学习目标:
了解coco数据集!!!( 进行图像识别的数据集)
学习内容:
1、 coco的特点
2、 coco数据集基本知识
3、 coco数据集的注释解析
4、coco转voc
学习成果:
1.1
特点:(1) object segmentation (2) recognition in context (3) multiple objects per image (4) more than 300,000 images (5) more than 2 million instances (6)80 object categories (7) 5 titles per image (8)100,000 people focus
COCO(Common Objects in Context)数据集包含20万个图像
80个类别中有超过50万个目标标注。它是最广泛公开的目标检测数据库
平均每个图像有7.2个目标
1.2
该数据集主要解决3个问题:目标检测,目标之间的上下文关系,目标的2维上的精确定位。数据集的对比示意图:
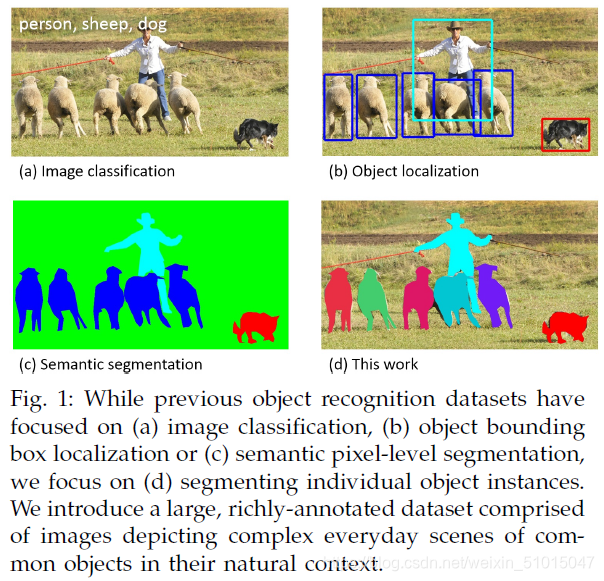

1.3
COCO通过大量使用Amazon Mechanical Turk来收集数据。COCO数据集现在有3种标注类型:object instances(目标实例), object keypoints(目标上的关键点), and image captions(看图说话),使用JSON文件存储。上面所述的三种类型,每种类型又包含了训练和验证,所以共6个JSON文件。
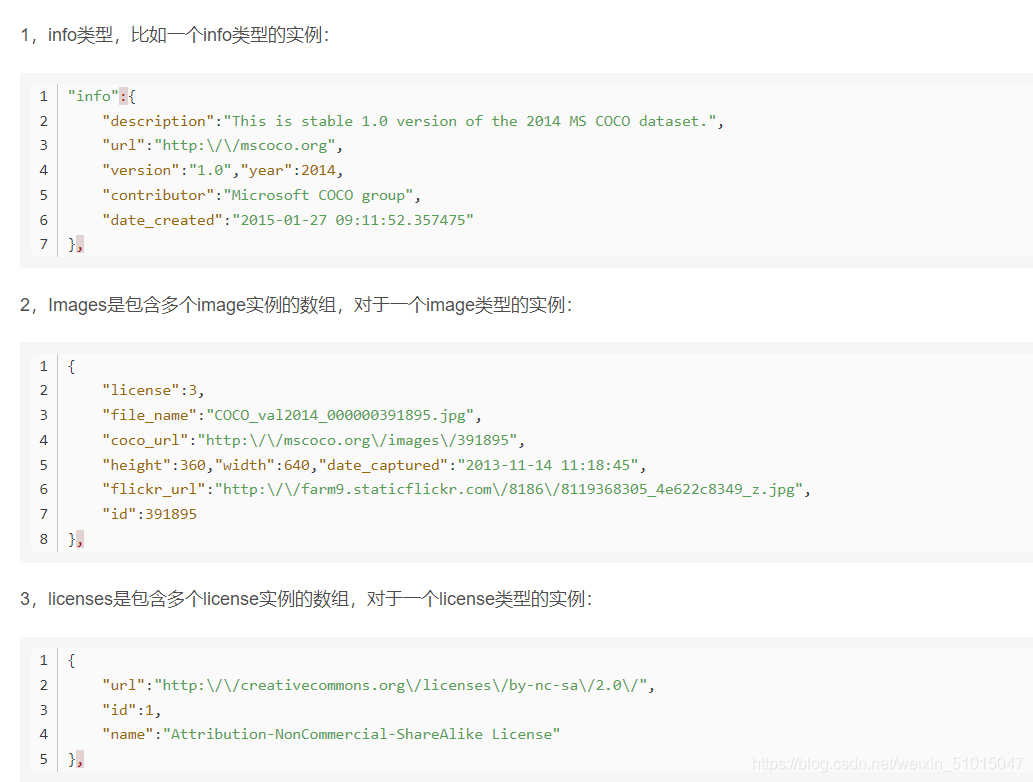
基本的JSON结构体类型:这3种类型共享下面所列的基本类型,包括info、image、license,而annotation类型则呈现出了多态:
##Object Instance这种格式的文件从头至尾按照顺序分为以下段落:
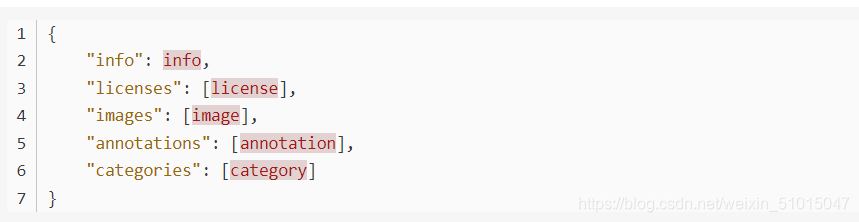
文件开始到结尾按照顺序就是这5段。其中,info、licenses、images这三个结构体/类型 在不同的JSON文件中这三个类型是一样的,定义是共享的。不共享的是annotation和category这两种结构体,他们在不同类型的JSON文件中是不一样的。
xml优缺点
(1)格式统一,符合标准;(2)容易与其他系统进行远程交互,数据传输比较方便。缺点:(1)XML文件庞大,文件格式复杂,传输占带宽;(2)服务器端和客户端都需要花费大量代码来解析XML,导致服务器端和客户端代码变得异常复杂且不易维护;(3)客户端不同浏览器之间解析XML的方式不一致,需要重复编写很多代码;(4)服务器端和客户端解析XML花费较多的资源和时间。
json优缺点
优点:
(1)数据格式比较简单,易于读写,格式都是压缩的,占用带宽小;
(2)易于解析,客户端JavaScript可以简单的通过eval_r()进行JSON数据的读取;
(3)支持多种语言,包括ActionScript, C, C#, ColdFusion, Java, JavaScript, Perl, PHP, Python, Ruby等服务器端语言,便于服务器端的解析;
(4)在PHP世界,已经有PHP-JSON和JSON-PHP出现了,偏于PHP序列化后的程序直接调用,PHP服务器端的对象、数组等能直接生成JSON格式,便于客户端的访问提取;
(5)因为JSON格式能直接为服务器端代码使用,大大简化了服务器端和客户端的代码开发量,且完成任务不变,并且易于维护。
缺点:
(1)没有XML格式这么推广的深入人心和喜用广泛,没有XML那么通用性;
(2)JSON格式目前在Web Service中推广还属于初级阶段。
具体实现
道一个数据集文件中包括图片与标签文件,如:


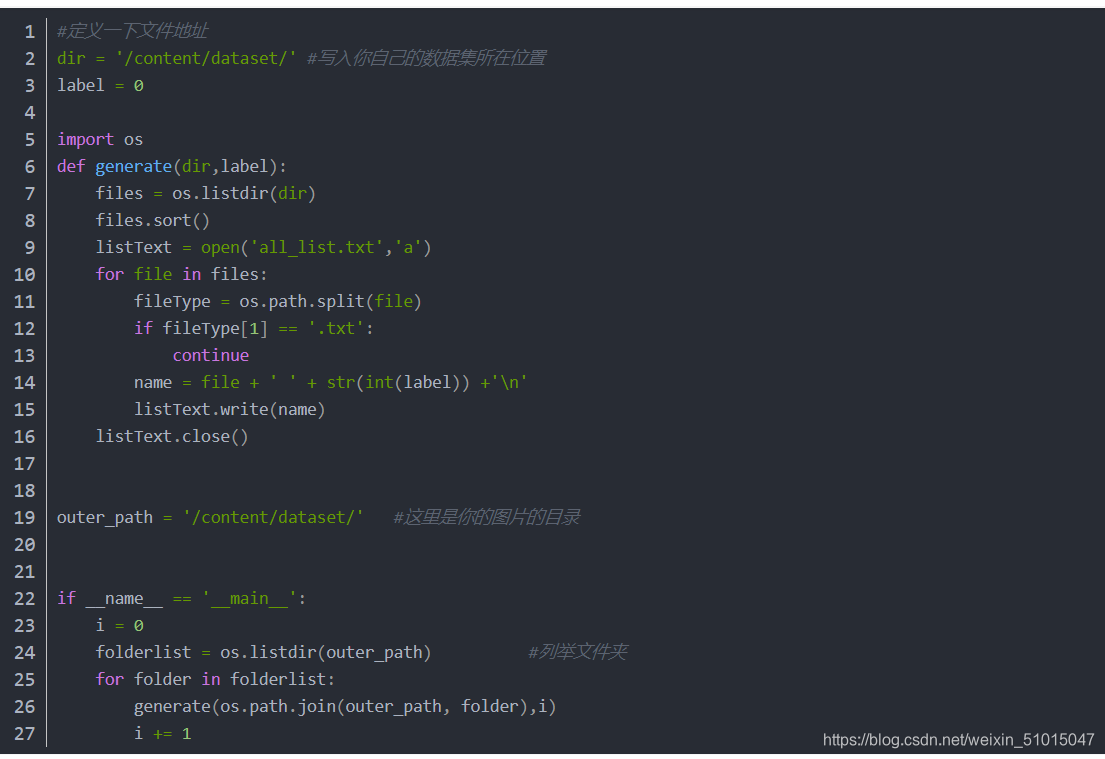
如何在将我们想要的label以一定格式写入txt文件呢?
通过这段脚本我们就可以实现以这种固定格式写入txt啦。
Pascal voc 转 coco
import os
import json
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import numpy as np
import cv2
def _isArrayLike(obj):
return hasattr(obj, '__iter__') and hasattr(obj, '__len__')
class voc2coco:
def __init__(self, devkit_path=None, year=None):
self.classes = ('__background__',
'aeroplane', 'bicycle', 'bird', 'boat',
'bottle', 'bus', 'car', 'cat', 'chair',
'cow', 'diningtable', 'dog', 'horse',
'motorbike', 'person', 'pottedplant',
'sheep', 'sofa', 'train', 'tvmonitor')
self.num_classes = len(self.classes)
assert 'VOCdevkit' in devkit_path, 'VOC地址不存在: {}'.format(devkit_path)
self.data_path = os.path.join(devkit_path, 'VOC' + year)
self.annotaions_path = os.path.join(self.data_path, 'Annotations')
self.image_set_path = os.path.join(self.data_path, 'ImageSets')
self.year = year
self.categories_to_ids_map = self._get_categories_to_ids_map()
self.categories_msg = self._categories_msg_generator()
def _load_annotation(self, ids=[]):
ids = ids if _isArrayLike(ids) else [ids]
image_msg = []
annotation_msg = []
annotation_id = 1
for index in ids:
filename = '{:0>6}'.format(index)
json_file = os.path.join(self.data_path, 'Segmentation_json', filename + '.json')
if os.path.exists(json_file):
img_file = os.path.join(self.data_path, 'JPEGImages', filename + '.jpg')
im = cv2.imread(img_file)
width = im.shape[1]
height = im.shape[0]
seg_data = json.load(open(json_file, 'r'))
assert type(seg_data) == type(dict()), 'annotation file format {} not supported'.format(type(seg_data))
for shape in seg_data['shapes']:
seg_msg = []
for point in shape['points']:
seg_msg += point
one_ann_msg = {"segmentation": [seg_msg],
"area": self._area_computer(shape['points']),
"iscrowd": 0,
"image_id": int(index),
"bbox": self._points_to_mbr(shape['points']),
"category_id": self.categories_to_ids_map[shape['label']],
"id": annotation_id,
"ignore": 0
}
annotation_msg.append(one_ann_msg)
annotation_id += 1
else:
xml_file = os.path.join(self.annotaions_path, filename + '.xml')
tree = ET.parse(xml_file)
size = tree.find('size')
objs = tree.findall('object')
width = size.find('width').text
height = size.find('height').text
for obj in objs:
bndbox = obj.find('bndbox')
[xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax] \
= [int(bndbox.find('xmin').text) - 1, int(bndbox.find('xmax').text),
int(bndbox.find('ymin').text) - 1, int(bndbox.find('ymax').text)]
if xmin < 0:
xmin = 0
if ymin < 0:
ymin = 0
bbox = [xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax]
one_ann_msg = {"segmentation": self._bbox_to_mask(bbox),
"area": self._bbox_area_computer(bbox),
"iscrowd": 0,
"image_id": int(index),
"bbox": [xmin, ymin, xmax - xmin, ymax - ymin],
"category_id": self.categories_to_ids_map[obj.find('name').text],
"id": annotation_id,
"ignore": 0
}
annotation_msg.append(one_ann_msg)
annotation_id += 1
one_image_msg = {"file_name": filename + ".jpg",
"height": int(height),
"width": int(width),
"id": int(index)
}
image_msg.append(one_image_msg)
return image_msg, annotation_msg
def _bbox_to_mask(self, bbox):
assert len(bbox) == 4, 'Wrong bndbox!'
mask = [bbox[0], bbox[2], bbox[0], bbox[3], bbox[1], bbox[3], bbox[1], bbox[2]]
return [mask]
def _bbox_area_computer(self, bbox):
width = bbox[1] - bbox[0]
height = bbox[3] - bbox[2]
return width * height
def _save_json_file(self, filename=None, data=None):
json_path = os.path.join(self.data_path, 'cocoformatJson')
assert filename is not None, 'lack filename'
if os.path.exists(json_path) == False:
os.mkdir(json_path)
if not filename.endswith('.json'):
filename += '.json'
assert type(data) == type(dict()), 'data format {} not supported'.format(type(data))
with open(os.path.join(json_path, filename), 'w') as f:
f.write(json.dumps(data))
def _get_categories_to_ids_map(self):
return dict(zip(self.classes, range(self.num_classes)))
def _get_all_indexs(self):
ids = []
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(self.annotaions_path, topdown=False):
for f in files:
if str(f).endswith('.xml'):
id = int(str(f).strip('.xml'))
ids.append(id)
assert ids is not None, 'There is none xml file in {}'.format(self.annotaions_path)
return ids
def _get_indexs_by_image_set(self, image_set=None):
if image_set is None:
return self._get_all_indexs()
else:
image_set_path = os.path.join(self.image_set_path, 'Main', image_set + '.txt')
assert os.path.exists(image_set_path), 'Path does not exist: {}'.format(image_set_path)
with open(image_set_path) as f:
ids = [x.strip() for x in f.readlines()]
return ids
def _points_to_mbr(self, points):
assert _isArrayLike(points), 'Points should be array like!'
x = [point[0] for point in points]
y = [point[1] for point in points]
assert len(x) == len(y), 'Wrong point quantity'
xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax = min(x), max(x), min(y), max(y)
height = ymax - ymin
width = xmax - xmin
return [xmin, ymin, width, height]
def _categories_msg_generator(self):
categories_msg = []
for category in self.classes:
if category == '__background__':
continue
one_categories_msg = {"supercategory": "none",
"id": self.categories_to_ids_map[category],
"name": category
}
categories_msg.append(one_categories_msg)
return categories_msg
def _area_computer(self, points):
assert _isArrayLike(points), 'Points should be array like!'
tmp_contour = []
for point in points:
tmp_contour.append([point])
contour = np.array(tmp_contour, dtype=np.int32)
area = cv2.contourArea(contour)
return area
def voc_to_coco_converter(self):
img_sets = ['trainval', 'test']
for img_set in img_sets:
ids = self._get_indexs_by_image_set(img_set)
img_msg, ann_msg = self._load_annotation(ids)
result_json = {"images": img_msg,
"type": "instances",
"annotations": ann_msg,
"categories": self.categories_msg}
self._save_json_file('voc_' + self.year + '_' + img_set, result_json)
def demo():
# 转换pascal地址是'./VOC2007/VOCdevkit/VOC2007/ImageSets/Main/trainval.txt'
converter = voc2coco('./VOC2007/VOCdevkit', '2007')
converter.voc_to_coco_converter()
if __name__ == "__main__":
demo()





















 6360
6360











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








