Thymeleaf 模板引擎
Thymeleaf是新一代模板引擎,它与Velocity、FreeMarker等模板引擎类似,可以完全替代JSP。在spring4.0中推荐使用thymeleaf来做前端引擎。
Thymeleaf官网:https://www.thymeleaf.org/
Thymeleaf在线文档:https://www.thymeleaf.org/doc/tutorials/3.0/usingthymeleaf.html
Thymeleaf在Github的主页:https://github.com/thymeleaf/thymeleaf
一、pom 依赖文件
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework.boot/spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
<version>2.4.5</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/commons-lang/commons-lang -->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-lang</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang</artifactId>
<version>2.6</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Maven依赖关系以获取Thymeleaf 3(核心)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf</artifactId>
<version>3.0.12.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring 4集成包(这可能是Spring应用程序所需的一切)-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-spring4</artifactId>
<version>3.0.12.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
查看 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf 包
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/";
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html";
结论:只要需要使用 thymeleaf ,只需要导入对应的依赖就可以了!我们将 html 放在我们的 templates 目录下即可!
二、Thymeleaf小试牛刀
在controller包下新建IndexController.java
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class IndexController {
@RequestMapping("/test")
public String test(Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg","hello springboot");
return "test";
}
}
在resources/templates目录下新建test.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div th:text="${msg}"></div>
</body>
</html>
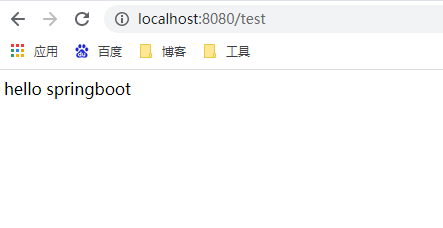
运行项目,访问localhost:8080/test
三、Thymeleaf语法
3.1、标准表达式语法
- 1.变量表达式
- 2.选择或星号表达式
- 3.文字国际化表达式
- 4.URL表达式
☀ 变量表达式
变量表达式即OGNL表达式或Spring EL表达式(在Spring术语中也叫model attributes)。如下所示:
${session.user.name}
它们将以HTML标签的一个属性来表示:
<span th:text="${book.author.name}">
<li th:each="book : ${books}">
☀ 选择(星号)表达式
选择表达式很像变量表达式,不过它们用一个预先选择的对象来代替上下文变量容器(map)来执行,如下:
*{customer.name}
被指定的object由th:object属性定义:
<div th:object="${book}">
...
<span th:text="*{title}">...</span>
...
</div>
☀ 文字国际化表达式
文字国际化表达式允许我们从一个外部文件获取区域文字信息(.properties),用Key索引Value,还可以提供一组参数(可选).
#{main.title}
#{message.entrycreated(${entryId})}
可以在模板文件中找到这样的表达式代码:
<table>
...
<th th:text="#{header.address.city}">...</th>
<th th:text="#{header.address.country}">...</th>
...
</table>
☀ URL表达式
URL表达式指的是把一个有用的上下文或回话信息添加到URL,这个过程经常被叫做URL重写。
@{/order/list}
URL还可以设置参数:
@{/order/details(id=${orderId})}
相对路径:
@{../documents/report}
让我们看这些表达式:
<form th:action="@{/createOrder}">
<a href="main.html" th:href="@{/main}">
变量表达式和星号表达有什么区别吗?
如果不考虑上下文的情况下,两者没有区别;星号语法评估在选定对象上表达,而不是整个上下文
什么是选定对象?就是父标签的值,如下:
<div th:object="${session.user}">
<p>Name: <span th:text="*{firstName}">Sebastian</span>.</p>
<p>Surname: <span th:text="*{lastName}">Pepper</span>.</p>
<p>Nationality: <span th:text="*{nationality}">Saturn</span>.</p>
</div>
这是完全等价于:
<div th:object="${session.user}">
<p>Name: <span th:text="${session.user.firstName}">Sebastian</span>.</p>
<p>Surname: <span th:text="${session.user.lastName}">Pepper</span>.</p>
<p>Nationality: <span th:text="${session.user.nationality}">Saturn</span>.</p>
</div>
当然,美元符号和星号语法可以混合使用:
<div th:object="${session.user}">
<p>Name: <span th:text="*{firstName}">Sebastian</span>.</p>
<p>Surname: <span th:text="${session.user.lastName}">Pepper</span>.</p>
<p>Nationality: <span th:text="*{nationality}">Saturn</span>.</p>
</div>
表达式支持的语法
字面(Literals)
- 文本文字(Text literals):
'one text', 'Another one!',… - 数字文本(Number literals):
0, 34, 3.0, 12.3,… - 布尔文本(Boolean literals):
true, false - 空(Null literal):
null - 文字标记(Literal tokens):
one, sometext, main,…
文本操作(Text operations)
- 字符串连接(String concatenation):
+ - 文本替换(Literal substitutions):
|The name is ${name}|
算术运算(Arithmetic operations)
- 二元运算符(Binary operators):
+, -, *, /, % - 减号(单目运算符)Minus sign (unary operator):
-
布尔操作(Boolean operations)
- 二元运算符(Binary operators):
and, or - 布尔否定(一元运算符)Boolean negation (unary operator):
!, not
比较和等价(Comparisons and equality)
- 比较(Comparators):
>, <, >=, <= (gt, lt, ge, le) - 等值运算符(Equality operators):
==, != (eq, ne)
条件运算符(Conditional operators)
- If-then:
(if) ? (then) - If-then-else:
(if) ? (then) : (else) - Default: (value) ?:
(defaultvalue)
所有这些特征可以被组合并嵌套:
'User is of type ' + (${user.isAdmin()} ? 'Administrator' : (${user.type} ?: 'Unknown'))
3.2、常用th标签
Text(tag body modification【标签体改造】)
| 关键字 | 功能介绍 | 案例 |
|---|---|---|
| th:text | 文本替换 | <p th:text="${collect.description}">description</p> |
| th:utext | 支持html的文本替换 | <p th:utext="${htmlcontent}">conten</p> |
IndexController.java内容:
@Controller
public class IndexController {
@RequestMapping("/test")
public String test(Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg","<h1>hello springboot</h1>");
return "test";
}
}
test.html内容:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div th:text="${msg}"></div>
<div th:utext="${msg}"></div>
</body>
</html>
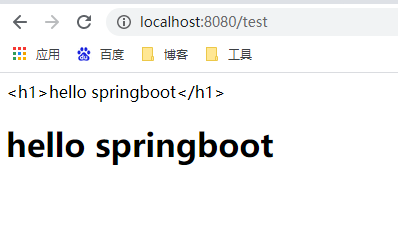
运行项目,访问localhost:8080/test
Fragment inclusion(片段的包含)
| 关键字 | 功能介绍 | 案例 |
|---|---|---|
| th:include | 布局标签,替换内容到引入的文件 | <head th:include="layout :: htmlhead" th:with="title='xx'"></head> /> |
Fragment iteration(片段的迭代)
| 关键字 | 功能介绍 | 案例 |
|---|---|---|
| th:each | 属性赋值 | <tr th:each="user,userStat:${users}"> |
| th:each | 属性取值 | <tr th:each="user:${users}" th:text="${user}"></tr> |
th:each 属性取值 :
model.addAttribute("users", Arrays.asList("张三","李四"));
<!--建议写法-->
<h3 th:each="user:${users}" th:text="${user}"></h3>
<!--同效果行内写法-->
<h3 th:each="user:${users}">[[${user}]]</h3>

Condition evaluation(条件评估)
| 关键字 | 功能介绍 | 案例 |
|---|---|---|
| th:if | 判断条件 | <a th:if="${userId == collect.userId}" > |
| th:unless | 和th:if判断相反 | <a th:href="@{/login}" th:unless=${session.user != null}>Login</a> |
| th:switch | 多路选择 配合th:case 使用 | <div th:switch="${user.role}"> |
| th:case | th:switch的一个分支 | <p th:case="'admin'">User is an administrator</p> |
Local variable definition(局部变量的定义)
| 关键字 | 功能介绍 | 案例 |
|---|---|---|
| th:object | 替换对象 | <div th:object="${session.user}"> |
| th:with | 变量赋值运算 | <div th:with="isEven=${prodStat.count}%2==0"></div> |
General attribute modification(通用属性修改)
| 关键字 | 功能介绍 | 案例 |
|---|---|---|
| th:attr | 设置标签属性,多个属性可以用逗号分隔 | 比如 th:attr="src=@{/image/aa.jpg},title=#{logo}",此标签不太优雅,一般用的比较少。 |
| th:attrappend | 将求值的结果附加(后缀)到现有属性值。 | <input type="button" value="Do it!" class="btn" th:attrappend="class=${' ' + cssStyle}" /> |
| th:attrprepend | 将求值的结果附加(前缀)到现有属性值。 | <input type="button" value="Do it!" class="btn" th:attrprepend="class=${' ' + cssStyle}" /> |
Specific attribute modification(特定属性修改)
| 关键字 | 功能介绍 | 案例 |
|---|---|---|
| th:value | 属性赋值 | <input th:value="${user.name}" /> |
| th:href | 链接地址 | <a th:href="@{/login}" th:unless=${session.user != null}>Login</a> /> |
| th:src | 图片类地址引入 | <img class="img-responsive" alt="App Logo" th:src="@{/img/logo.png}" /> |
| … | … | … |
Fragment specification(片段规范)
| 关键字 | 功能介绍 | 案例 |
|---|---|---|
| th:fragment | 布局标签,定义一个代码片段,方便其它地方引用 | <div th:fragment="alert"> |
Fragment removal(片段删除)
| 关键字 | 功能介绍 | 案例 |
|---|---|---|
| th:remove | 删除某个属性 | <tr th:remove="all"> 1.all:删除包含标签和所有的孩子。 |










 本文介绍了如何在Spring Boot 4.0中集成Thymeleaf模板引擎,包括pom.xml的依赖配置,控制器实现与HTML模板的交互,以及Thymeleaf的基本语法和标签使用。通过实例演示了如何在项目中快速上手Thymeleaf进行前端开发。
本文介绍了如何在Spring Boot 4.0中集成Thymeleaf模板引擎,包括pom.xml的依赖配置,控制器实现与HTML模板的交互,以及Thymeleaf的基本语法和标签使用。通过实例演示了如何在项目中快速上手Thymeleaf进行前端开发。

















 7921
7921

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










