , 80);
insert into Score values('03' , '01' , 80);
insert into Score values('03' , '02' , 80);
insert into Score values('03' , '03' , 80);
insert into Score values('04' , '01' , 50);
insert into Score values('04' , '02' , 30);
insert into Score values('04' , '03' , 20);
insert into Score values('05' , '01' , 76);
insert into Score values('05' , '02' , 87);
insert into Score values('06' , '01' , 31);
insert into Score values('06' , '03' , 34);
insert into Score values('07' , '02' , 89);
insert into Score values('07' , '03' , 98);
//查询’张三‘老师授课的同学的信息
SELECT a.*
FROM student a
join scroe b ON a.s_id = b.s_id
WHERE b.c_id IN(
SELECT c_id FROM teach WHERE t_id=(
SELECT t_id FROM teacher WHERE t_name = '张三'
)
)
//查询学过编号'01'课程但没有学过编号为'02'课程的学生信息
SELECT a.*
FROM student a
WHERE a.s_id in(
SELECT s_id FROM scroe WHERE c_id = '01'
)
AND
a.s_id NOT IN (
SELECT s_id FROM scroe WHERE c_id = '02'
);
总结:
1、多表连接,其实就是两个或两个以上的表进行连接行成一个新的关系表,然后再按照操作单表时的方法来操作这个新的关系表。
2、多表连接时,如果使用子查询的方式,可以先将多余的数据剔除,形成我们想要的数据表(可以理解成是一个虚拟表),然后再进行连接,能够提高表连接时的效率。
3、多表连接,本质上最后还是单表操作,所以单表操作查询语句一定要掌握透彻,不管多么复杂的多表连接SQL语句,先分清外层查询是什么,再看嵌套的子查询是什么。





















 1160
1160











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








