一、状态转移方程
根据(3)的介绍,得到了加速度的变化量,如果采用数值法,可以模拟出轨道的预报,在本节中,将讨论将轨道预报模型线性化,求出轨道的状态转移方程。根据前面的公式,整个状态转移方程可以写为
其中
根据上式求得加速度关于位置的关系式为

求得当m=0时
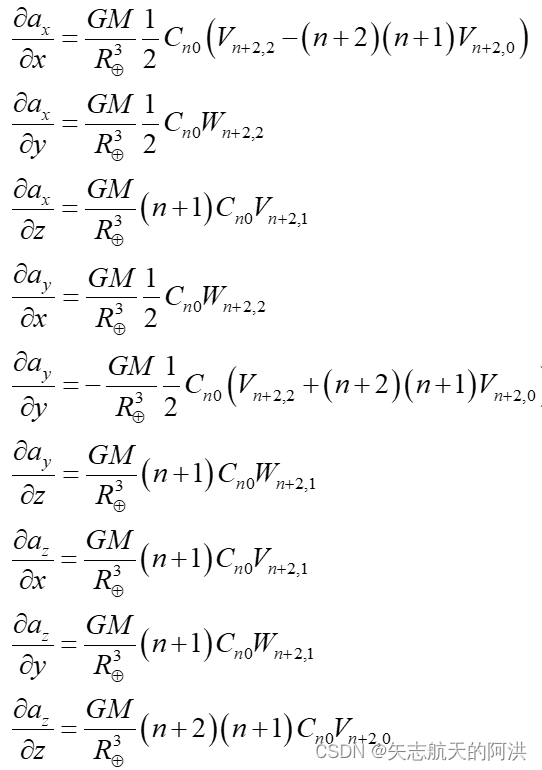
当m=1时
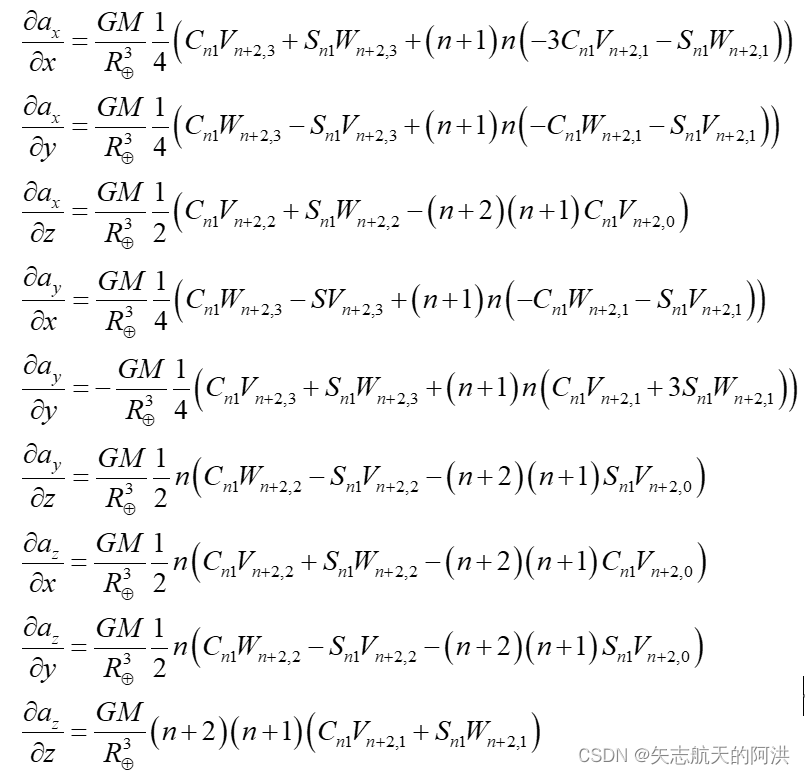
当m>1时
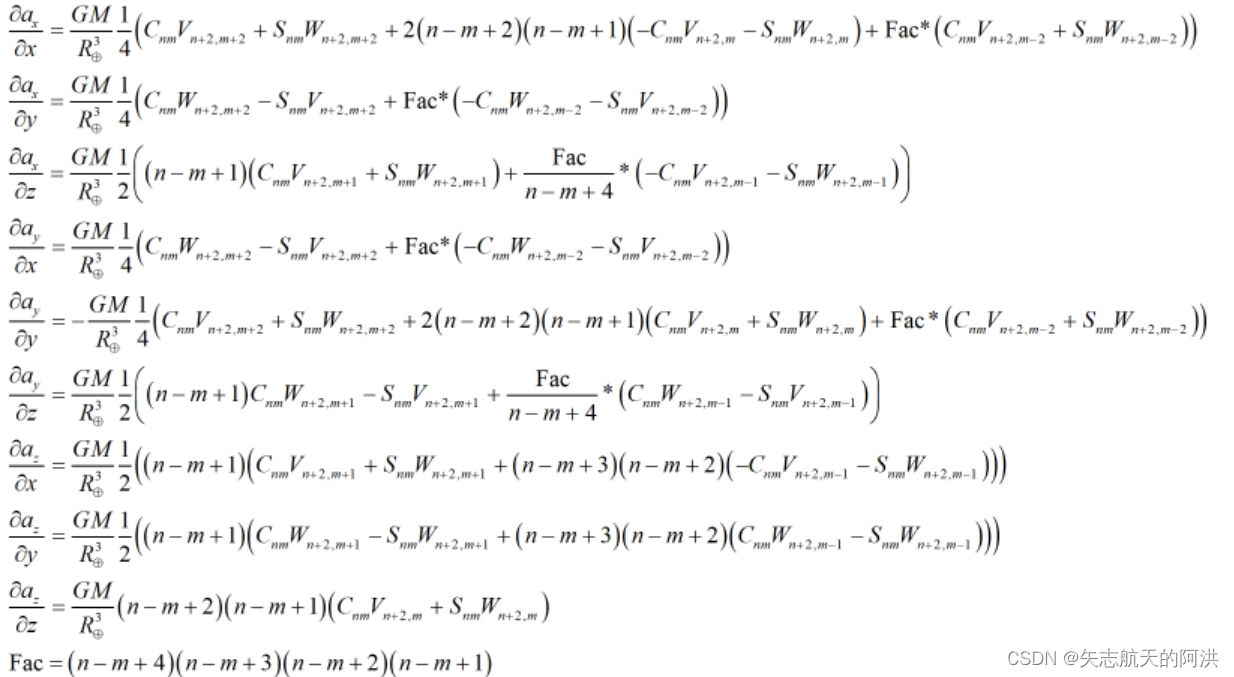
通过上式可以得到瞬时真地球坐标系下的状态转移方程,而瞬时真天球坐标系下的状态转移方程为,根据(2)中已经求得两个坐标系之间的转换矩阵
二、实现代码
根据上文的介绍,即可求得轨道的状态转移方程,代码如下:
%--------------------------------------------------------------------------
%
% EarthHarmGrad: Computes the gradient of the Earth's harmonic gravity field
%
% Inputs:
% r Satellite position vector in the inertial system
% U Transformation matrix to body-fixed system
% n_max Maximum degree
% m_max Maximum order (m_max<=n_max; m_max=0 for zonals, only)
% CS Spherical harmonics coefficients (un-normalized)
%
% Output:
% G Gradient in the ICRF/EME2000 system
%
% Last modified: 2020/03/25 Meysam Mahooti
%
%--------------------------------------------------------------------------
function G = EarthHarmGrad(r, U, n_max, m_max )
global CS
r_ref = 6378.1363e3; % Earth's radius [m]; GGM03S
gm = 398600.4415e9; % [m^3/s^2]; GGM03S
% Body-fixed position
r_bf = U * r;
% Auxiliary quantities
r_sqr = dot(r_bf,r_bf); % Square of distance
rho = r_ref*r_ref/r_sqr;
x0 = r_ref*r_bf(1)/r_sqr; % Normalized
y0 = r_ref*r_bf(2)/r_sqr; % coordinates
z0 = r_ref*r_bf(3)/r_sqr;
%
% Evaluate harmonic functions
% V_nm = (r_ref/r)^(n+1) * P_nm(sin(phi)) * cos(m*lambda)
% and
% W_nm = (r_ref/r)^(n+1) * P_nm(sin(phi)) * sin(m*lambda)
% up to degree and order n_max+1
%
% Calculate zonal terms V(n,0); set W(n,0)=0.0
V(1,1) = r_ref/sqrt(r_sqr);
W(1,1) = 0;
V(2,1) = z0 * V(1,1);
W(2,1) = 0;
for n=2:n_max+2
V(n+1,1) = ( (2*n-1) * z0 * V(n,1) - (n-1) * rho * V(n-1,1) )/n;
W(n+1,1) = 0;
end
% Calculate tesseral and sectorial terms
for m=1:m_max+2
% Calculate V(m,m) .. V(n_max+1,m)
V(m+1,m+1) = (2*m-1) * ( x0*V(m,m) - y0*W(m,m) );
W(m+1,m+1) = (2*m-1) * ( x0*W(m,m) + y0*V(m,m) );
if (m<=n_max+1)
V(m+2,m+1) = (2*m+1) * z0 * V(m+1,m+1);
W(m+2,m+1) = (2*m+1) * z0 * W(m+1,m+1);
end
for n=m+2:n_max+2
V(n+1,m+1) = ( (2*n-1)*z0*V(n,m+1) - (n+m-1)*rho*V(n-1,m+1) )/(n-m);
W(n+1,m+1) = ( (2*n-1)*z0*W(n,m+1) - (n+m-1)*rho*W(n-1,m+1) )/(n-m);
end
end
% Calculate Gradients dadx,dady,dadz
daxdx = 0;
daxdy = 0;
daxdz = 0;
daydx = 0;
daydy = 0;
daydz = 0;
dazdx = 0;
dazdy = 0;
dazdz = 0;
for m=0:m_max
for n=m:n_max
if (m==0)
C = CS(n+1,1); % = C_n,0
daxdx = daxdx + 0.5 * C * ( V(n+3,3) - (n+2) * (n+1) * V(n+3,1) );
daxdy = daxdy + 0.5 * C * W(n+3,3);
daxdz = daxdz + (n+1)* C * V(n+3,2);
daydx = daydx + 0.5 * C * W(n+3,3);
daydy = daydy - 0.5 * C * ( V(n+3,3) + (n+2) * (n+1) * V(n+3,1) );
daydz = daydz + (n+1)* C * W(n+3,2);
dazdx = dazdx + (n+1) * C * V(n+3,2);
dazdy = dazdy + (n+1) * C * W(n+3,2);
dazdz = dazdz + (n+2) * (n+1) * C * V(n+3,1);
else
if (m==1)
C = CS(n+1,2); % = C_n,1
S = CS(1,n+1); % = S_n,1
daxdx = daxdx + 0.25 * ( C * V(n+3,4) + S * W(n+3,4) + (n+1) * n * ( - 3 * C * V(n+3,2) - S * W(n+3,2) ) );
daxdy = daxdy + 0.25 * ( C * W(n+3,4) - S * V(n+3,4) + (n+1) * n * ( - C * W(n+3,2) - S * V(n+3,2) ) );
daxdz = daxdz + 0.5 * n * ( C * V(n+3,3) + S * W(n+3,3) - (n+2) * (n+1) * C * V(n+3,1) );
daydx = daydx + 0.25 * ( C * W(n+3,4) - S * V(n+3,4) + (n+1) * n * ( - C * W(n+3,2) - S * V(n+3,2) ) );
daydy = daydy - 0.25 * ( C * V(n+3,4) + S * W(n+3,4) + (n+1) * n * ( C * V(n+3,2) + 3 * S * W(n+3,2) ) );
daydz = daydz + 0.5 * n * ( C * W(n+3,3) - S * V(n+3,3) - (n+2) * (n+1) * S * V(n+3,1) );
dazdx = dazdx + 0.5 * n * ( C * V(n+3,3) + S * W(n+3,3) - (n+2) * (n+1) * C * V(n+3,1) );
dazdy = dazdy + 0.5 * n * ( C * W(n+3,3) - S * V(n+3,3) - (n+2) * (n+1) * S * V(n+3,1) );
dazdz = dazdz + (n+1)* n * ( C * V(n+3,2) + S * W(n+3,2) );
else
C = CS(n+1,m+1); % = C_n,m
S = CS(m,n+1); % = S_n,m
Fac = (n-m+4) * (n-m+3) * (n-m+2) * (n-m+1);
daxdx = daxdx + 0.25 * ( C * V(n+3,m+3) + S * W(n+3,m+3) + 2 * (n-m+2) * (n-m+1) * ( - C * V(n+3,m+1) - S * W(n+3,m+1) )...
+ Fac * ( C * V(n+3,m-1) + S * W(n+3,m-1) ) );
daxdy = daxdy + 0.25 * ( C * W(n+3,m+3) - S * V(n+3,m+3) + Fac * ( - C * W(n+3,m-1) + S * V(n+3,m-1) ) );
daxdz = daxdz + 0.5 * ( (n-m+1) * ( C * V(n+3,m+2) + S * W(n+3,m+2) ) + Fac/(n-m+4) * ( - C * V(n+3,m) - S * W(n+3,m) ) );
daydx = daydx + 0.25 * ( C * W(n+3,m+3) - S * V(n+3,m+3) + Fac * ( - C * W(n+3,m-1) + S * V(n+3,m-1) ) );
daydy = daydy - 0.25 * ( C * V(n+3,m+3) + S * W(n+3,m+3) + 2 * (n-m+2) * (n-m+1) * ( C * V(n+3,m+1) + S * W(n+3,m+1) ) +...
Fac * ( C * V(n+3,m-1) + S * W(n+3,m-1) ) );
daydz = daydz + 0.5 * ( (n-m+1) * ( C * W(n+3,m+2) - S * V(n+3,m+2) ) + Fac/(n-m+4) * ( C * W(n+3,m) - S * V(n+3,m) ) );
dazdx = dazdx + 0.5 * (n-m+1) * ( C * V(n+3,m+2) + S * W(n+3,m+2) + (n-m+3) * (n-m+2) * ( - C * V(n+3,m) - S * W(n+3,m) ) );
dazdy = dazdy + 0.5 * (n-m+1) * ( C * W(n+3,m+2) - S * V(n+3,m+2) + (n-m+3) * (n-m+2) * ( C * W(n+3,m) - S * V(n+3,m) ) );
dazdz = dazdz + (n-m+2) * (n-m+1) * ( C * V(n+3,m+1) + S * W(n+3,m+1) );
end
end
end
end
% Body-fixed partial derivatives of acceleration
dadx = (gm/(r_ref^3))*[daxdx,daydx,dazdx]';
dady = (gm/(r_ref^3))*[daxdy,daydy,dazdy]';
dadz = (gm/(r_ref^3))*[daxdz,daydz,dazdz]';
G(:,1) = dadx;
G(:,2) = dady;
G(:,3) = dadz;
% Inertial acceleration
G = inv(U)*G*U;





















 688
688











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








