LEC 2.1 Financial markets and automated trading
A security is a tradable financial asset; 可交易的金融资产
financial markets are where securities are traded.
A simple breakdown of markets by type of security is : (按证券类型对security的简单划分)
• Capital markets (equities and fixed income) 资本市场(股票 及 固定收入)
• Foreign exchange markets 外汇交易市场
• Money markets 货币市场
• Derivative markets (e.g. futures and options) 衍生市场
>> For equities and futures trading, exchanges have been prominent (our focus); whereas for many other markets over the counter (OTC) trading has predominated, but this is changing
Buy side vs Sell side
>> Buy Side: the side of the market that buys large amounts of securities for money or fund management (examples include asset managers, private equity funds, mutual funds, life
insurance companies, unit trusts, hedge funds, and pension funds)
>> Sell Side: the other side of the financial market, including prime brokers and broker-dealers (often investment banks), which deals with the creation, promotion, and selling of traded securities to the buy side
>> The computer-based trading applications that we will cover will relate to both the buy side and sell side.
Active vs Passive investment
Passive investments track the market (e.g., an index fund that tracks the S&P500)
• Active strategies make trading decisions to try and beat passive investment benchmarks COMP226 material is relevant for both investment styles, e.g.:
• Execution algorithms (end of Topic 2 "Market Microstructure") are relevant when an index tracker fund has to rebalance.
• Topic 3 "Performance Measurement" is relevant for comparing strategies, be they active or passive.
• Topic 4 "Trading strategies" mainly considers active strategies; while Topic 5 on backtesting is relevant for both active and passive strategies.
Automated trading
Definition : Automated/algorithmic trading: trading decisions are made by computer programs (as opposed to humans)
We will focus on equities and futures markets because of the prevelance of automated trading in those markets Many innovations in automated trading started in equities and futures markets, though automated trading is becoming ever more present in all markets
LEC 2.2 Equities markets 产权投资市场
Shares(股份) allow firms to finance themselves(公共所有制) via public ownership(融资)
• A share represents a portion of firm's inherent value(公司固有价值)or equity(权益)
• The number of shares at a given time is known. But
• Firms may issue or buy back shares(发行或回收股份), or
• make periodic dividend payments to shareholders 定期向股份持有者支付股息
• These corporate actions 公司行为 are important when valuing equities and evaluating trading strategies 评估股票和评估交易策略
• These actions are represented via adjusted prices 调整后的价格 for equities
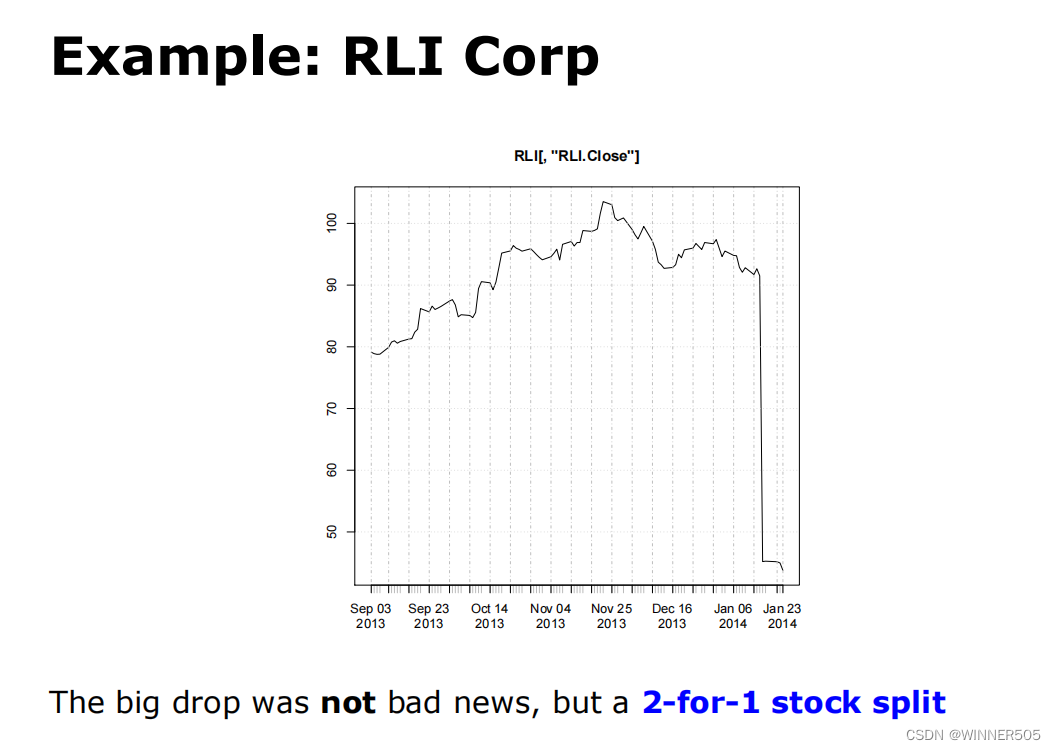
把一份股票拆成两份股票的拆股 stock split
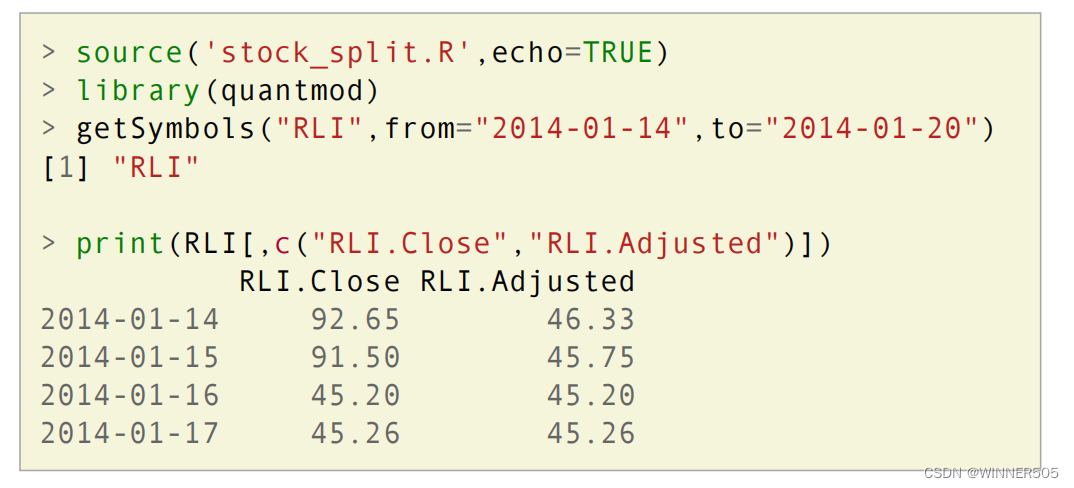
Adjustment formulas
Cash dividends (现金股利)
含义: dividend value deducted from close price
E.g. assume close price is $25 pre-adjustment and a $2.50 dividend is paid on every share. The adjusted close price would be $22.50 ($25-$2.50). 这里cash dividends就是2.5
Stock dividends/stock splits (股票分割)
含义: close price divided by factor by which number of shares has increased
E.g. stock dividend of 2 shares for every share owned gives a multiplicative adjustment of 1/(2+1). So a pre-adjustment price of $25 becomes $8.33 (rounding required).
E.g. a 2:1 stock split gives a multiplicative adjustment factor of 1/2. So a pre-adjustment price of $25 would become $12.50.
These are simplest and most common corporate actions. There can be much more complicated actions such at rights offerings.
Notes:
Sometimes we will not pay proper care and attention to adjustments (we do not have money on the line).
However, you need to be aware of how important corporate actions are when using historial data for real trading in equities and corporate bond markets.
This is an example of a general point: it is crucial to understand the correct interpretation of financialdata. Data cleaning, pre-processing is an important part of developing trading strategies.
Equities markets have extremely high volumes of automated trading - it can account for over 70% of trading volume on equities exchanges on some days.
• Moreover, automated trading is supported across the different types of execution venue for equities markets, namely, both limit order books and dark pools.
LEC 2.3 Futures Markets, ETFs, and Trading Venues
目录:
• Futures 期货
• Options
• Swaps
• Credit Derivatives 信用衍生品
Futures
>> A forward (远期合约) is an agreement to buy or sell a fixed quantity of a given asset at a certain price at a specific date in the future
>> A futures contract is a forward with standardized terms
>> Examples :
• S&P 500 E-mini Futures
• FTSE 100 Futures
• Crude Oil Futures
• Eurodollar futures (interest rate futures)
• CME Euro FX Futures
>> Futures exist for a wide array of underlying assets 广泛的基础资产?
>> Futures markets are
• exchange-based order-driven markets (订单驱动市场); and
• automated trading is prevalent 自动化交易非常普遍
Futures Contracts
Futures contracts have a fixed expiry 固定到期 (定期)
• Multiple futures contracts with different expiries can be traded at any one time
• This provides trading opportunities such as spread trading: trading one contract against another for the same underlying
• It also means there is no single data set:
• Often, a futures "continuous contract" data set is formed by "glueing together" individual contracts
• One of the most common approaches is to back-adjust by adding the price gaps on to earlier prices
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) - 交易型开放式指数基金
• Tradable share (流通股:可交易的股份)in an investment fund 投资基金
• Since they represent baskets of assets they are an effective way to gain exposure to whole sectors or markets(much like index futures) - 有效的方式去获得整个行业和市场的关注
• There are index, commodity, bond and currency ETFs
ETFs are becoming ever more utilized by algorithmic traders; we will not revisit them much in this module, except to mention them in the context of an example momentum strategy under Topic 4.
Trading mechanisms - 贸易机构
• Dealers (buys/sells securities on their own account) - 交易商
• Brokers (buys/sells securities solely for clients) - 经纪人
• Broker-Dealers (often investment banks 投资银行) do both roles - 债劵经纪人
• Limit Order Books (typically run by public exchanges)
• Dark Pools (run e.g. by broker-dealers or public exchanges) 资金暗池
Limit order books and dark pools allow automated trading; we will cover these trading mechanisms in detail
Exchanges and alternative venues 交易场所
Traditional venue is the exchange, e.g. LSE or NYSE
• Alternative venues are now allowed. Different names:
• Europe: Multi-lateral Trading Facility (MTF)
• US: Alternative Trading System (ATS)
These typically provide limit order books and often also dark pools
LEC 2.4 limit order books
Limit order book markets
• In academic work, often called Continuous Double Auctions
• Mechanism to match buyers and sellers - 匹配买家和卖家的机制
• Consists of two types of order
• Limit orders
• Market orders
Limit order
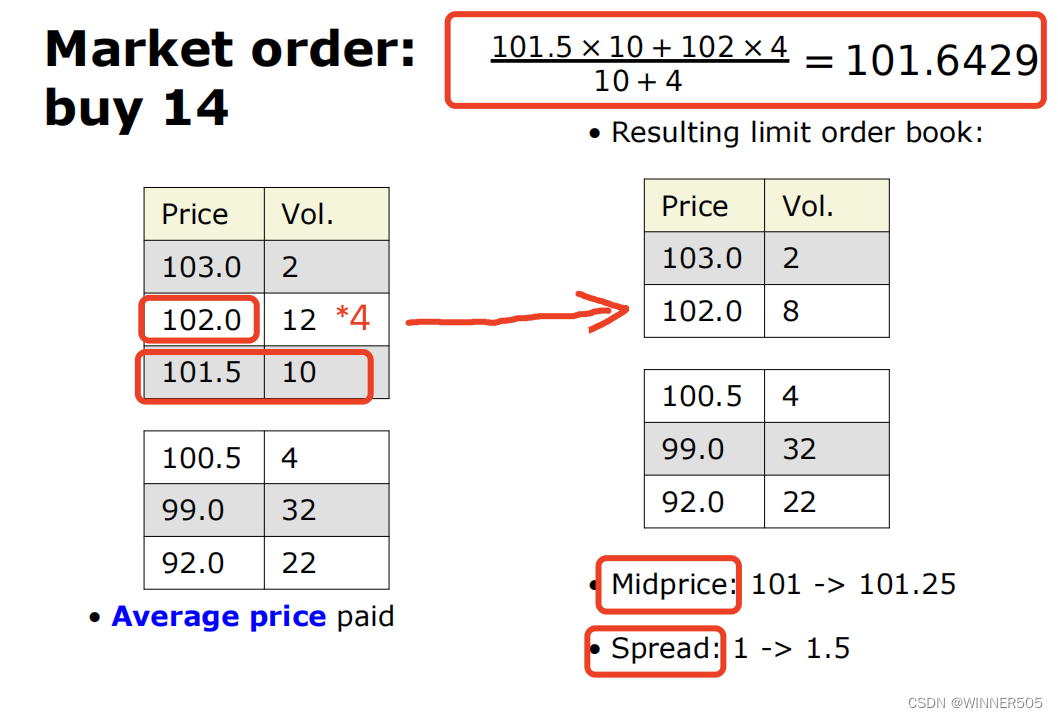
Limit orders are matched and/or stored
• Market orders are matched against limit orders if possible
• Unmatched limit orders are stored in the order book
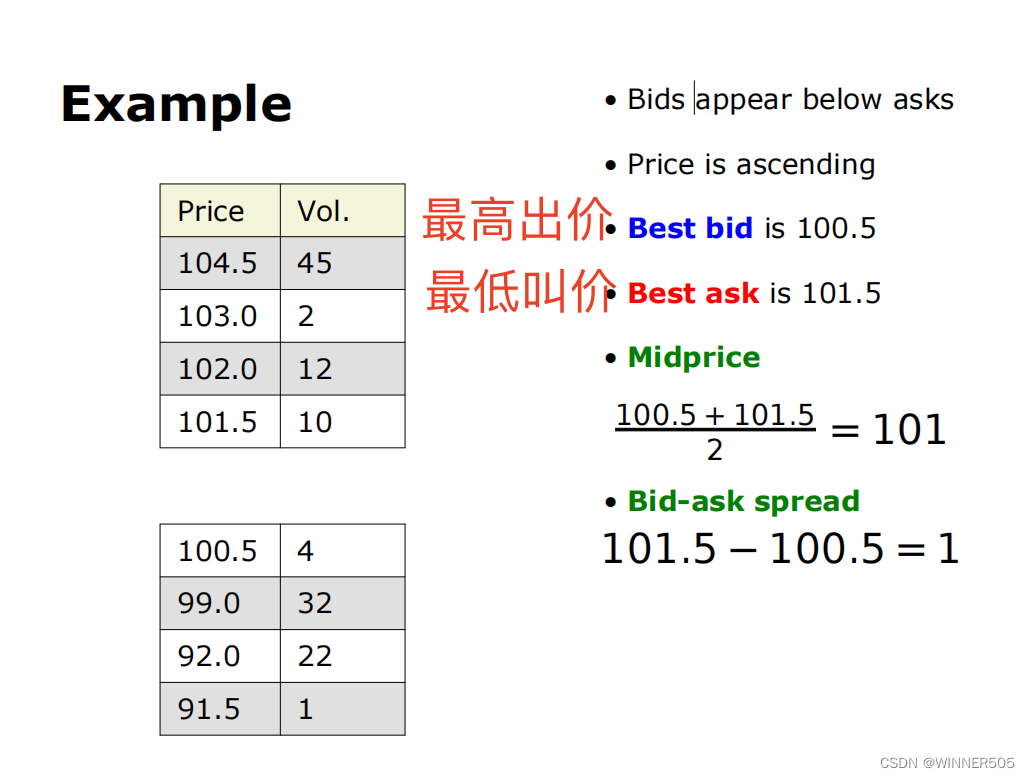
• Buy orders or bids(出价) are stored in the bid book
• Sell orders or asks/offers(叫价) are stored in the ask book
Tick sizes 最小报价单位 and bid-ask spreads买卖差价
• Tick size: smallest increment in price that an equity, future, or other exchange-traded instrument can move by 最小价格变量单位
• Tick sizes can be fixed (e.g. $0.01, which is common for US equities, or a fixed number of points like 0.25 for an equities futures index), or may vary according to the current price
• For heavily-traded instruments the bid-ask spread will often be equal to the tick size ("the spread is one tick") 买卖差价通常等同于tick size
• Similarly, it is often argued that smaller bid-ask spreads indicate more efficient markets because a wide spread indicates uncertainty about the "real price". 买卖差价越小,市场效率越高,因为差价越大表明实际价格越难以去评估
Buying versus selling
>> Short selling (also known as shorting or going short) is the practice of selling securities or other financial instruments that are not currently owned, and subsequently repurchasing them ("covering") - 卖空,卖目前并没有持有的证券或金融产品,然后再买回来
>> In the event of an interim price decline, the short seller will profit, since the cost of (re)purchase will be less than the proceeds which were received upon the initial (short) sale
- 卖出之后如果价格下降,那么short seller就会有收益,因为他们再买回来的时候价格更低
>> Shorting is a prevalent practice(非常普遍) in equities markets 产权投资市场
Limit orders versus market orders
• Limit orders guarantee price but not execution
• Market orders guarantee execution (almost always) but not price
• For market orders, slippage 下滑 is an important consideration
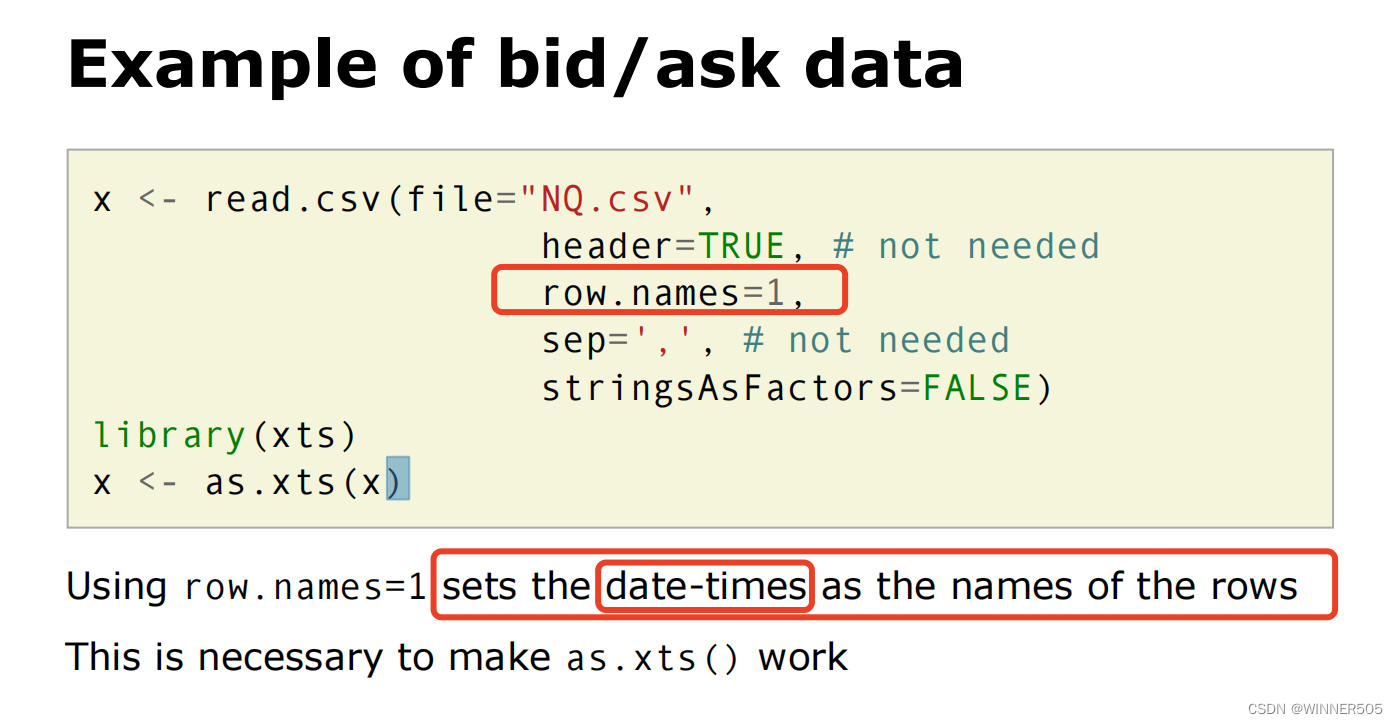
Market data
Trading models are developed using historical market data. There are several granularities of market data : 市场数据粒度
• Time-based Bars, e.g., daily, 1-minute bars
• Tick data (tick stands for the change in prices due to a trade)
• Just trades
• Level 1: trades, best bid, best ask
• Level 2: trades, multiple price levels (e.g. 5) in the book






















 1767
1767











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








