前缀树
前缀树介绍
例题:一个字符串类型的数组arr1,另一个字符串类型的数组arr2。
(1)arr2中有哪些字符,是在arr1中出现的
(2)arr2中有哪些字符,是在arr1中的某个字符串的前缀出现
(3)arr2中出现次数最多的前缀
- 经典前缀树:字符串写在“路”上
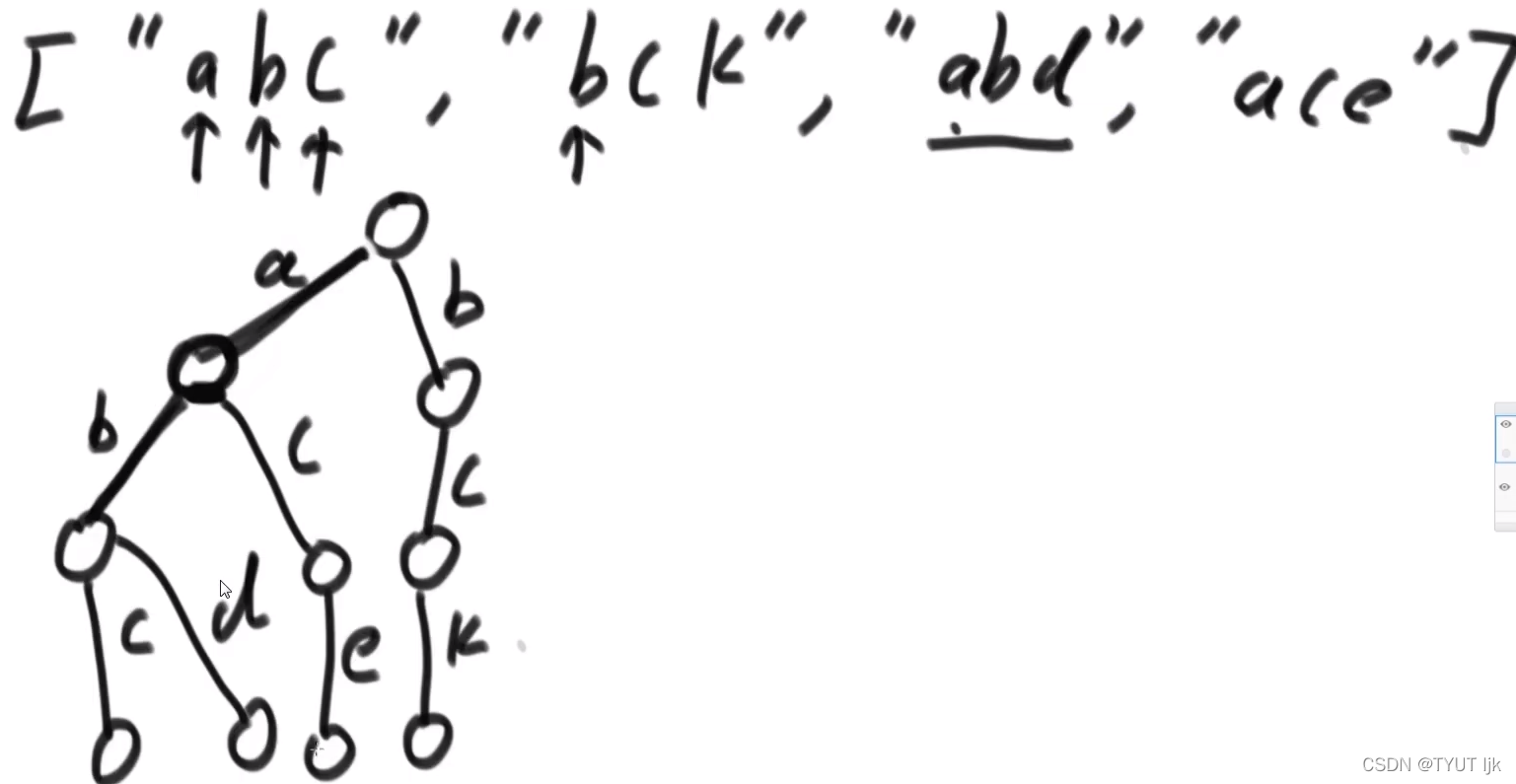
数据结构
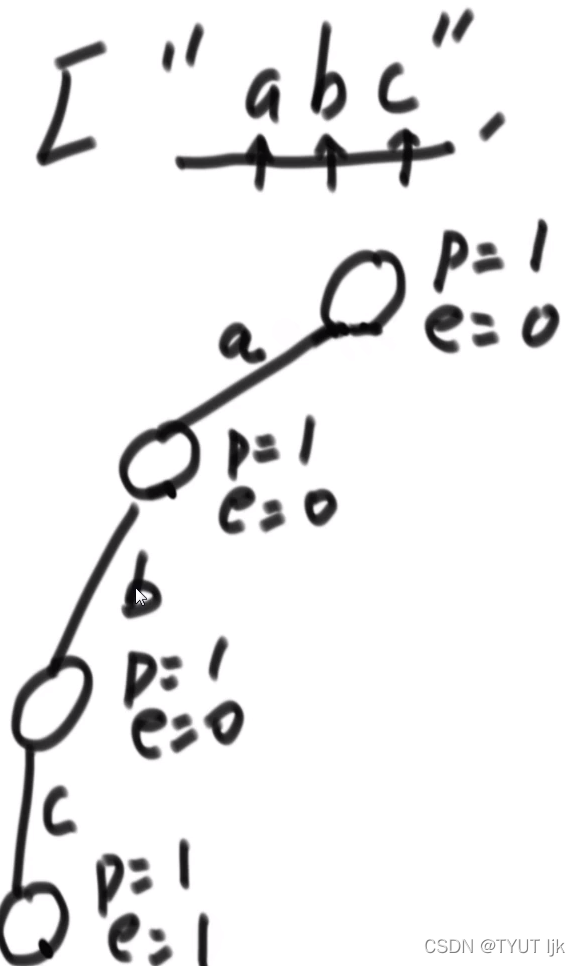
前缀树节点
public static class TrieNode{
public int pass; //表示形成前缀树时,该节点经过的次数
public int end; //该节点是多少个字符串的结尾节点
public TrieNode[] nexts; //类似于HashMap<char, Node> nexts; 当字符特别多的时候可以使用HashMap
public TrieNode(){
//构造函数初始化
pass = 0;
end = 0;
//nexts[0] == null 没有走向'a'的路
//nexts[0] != null 有走向'a'的路
//……
//next[25] != null 有走向'z'的路
nexts = new TrieNode[26];
}
}
public static class Trie{
//头节点
private TrieNode root;
public Trie(){
//初始化
root = new TrieNode();
}
//插入,删除,查找……方法
}
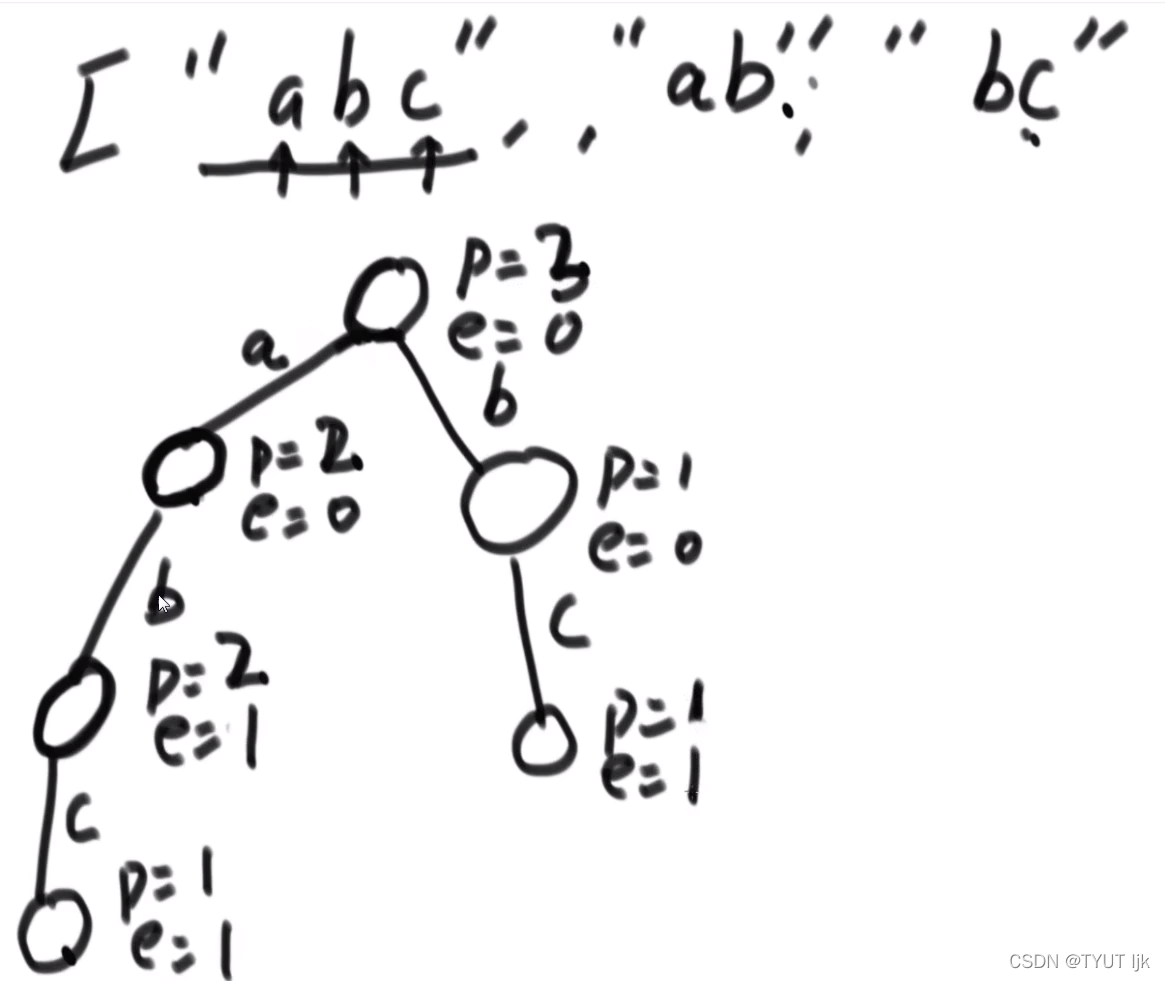
使用场景
- 字符串的查找
- 部分字符的在字符串中作为前缀的使用次数
主要方法
添加字符串
public static class Trie{
//头节点
private TrieNode root;
public Trie(){
//初始化
root = new TrieNode();
}
public void insert(String word){
//沿途的pass++,结束节点的end++
if (word == null){
return;
}
//将字符串转化为字符数组
char[] chars = word.toCharArray();
TrieNode node = root;
root.pass++; //通过根节点
int index = 0;
for (char ch : chars) {
//遍历字符数组
index = ch - 'a'; //由字符,对应到路
if (node.nexts[index] == null) {
//判断该路是否存在
node.nexts[index] = new TrieNode();
}
node = node.nexts[index]; //移动node
node.pass++;
}
node.end++; //最后一个节点
}
}
检查字符串加入次数
public int search(String word){
//查看结束节点的end
if (word== null){
return 0;
}
char[] chars = word.toCharArray();
TrieNode node = root;
int index = 0;
for (char ch : chars){
index = ch - 'a';
if (node.nexts[index] == null){
//不存在该字符串
return 0;
}
node = node.nexts[index];
}
return node.end;
}
检查以pre为前缀的字符串个数
public int prefixNumber(String pre){
//查看结束节点的pass
if (pre == null){
return 0;
}
char[] chars = pre.toCharArray();
TrieNode node = root;
int index = 0;
for (char ch : chars){
index = ch - 'a';
if (node.nexts[index] == null){
//不存在该前缀
return 0;
}
node = node.nexts[index];
}
return node.pass;
}
删除字符串
public void delete(String word){
//沿途节点的pass--,结束节点的end--
//如果沿途节点--pass == 0,直接释放该节点及其以后节点
if (search(word) == 0){
return;
}
char[] chars = word.toCharArray();
TrieNode node = root;
root.pass--;
int index = 0;
for (char ch : chars){
index = ch - 'a';
if (--node.nexts[index].pass == 0){
//java写法,C++要遍历
node.nexts[index] = null;
}
node = node.nexts[index];
}
node.end--;
}
贪心算法
概述
- 在某一个标准下,优先考虑满足标准的样本,最后考虑最不满足标准的样本,最终得到一个答案的算法,叫作贪心算法
- 也就是说,不从整体最优上加以考虑,所做出的是某种意义上的局部最优解
- 局部 —?--->整体最优
题目一:会议室安排(任务安排)

- 贪心策略一:先安排开始时间早的?错误:只可能是局部最优不可能全局最优
- 贪心策略二:先安排持续时间短的?错误:若短时间的任务同时于多个别的任务时间重合则会导致会议室使用效率下降‘
- 贪心策略三:先安排结束时间早的?正确
public static class Program{
//项目类
public int start; //开始时间
public int end; //结束时间
public Program(int start, int end){
//初始化
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
}
public static class ProgramComparator implements Comparator<Program>{
//比较器
@Override
public int compare(Program o1, Program o2){
return o1.end - o2.end;
}
}
public static int bestArrange(Program[] programs, int timePoint){
//timePoint:开始时间 + 目前时间
//按照结束时间对项目进行排序
Arrays.sort(programs, new ProgramComparator());
int result = 0; //记录项目个数
for (Program program : programs){
//按照结束时间的次序遍历
if (timePoint <= program.start){
//当目前的时间小于项目开始的时间
result++;
timePoint = program.end;
}
}
return result;
}
题目二:分割金条(哈夫曼编码)

- 贪心策略:将数组中的数字组成哈夫曼树,整个哈夫曼树就是分割的最小代价
- 技巧:使用小根堆构造哈夫曼树
public static int lessMoney(int[] arr){
//使用小根堆构造哈夫曼树
PriorityQueue<Integer> heap = new PriorityQueue<>();
for (int i : arr){
//将数组加入小根堆
heap.add(i);
}
int sum = 0;
while (!heap.isEmpty()){
int temp = heap.poll() + heap.poll();
sum += temp;
heap.add(temp);
}
return sum;
}
题目三:投资问题

- 贪心策略:使用初始资金的大小先挑选出初始资金大于花费的项目,再从这些项目中挑选出利润最大的项目优先去做,每次做完项目积累到资金后立刻重新挑选
- 技巧:先建立costs花费数组的小根堆(类似于锁)解锁花费小于资金的项目到profits建立的大根堆中,从大根堆中选取项目
public static class Project{
public int cost; //花费
public int profit; //利润
public Project(int cost, int profit){
//初始化
this.cost = cost;
this.profit = profit;
}
}
public static class minCostComparator implements Comparator<Project>{
//花费的比较器
@Override
public int compare(Project o1, Project o2){
return o1.cost - o2.cost;
}
}
public static class maxProfitComparator implements Comparator<Project>{
//利润的比较器
@Override
public int compare(Project o1, Project o2){
return o2.profit - o1.profit;
}
}
public static int maxMoney(int k, int m, int[] costs, int[] profits){
//花费的小根堆
PriorityQueue<Project> minCosts= new PriorityQueue<>(new minCostComparator());
//利润的大根堆
PriorityQueue<Project> maxProfits = new PriorityQueue<>(new maxProfitComparator());
for (int i = 0; i < costs.length; i++){
//项目加入花费的小根堆
minCosts.add(new Project(costs[i], profits[i]));
}
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++){
//完成k个项目
while (!minCosts.isEmpty() && minCosts.peek().cost < m){
//解锁满足条件的项目到利润的大根堆
maxProfits.add(minCosts.poll());
}
if (maxProfits.isEmpty()){
//能够实现的项目已经全部完成
return m;
}
//选择利润中最大的一个
m += maxProfits.poll().profit;
}
return m;
}
题目四:数据流求中位数(大根堆与小根堆的结合)

- 思路:加入数据时一分为二,较大的一部分,较小的一部分,便可以随时得到中位数
- 技巧:
(1)准备一个大根堆和一个小根堆
(2)每次加入数字时先与大根堆的堆顶进行元素的比较(当前元素 <= 大根堆堆顶)
(3)若是则进入大根堆,若否则进入小根堆
(4)进行大小根堆规模的比较,若规模的大小差值达到2则将规模较大的堆顶加入规模较小的堆
(5)重复2,3,4则较小的部分在大根堆中,较大的部分在小根堆中,中位数便可通过两个堆顶获得
public static class maxInt implements Comparator<Integer>{
//大根堆的比较器
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2){
return o2 - o1;
}
}
public static int getMedian(int[] nums){
//数据流num返回中位数
//小根堆
PriorityQueue<Integer> minHeap = new PriorityQueue<>();
//大根堆
PriorityQueue<Integer> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>(new maxInt());
//第一个元素进入大根堆
maxHeap.add(nums[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++){
//遍历数组
if (nums[i] <= maxHeap.peek()){
//判断加入大根堆还是小根堆
maxHeap.add(nums[i]);
}
else {
minHeap.add(nums[i]);
}
if (maxHeap.size() - minHeap.size() == 2){
//大根堆的规模比小根堆的规模大 2
minHeap.add(maxHeap.poll());
}
else if (minHeap.size() - maxHeap.size() == 2){
//小根堆的规模比大根堆的规模大 2
maxHeap.add(minHeap.poll());
}
}
if (minHeap.size() == maxHeap.size()){
//nums数组为偶数个
return (minHeap.poll() + maxHeap.poll())/ 2;
}
else if (minHeap.size() - maxHeap.size() == 1){
//小根堆多一个
return minHeap.poll();
}
else {
//大根堆多一个
return maxHeap.poll();
}
}






















 227
227











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










