LEC 2
>> 4 kinds of files to work
1. Source Code files
(a *.c files
(b Contain function definitions
2. Header files
(a *.h files
(b Contain function declarations (function prototypes)
(c Contain various preprocessor statements
(d Allow source code files to access externally-defined functions
3. Object files
(a *.o files (or *.obj on Windows)
(b The output of the compiler
(c Contain function definitions in binary form
(d Not executable by themselves
4. Binary files
(a No suffix on macOS or Unix OS (*.exe on Windows)
(b The output of the Linker
(c Made from (a few) object files
(d Can be directly executed
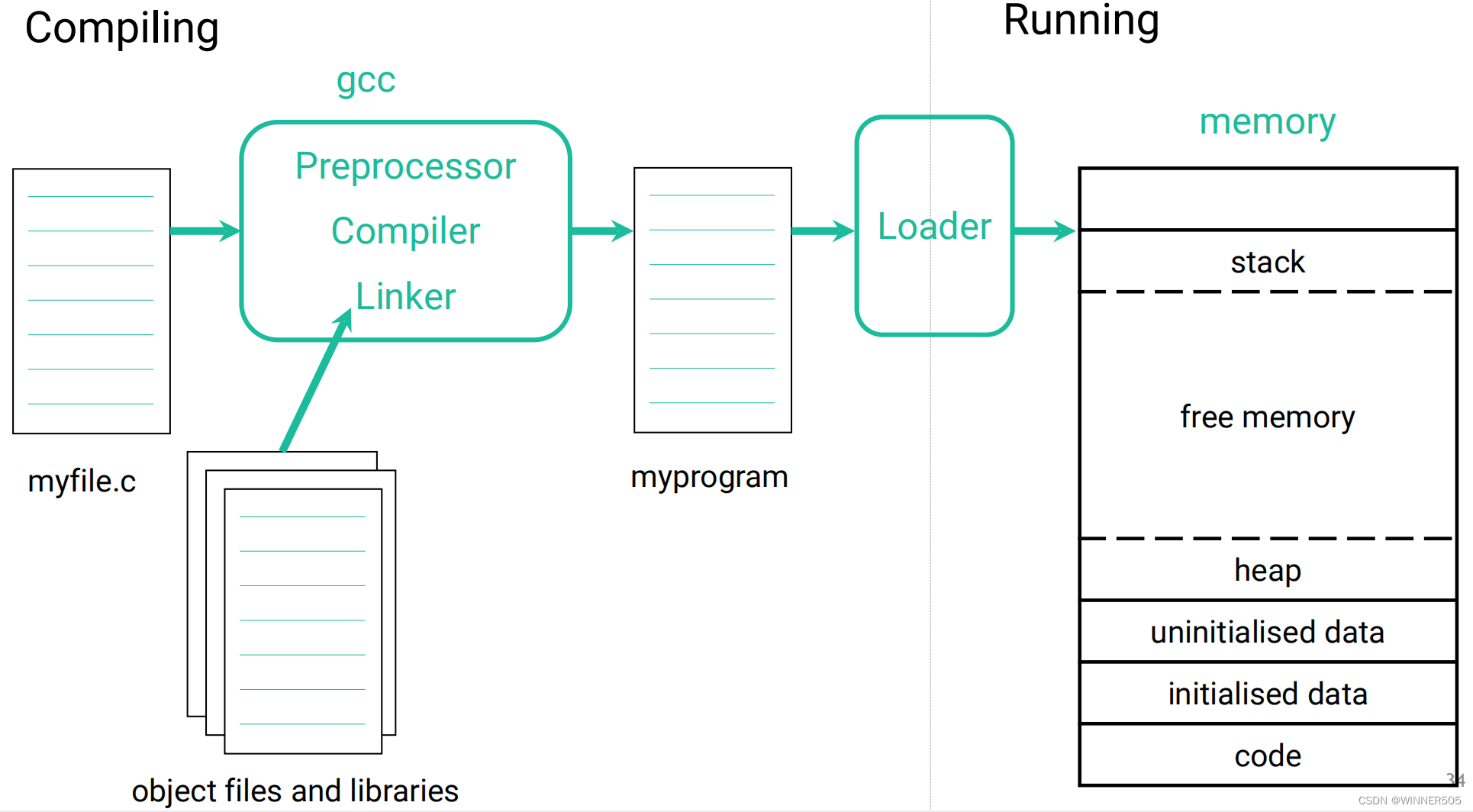
The Preprocessor
(Before the C compiler starts compiling a source code file, the file is processed by the preprocessor)
>> It is invoked automatically by the compiler before compilation proper begins.
>> It converts source code (*.c) files, which may exist as a real file or be stored in memory for a short time before being sent to the Compiler.
>> Preprocessor commands start with “#”
For example : #include #define #undef #ifdef #ifundef #error #if #else #elif #endif #pragma
>> #include <stdio.h> : 在compile前,粘贴stdio.h的内容到#include的位置
C compilers do not allow using a function unless it has previously been declared or defined in the file.
#include statements are thus the way to re-use previously written code in C programs ( like printf 这种,他的declared就在stdio.h文件里)
>> #define
To include header files, which mainly contain function declarations and #define statements, e.g.,
The Compiler
It turns the source code into an object code file, which contains the binary version of the source code (not executableyet).
>> -c option

>> -o option

The Linker
It links together object files (.o files) into a binary executable.
• It is a separate program called ld.
• It is invoked automatically when using the Compiler.
% gcc foo.o bar.o baz.o –o myprogram
This tells the compiler to link together 3 object files (foo.o, bar.o and baz.o) into a binary executable file named myprogram. 这个myprogram就是可以run的
% ./myprogram
C Language Basics
• The main ( ) function
• Statements
• C Skeleton
• Identifiers
• Keywords
• Basic data variables and types
• Constants
>> The main() function
1. "main” is a C keyword. We must not use it for any other variable.
2. Good programming practice tells us that we should not ourselves call Main() in our code.
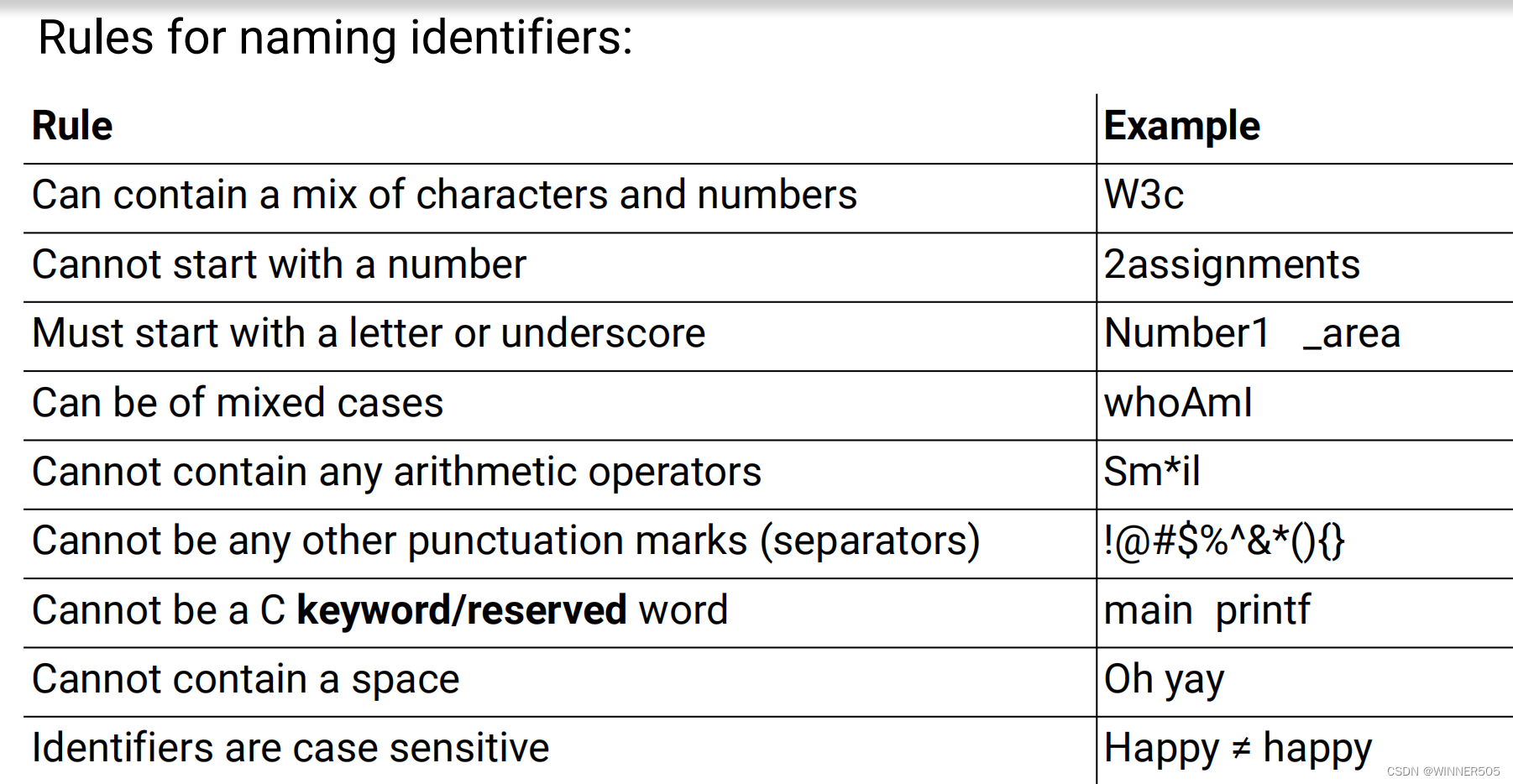
>> Identifiers
>> Basic data variables and types
1. Integers : char / int / short / long / long long
2. Unsigned integers
3. Floating point numbers : float / double
4. Chars : Numeric digits: 0 – 9 / Letters: a – z and A – Z / Space (blank) / Special characters: !@£$%^&*()






















 774
774











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








