https://codeforces.com/contest/1615/problem/E
E. Purple Crayon
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Two players, Red and Blue, are at it again, and this time they're playing with crayons! The mischievous duo is now vandalizing a rooted tree, by coloring the nodes while playing their favorite game.
The game works as follows: there is a tree of size nn, rooted at node 11, where each node is initially white. Red and Blue get one turn each. Red goes first.
In Red's turn, he can do the following operation any number of times:
- Pick any subtree of the rooted tree, and color every node in the subtree red.
However, to make the game fair, Red is only allowed to color kk nodes of the tree. In other words, after Red's turn, at most kk of the nodes can be colored red.
Then, it's Blue's turn. Blue can do the following operation any number of times:
- Pick any subtree of the rooted tree, and color every node in the subtree blue. However, he's not allowed to choose a subtree that contains a node already colored red, as that would make the node purple and no one likes purple crayon.
Note: there's no restriction on the number of nodes Blue can color, as long as he doesn't color a node that Red has already colored.
After the two turns, the score of the game is determined as follows: let ww be the number of white nodes, rr be the number of red nodes, and bb be the number of blue nodes. The score of the game is w⋅(r−b)w⋅(r−b).
Red wants to maximize this score, and Blue wants to minimize it. If both players play optimally, what will the final score of the game be?
Input
The first line contains two integers nn and kk (2≤n≤2⋅1052≤n≤2⋅105; 1≤k≤n1≤k≤n) — the number of vertices in the tree and the maximum number of red nodes.
Next n−1n−1 lines contains description of edges. The ii-th line contains two space separated integers uiui and vivi (1≤ui,vi≤n1≤ui,vi≤n; ui≠viui≠vi) — the ii-th edge of the tree.
It's guaranteed that given edges form a tree.
Output
Print one integer — the resulting score if both Red and Blue play optimally.
Examples
input
Copy
4 2 1 2 1 3 1 4output
Copy
1input
Copy
5 2 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5output
Copy
6input
Copy
7 2 1 2 1 3 4 2 3 5 6 3 6 7output
Copy
4input
Copy
4 1 1 2 1 3 1 4output
Copy
-1Note
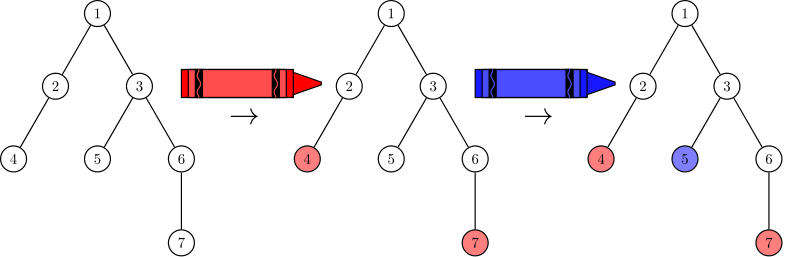
In the first test case, the optimal strategy is as follows:
- Red chooses to color the subtrees of nodes 22 and 33.
- Blue chooses to color the subtree of node 44.
At the end of this process, nodes 22 and 33 are red, node 44 is blue, and node 11 is white. The score of the game is 1⋅(2−1)=11⋅(2−1)=1.
In the second test case, the optimal strategy is as follows:
- Red chooses to color the subtree of node 44. This colors both nodes 44 and 55.
- Blue does not have any options, so nothing is colored blue.
At the end of this process, nodes 44 and 55 are red, and nodes 11, 22 and 33 are white. The score of the game is 3⋅(2−0)=63⋅(2−0)=6.
For the third test case:
The score of the game is 4⋅(2−1)=44⋅(2−1)=4.
题目大意:红色先在图中某棵子树画上红色,至多画k个点,然后蓝色相同操作,不过蓝色没有个数限制,不过所选的子树不能有红色的点。第一个人想w * (r - b) 最大, 第二个想最小。
解题思路:首先很容易想到如果想让让公式最大那么肯定得让b最少,那么R尽量把叶子结点染成红色,当无法全部染成红色,那么我们优先选择到根节点路径最大的叶子结点染成红色,然后反向建树优先把路径大的点的路径找到,当选择某条路径遍历过直接返回即可,最后要在r和b的范围类找最值。
AC代码:
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define ll long long
#define PII pair<long long, long long>
#define fir first
#define sec second
const int N = 3e5 + 100, M = 1e6+100;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int h[N], h1[N], e[M], ne[M], w[N], idx, d[N];
int n, m;
PII p[N], tmp[N];
bool leaf[N];
void add(int a, int b) {
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx++;
}
void add1(int a, int b) {
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h1[a], h1[a] = idx++;
}
bool cmp(PII x, PII y) {
if (x.first == y.first) return x.second < y.second;
return x.first > y.first;
}
int cnt = 0;
void dfs1(int x, int fa, int len) {
p[cnt++] = { len, x };
bool f = true;
for (int i = h[x]; ~i; i = ne[i]) {
int u = e[i];
if (u == fa) continue;
f = false;
add1(u, x);
dfs1(u, x, len + 1);
}
if (f) leaf[x] = true;
}
int dfs2(int x) {
for (int i = h1[x]; ~i; i = ne[i]) {
int u = e[i];
if (d[u]) continue;
d[x] += dfs2(u);
}
d[x]++;
return d[x];
}
signed main() {
scanf("%lld%lld", &n, &m);
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
memset(h1, -1, sizeof h1);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int u, v;
scanf("%lld%lld", &u, &v);
add(u, v), add(v, u);
}
dfs1(1, 0, 1);
sort(p, p + cnt, cmp);
int tlen = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i++) {
if (d[p[i].second]) continue;
int len = dfs2(p[i].sec);
if (leaf[p[i].sec]) {
tmp[tlen++] = { len, p[i].second };
}
}
sort(tmp, tmp + tlen, cmp);
ll r = 0, b = 0;
int tc = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < tlen; i++) {
if (tc < m) {
r++;
tc++;
}
else
b = b + tmp[i].fir;
}
ll ans = (n - r - b) * (r - b);
for (int i = r + 1; i <= m; i++) {
ans = max(((ll)n - i) * i, ans);
}
for (int i = r; i <= b; i++) {
ans = min((n - r - i) * (r - i), ans);
}
cout << ans << '\n';
return 0;
}总结一下昨晚:找了好久bug居然忘记讨论b了,这种bug居然找了那么久,平时做题太过在意代码的正确性,从而忽视了某些细节,做题一个一步一步找问题,不能一直重复找那几个点,一个个研究。






















 1263
1263











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








