要求 :分辨出一个随机颜色(红色,蓝色)的图形(圆形,矩形,三角形)
思路 : HSV色块识别+轮廓提取+同一高度面积识别
一、HSV模型
HSV(Hue, Saturation, Value)是根据颜色的直观特性由A. R. Smith在1978年创建的一种颜色空间, 也称六角锥体模型(Hexcone Model)。这个模型中颜色的参数分别是:色调(H),饱和度(S),明度(V)。
HSV色彩空间
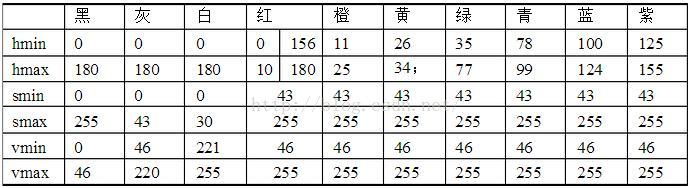
注意:红色的H空间有两部分,需要将两部分融合后提取轮廓。
二、提取轮廓后,固定高度下分别检测圆形、正方形、三角形的面积阈值。
示例代码如下:
# encoding=utf-8
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
import time
import serial
def analysis(frame):
global red_triangle
global red_rectangle
global red_circle
global blue_triangle
global blue_rectangle
global blue_circle
h,w,ch = frame.shape
result = np.zeros((h, w, ch), dtyp







 本文介绍了使用HSV模型结合OpenCV库,通过Python在树莓派上实现对红色和蓝色的圆形、矩形和三角形的识别。首先,利用HSV进行颜色筛选,接着通过轮廓提取来判断形状,再根据固定高度下的面积阈值来识别不同形状。
本文介绍了使用HSV模型结合OpenCV库,通过Python在树莓派上实现对红色和蓝色的圆形、矩形和三角形的识别。首先,利用HSV进行颜色筛选,接着通过轮廓提取来判断形状,再根据固定高度下的面积阈值来识别不同形状。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 854
854

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








