🎉welcome🎉
✒️博主介绍:一名大一的智能制造专业学生,在学习C/C++的路上会越走越远,后面不定期更新有关C/C++语法,数据结构,算法,Linux,ue5使用,制作游戏的心得,和大家一起共同成长。
✈️C++专栏:C++爬塔日记
😘博客制作不易,👍点赞+⭐收藏+➕关注
前情回顾
在上一块石碑中,我学到了如何去使用一些常用的排序算法,同时下一块石碑也显露出来…
- 🚄上章地址:第九章(13):STL之常用排序算法
常用拷贝算法
- 拷贝算法通常使用的就只有一种:
copy//将容器指定范围之内的数据拷贝到另一个容器当中
copy
- copy,翻译过来就是拷贝,它的作用也确实是拷贝,将一个容器内的一个区间内的元素拷贝给另一个容器,注意,要提前给要拷贝进去的容器开辟好空间
copy(beg,end,dest);
使用:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
void print(vector<int>& a)
{
for (auto b = a.begin(); b < a.end(); b++)
{
cout << *b << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
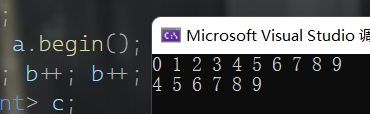
void test1()
{
vector<int> a;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
a.push_back(i);
}
print(a);
auto b = a.begin();
b++; b++; b++; b++;
vector<int> c;
c.resize(6);
copy(b, a.end(), c.begin());
print(c);
}
int main()
{
test1();
return 0;
}
常用替换算法
- 替换算法,其实本质是和拷贝是一样的,拷贝也可以属于替换算法,拷贝过去的元素也就是一个区间内的元素把另一个区间内的元素替换掉了,常用的替换算法有三种:
replace//将指定范围内的元素换成新的元素
replace_if//将指定范围内满足条件的元素替换成新的元素
swap//互换两个容器内的元素
replace
- replace它的作用是将区间内的指定元素替换成新元素
replace(beg,end,T old,T new)
- beg是区间的开始迭代器,end为区间结束迭代器,old是要被替换的旧元素,new是替换旧元素的新元素
使用:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
void print(vector<int>& a)
{
for (auto b = a.begin(); b < a.end(); b++)
{
cout << *b << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
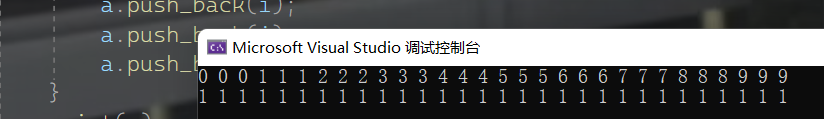
void test1()
{
vector<int>a;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
a.push_back(i);
a.push_back(i);
a.push_back(i);
}
print(a);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
replace(a.begin(), a.end(), i, 1);
print(a);
}
int main()
{
test1();
return 0;
}
replac_if
- replace_if的作用与replace的作用基本是一致的,但是他它是满足条件的元素替换成新元素
replace_if(beg,end,_pred,T new)
- beg是区间的开始迭代器,end为区间结束迭代器,_pred是谓词,满足谓词条件的是要被替换的旧元素,new是替换旧元素的新元素
使用:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
void print(vector<int>& a)
{
for (auto b = a.begin(); b < a.end(); b++)
{
cout << *b << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
bool big(int a)
{
return a > 0;
}
void test1()
{
vector<int>a;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
a.push_back(i);
a.push_back(i);
a.push_back(i);
}
print(a);
replace_if(a.begin(), a.end(),big , 1);
print(a);
}
int main()
{
test1();
return 0;
}

swap
- swap是交换两个容器内的元素,这里的容器一定是同种的容器
swap(cc1,c2)
- c1是容器1,c2是容器2
使用:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
void print(vector<int>& a)
{
for (auto b = a.begin(); b < a.end(); b++)
{
cout << *b << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
bool big(int a)
{
return a > 0;
}
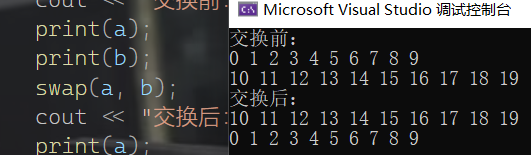
void test1()
{
vector<int>a, b;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
a.push_back(i);
b.push_back(i + 10);
}
cout << "交换前:" << endl;
print(a);
print(b);
swap(a, b);
cout << "交换后:" << endl;
print(a);
print(b);
}
int main()
{
test1();
return 0;
}
下一座石碑
- 这座石碑倒下了,露出了下一座石碑…
😘预知后事如何,关注新专栏,和我一起征服C++这座巨塔
🚀专栏:C++爬塔日记
🙉都看到这里了,留下你们的👍点赞+⭐收藏+📋评论吧🙉






















 2487
2487











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










