📟作者主页:慢热的陕西人
🌴专栏链接:力扣刷题日记
📣欢迎各位大佬👍点赞🔥关注🚓收藏,🍉留言
1.复杂度

2.递归
2.1递归实现指数型枚举
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; #define N 16 int st[N]; int n; void dfs(int u) //0表示空,1表示不选,2表示选 { if(u > n) { for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) if(st[i] == 2) printf("%d ", i); printf("\n"); return; } st[u] = 1; //表示我们不选第u个数字 dfs(u + 1); st[u] = 0; //恢复数组 st[u] = 2; //表示我们选第u个数字 dfs(u + 1); st[u] = 0; // 最后恢复数组 } int main() { cin >> n; dfs(1); //表示遍历到第0位 return 0; }
2.2递归实现排列型枚举
#include<iostream> #include<cstring> #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; #define N 10 int state[N]; //0表示未用,1表示使用 int ways[N]; //存储我们的答案 int n; void dfs(int u) { if(u > n) //边界 { for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) printf("%d ", ways[i]); printf("\n"); return; } for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { if(state[i] == 0) { state[i] = 1; //表示占用了u ways[u] = i; //将u加入到答案 dfs(u + 1); //遍历下一个位置 ways[u] = 0; state[i] = 0; //恢复现场 } } } int main() { cin >> n; dfs(1); return 0; }
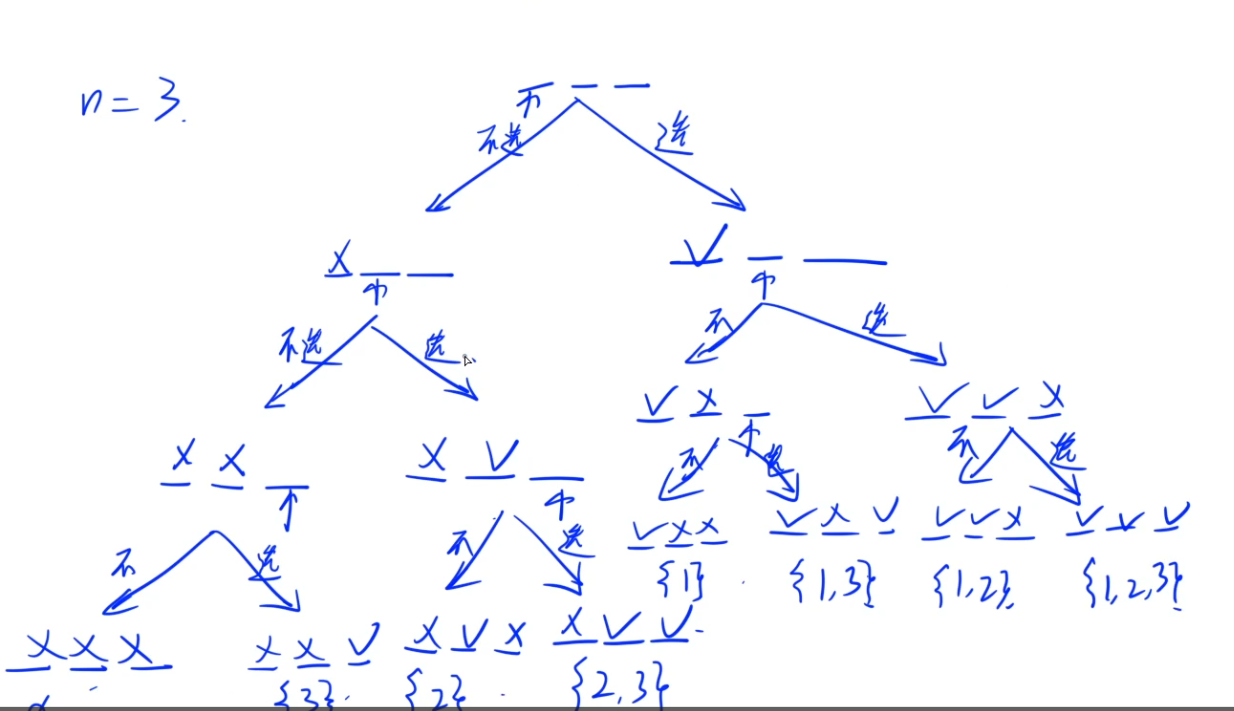
2.3递归实现组合型枚举
两种方法解决:
- 将例一不符合长度的答案去掉即可
- 只需要满足答案的前一个数字比后一个数字大即可
#include<iostream> #include<cstring> #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; #define M 25 int ways[M]; //存储我们的答案 int n,m; void dfs(int u, int st) { if(n + u - st < m) return; //剪枝,选上后面的所有的数都不够答案的数量 if(u == m + 1) { for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) printf("%d ", ways[i]); printf("\n"); return; } for(int i = st; i <= n; ++i) { ways[u] = i; dfs(u + 1, i + 1); //从大于当前插入的数字开始遍历 ways[u] = 0; } } int main() { cin >> n >> m; dfs(1, 1); return 0; }
2.4带分数
链接:[P1426 - 蓝桥杯]带分数 - New Online Judge (ecustacm.cn)
[P8599 蓝桥杯 2013 省 B] 带分数 - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
思路: 设 n = a + b / c,化简为 n * c = a * c + b;
那么我们先寻找a, 在a的基础上寻找c, 在a,c已知的情况下,去计算b。
细节注意要b的类型longlong,不然只能过部分。
因为算法需要去枚举答案,所以选用了递归的思路。
#include<iostream> #include<cstring> #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; #define N 10 bool st[N], buckup[N]; int ans; int n; bool check(int a, int c) { long long b = (long long)c * n - c * a; //注意数据的大小,部分ac!!!! if(!a || !b || !c) return false; //优化存在零的话直接返回错误 memcpy(buckup, st, sizeof st); while(b) { int x = b % 10; //取个位 b /= 10; //去掉个位 if(!x || buckup[x]) return false; //存在0,或者对应的数字已经被占用则不是答案 buckup[x] = true; } for(int i = 1; i <= 9; ++i) if(!buckup[i]) return false; return true; } void dfs_c(int u, int a, int c) { if(u == n) return; //当位数达到9位的时候,代表无解 if(check(a, c)) ans++; //检查当前a,c的值,存在一个b成立,则使得答案++ for(int i = 1; i <= 9; ++i) if(!st[i]) { st[i] = true; dfs_c(u + 1, a, c * 10 + i); st[i] = false; //恢复现场 } } void dfs_a(int u, int a) { if(a >= n) return; if(a) dfs_c(u, a, 0); //计算当前a下,c的值,c的值从零开始 for(int i = 1; i <= 9; ++i) if(!st[i]) //当前数字没有被使用的话 { st[i] = true; //使用当前的数字 dfs_a(u + 1, a * 10 + i); st[i] = false; //恢复现场 } } int main() { cin >> n; dfs_a(0, 0); //表示从第零开始,a = 0; cout << ans << endl; return 0; }
2.5费解的开关:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int dx[6] = { -1, 0, 1, 0, 0 }, dy[6] = { 0, 1, 0, -1, 0 };
char g[6][6], bk[6][6];
void turn(int x, int y)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
{
int a = x + dx[i], b = y + dy[i];
//越界的话则进行下一次遍历
if (a < 0 || a >= 5 || b < 0 || b >= 5) continue;
g[a][b] ^= 1; //反转对应的开关
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n--)
{
int res = 10; //设置一个较大的值
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) cin >> g[i];
for (int op = 0; op < 32; ++op) //第一行的32种可能
{
memcpy(bk, g, sizeof(g));
int step = 0; //设置当前的步数为0
//1.先按第一行
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i)
if (op >> i & 1)
{
step++;
turn(0, i); //反转[1,i + 1];
}
//2.接下来处理剩下的234行
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < 5; ++j)
{
if (g[i][j] == '0')
{
step++;
turn(i + 1, j);
}
}
//3.检查第五行是否全亮
bool black = false;
for (int j = 0; j < 5; ++j)
{
if (g[4][j] == '0')
{
black = true;
break;
}
}
if (!black) res = min(res, step);
memcpy(g, bk, sizeof(g));
}
if (res > 6) res = -1;
cout << res << endl;
}
return 0;
}
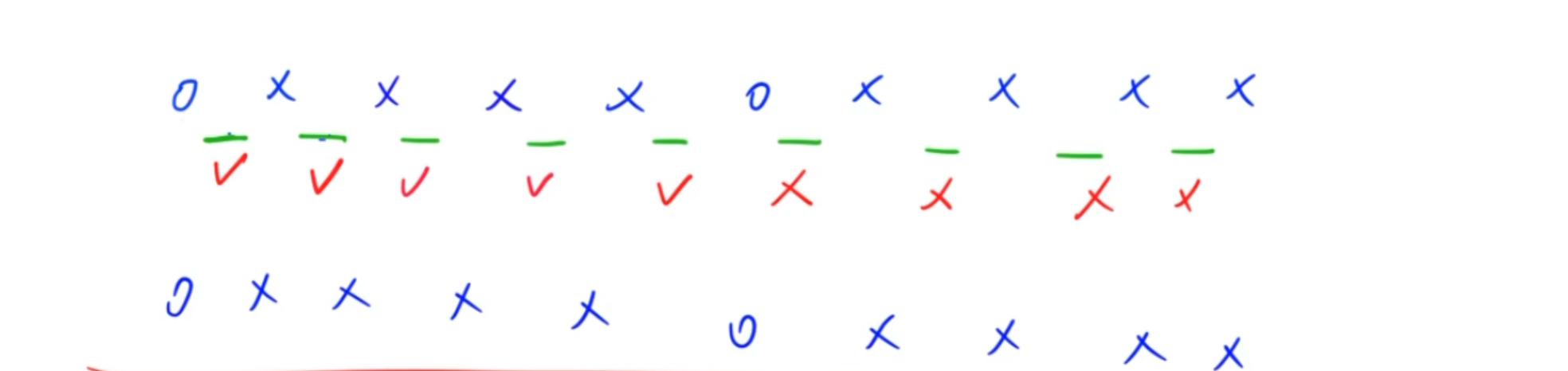
2.6翻硬币
题目链接:[P1428 - 蓝桥杯]翻硬币 - New Online Judge (ecustacm.cn)
思路:
将两个符号之间看作一个开关,那么两个符号改变,就相当于中间的按钮被按下。
那么左边的符号需要被改变,那么一定是中间的按钮需要被按下,并且一个按钮如果被按了两次,相当于没有被按下
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
char start[N], dest[N];
void turn(int i)
{
if(start[i] == 'o') start[i] = '*';
else start[i] = 'o'
}
int main()
{
cin >> start >> dest;
int n = strlen(start);
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i)
{
if(start[i] != dest[i])
{
turn(i), turn(i + 1);
res++;
}
}
cout << res;
return 0;
}
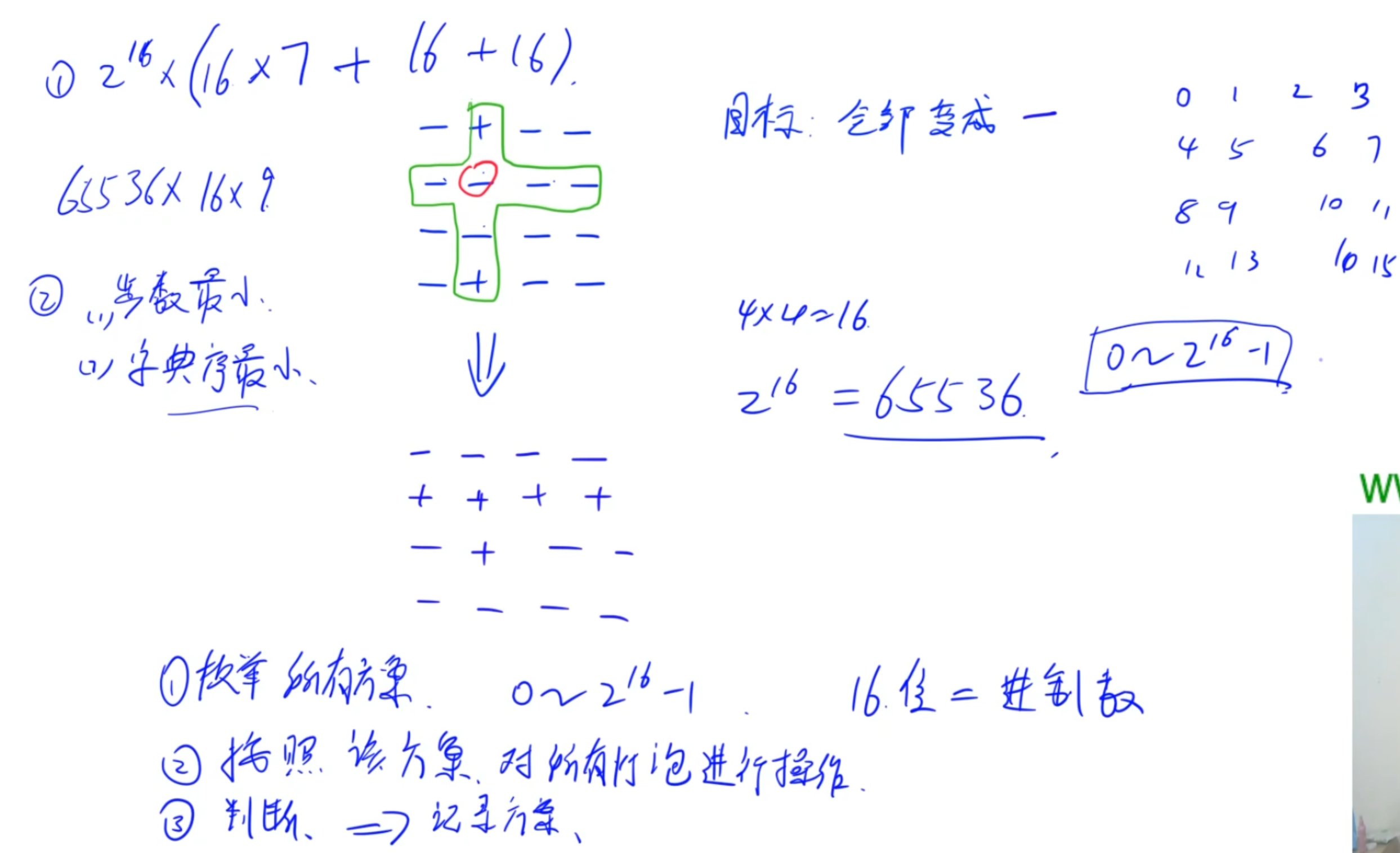
2.7飞行员兄弟
思路:数据量小,所以枚举所有的结果,然后找出步数最少的那个。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#define x first
#define y second
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
const int N = 5;
char g[N][N], bku[N][N];
int get(int x, int y) //通过坐标获取对应的序号
{
return 4 * x + y;
}
void turn_one(int x, int y) //通过坐标反转对应的开关
{
if(g[x][y] == '+') g[x][y] = '-';
else g[x][y] = '+';
}
void turn_all(int x, int y)
{
//反转受影响的开关
for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
turn_one(x, i);
turn_one(i, y);
}
//反转自己
turn_one(x,y);
}
int main()
{
for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) cin >> g[i]; //输入
vector<PII> res; //存储答案的数组,每个元素都是一个pair
for(int op = 0; op < 1 << 16; op++) //遍历2的16次方种可能
{
vector<PII> temp;
memcpy(bku, g, sizeof g); //备份输入
//操作
for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
for(int j = 0; j < 4; ++j)
if(op >> get(i, j) & 1)
{
temp.push_back({i, j});
turn_all(i, j);
}
//判断所有的灯泡是否全亮
bool has_closed = false;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
for(int j = 0; j < 4; ++j)
{
if(g[i][j] == '+')
{
has_closed = true;
}
}
if(has_closed == false)
{
if(res.empty() || res.size() > temp.size()) res = temp;
}
memcpy(g, bku, sizeof g);
}
cout << res.size() << endl;
for(auto op : res) cout << op.x + 1 << ' ' << op.y + 1 << endl;
return 0;
}

























 153
153











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










