欢迎来到我的算法探索博客,在这里,我将通过解析精选的LeetCode题目,与您分享深刻的解题思路、多元化的解决方案以及宝贵的实战经验,旨在帮助每一位读者提升编程技能,领略算法之美。
👉更多高频有趣LeetCode算法题
👉LeetCode高频面试题题单
引言:深搜与广搜
在解决岛屿问题时,我们常常离不开两种经典图搜索算法——深度优先搜索(DFS) 与 广度优先搜索(BFS)。
这两种算法虽然目标一致(遍历所有相连的陆地),但在实现方式、空间开销和思维模式上有明显的区别。掌握它们的核心思想与代码框架,是攻克岛屿系列题的关键。
区别
| 对比维度 | DFS(深度优先搜索) | BFS(广度优先搜索) |
|---|---|---|
| 遍历顺序 | 一条路走到尽头,直到无法继续再回溯 | 按层层推进的方式逐步扩展 |
| 实现方式 | 通常使用递归或栈 | 通常使用队列 |
| 空间复杂度 | 受递归深度影响,最坏 O(m×n) | 队列中可能存储同层节点,最坏 O(m×n) |
| 适用场景 | 更适合连通块标记、递归式思维的题 | 更适合最短路径、分层遍历的题 |
DFS 像是一根针插到底,BFS 像是水波一圈圈扩散。
在岛屿问题中,它们的核心目标都是找到“相连的 1 区域(陆地)”,只是实现路径不同。
代码框架
在 ACM 模式(标准输入输出)下,我们一般需要先读取矩阵,然后从每个未访问过的陆地(1)出发,使用 DFS 或 BFS 将整块岛屿“淹没”或“标记”为访问过。
“标记已访问”有两种常用方式:
1️⃣ 使用额外的visited数组(boolean[][])。创建一个与原网格同样大小的布尔数组visited,初始值都是false。
每当访问一个陆地格子,就把 visited[x][y] = true。
2️⃣ 原地修改grid(原网格标记)。直接在原网格中把已访问的陆地格子改成水(0),或者标记为其他数字,例如 -1。
⭐️深搜(DFS)通用框架
深搜可以使用递归或显式栈。递归实现更简洁,思路如下:
// 递归版 DFS 框架
private static final int[][] DIRS = {{-1,0},{1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}};
public static void dfs(int[][] grid, boolean[][] visited, int x, int y) {
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
visited[x][y] = true;
// 四个方向继续搜索
for(int[] dir : DIRS) {
int nx = x + dir[0];
int ny = y + dir[1];
// 越界判断
if(nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= m || ny >= n) continue;
// 未访问且为陆地则继续递归
if(!visited[nx][ny] && grid[nx][ny] == 1) {
visited[nx][ny] = true;
dfs(grid, visited, nx, ny);
}
}
}
💬 关于终止条件
在编写 DFS 时,终止条件是避免死循环和栈溢出的关键。
每一次递归调用,都应当有明确的“退出路径”,即当不满足继续搜索的条件时,函数应立即返回。
在上面的代码中,终止条件体现在两个地方:
-
越界判断:
当(nx, ny)超出网格边界时,直接continue。
这相当于提前剪枝,防止非法访问。 -
访问与状态判断:
当节点已访问或不是陆地(即grid[nx][ny] != 1)时,不再向下递归。
可以看到,DFS 的终止条件往往不是单独写在函数开头的 if 语句中,而是“隐含”在递归逻辑里:
当然如果你也可以这么编写代码:
// 递归版 DFS 框架
private static final int[][] DIRS = {{-1,0},{1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}};
public static void dfs(int[][] grid, boolean[][] visited, int x, int y) {
// 终止条件:遇到被访问过的陆地节点 或 遇到水域节点
if(visited[x][y] || grid[x][y] == 0) return;
visited[x][y] = true;
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
// 四个方向继续搜索
for(int[] dir : DIRS) {
int nx = x + dir[0];
int ny = y + dir[1];
// 越界判断
if(nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= m || ny >= n) continue;
// 继续递归
dfs(grid, visited, nx, ny);
}
}
⭐️广搜(BFS)通用框架
与 DFS 不同,广度优先搜索(BFS)是一种按层推进的遍历方式。
它使用 队列(Queue) 来记录待访问的节点,先访问起点,再依次扩展到所有相邻节点,直到队列为空。
// 队列版 BFS 框架
private static final int[][] DIRS = {{-1,0},{1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}};
public static void bfs(int[][] grid, boolean[][] visited, int x, int y) {
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
Queue<int[]> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(new int[]{x, y});
visited[x][y] = true;
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
int[] cur = que.poll();
int curx = cur[0], cury = cur[1];
for (int[] dir : DIRS) {
int nx = curx + dir[0];
int ny = cury + dir[1];
// 越界判断
if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= n || ny >= m) continue;
// 如果是未访问的陆地,则入队
if (!visited[nx][ny] && grid[nx][ny] == 1) {
visited[nx][ny] = true;
que.offer(new int[]{nx, ny});
}
}
}
}
💬 关于终止条件
在 BFS 中,终止条件与 DFS 不同。
BFS 并不是通过“递归返回”来结束搜索,而是依赖于队列的出队入队机制。
只要队列为空,就说明当前连通块的所有节点都已经访问完毕,搜索自然终止。
在具体实现中,终止条件主要体现在两方面:
-
队列为空时停止循环:
while (!que.isEmpty()) { ... }表示当没有新的节点需要访问时,整块岛屿的遍历结束。
-
过滤无效节点:
在循环内部,通过越界判断和访问判断:if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= n || ny >= m) continue; if (!visited[nx][ny] && grid[nx][ny] == 1) { ... }保证只会将合法、未访问、且为陆地的节点加入队列。
这既是防止死循环的关键,也是 BFS 的“剪枝”策略。
💡 注意: 后续代码的
Solution类是按照 LeetCode(力扣) 的题解格式编写的。
也就是说,如果你在力扣上做题(例如「200. 岛屿数量」),可以 直接复制Solution类的代码 到编辑器中运行,不需要Main方法和输入读取部分。
而Main函数和输入输出(Scanner 读入)部分,是 卡码网的 ACM 模式 使用的。
一、岛屿计数(Medium)
1.对应题目
2.解题思路
题目要求每座岛屿只能由水平或垂直方向相连的陆地组成。
我们的核心思路是:
当在网格中遇到一个 尚未访问的陆地节点(1) 时,说明我们发现了一座新的岛屿,于是计数器+1。
接着,从该节点出发,使用 DFS 或 BFS 将与之相连的所有陆地都遍历并标记为“已访问”,确保这部分陆地不会被重复统计。
当再次遇到已经访问过的陆地或 水域(0) 时,直接跳过。
最终,计数器的值即为岛屿的总数量。
3.深搜代码
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt(); // 行数
int m = sc.nextInt(); // 列数
int[][] grid = new int[n][m];
// 读取矩阵
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
grid[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
Solution solution = new Solution();
// 力扣200. 岛屿数量
System.out.println(solution.numIslands(grid));
}
}
class Solution {
private static final int[][] DIRS = {{-1,0},{1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}};
public int numIslands(int[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[n][m];
int res = 0;
// 遍历整个矩阵
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
// 如果是陆地且未访问过,说明发现新岛屿
if (grid[i][j] == 1 && !visited[i][j]) {
res++;
dfs(grid, visited, i, j);
}
}
}
return res;
}
// 深度优先搜索,沉没当前岛屿
private void dfs(int[][] grid, boolean[][] visited, int x, int y) {
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
visited[x][y] = true; // 标记访问
for (int[] dir : DIRS) {
int nx = x + dir[0];
int ny = y + dir[1];
// 越界跳过
if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= n || ny >= m) continue;
// 递归访问未访问的陆地
if (grid[nx][ny] == 1 && !visited[nx][ny]) {
dfs(grid, visited, nx, ny);
}
}
}
}
4.广搜代码
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt(); // 行数
int m = sc.nextInt(); // 列数
int[][] grid = new int[n][m];
// 读取矩阵
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
grid[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
Solution solution = new Solution();
// 力扣200. 岛屿数量
System.out.println(solution.numIslands(grid));
}
}
class Solution {
private static final int[][] DIRS = {{-1,0},{1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}};
public int numIslands(int[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[n][m];
int res = 0;
// 遍历整个矩阵
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
// 如果是陆地且未访问过,说明发现新岛屿
if (grid[i][j] == 1 && !visited[i][j]) {
res++;
bfs(grid, visited, i, j);
}
}
}
return res;
}
// 广度优先搜索(BFS)版 —— 用队列层层扩散
public static void bfs(int[][] grid, boolean[][] visited, int x, int y) {
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
// 队列用于存储待访问的坐标
Queue<int[]> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(new int[]{x, y});
visited[x][y] = true; // 标记起点已访问
// 当队列不为空时,不断扩展四周的陆地
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
int[] cur = que.poll();
int curx = cur[0];
int cury = cur[1];
// 遍历四个方向(上、下、左、右)
for (int[] dir : DIRS) {
int nx = curx + dir[0];
int ny = cury + dir[1];
// 越界检查
if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= n || ny >= m) continue;
// 如果是陆地且未访问过,则入队
if (!visited[nx][ny] && grid[nx][ny] == 1) {
visited[nx][ny] = true; // 标记为已访问
que.offer(new int[]{nx, ny}); // 加入队列等待后续扩展
}
}
}
}
}
二、岛屿最大面积(Medium)
1.对应题目
卡码网(ACM模式):100. 最大岛屿的面积
LeetCode:695. 岛屿的最大面积
2.解题思路
题目要求计算网格中最大的岛屿面积,也就是由相连的陆地节点组成的最大连通块的大小。
我们的核心思路是:
当在网格中遇到一个 尚未访问的陆地节点(1) 时,就从该节点出发,通过 DFS 或 BFS 遍历整座岛屿,并统计当前岛屿的面积(即节点数)。
📌Tips:这里有两种统计当前岛屿面积的办法:
方案 1(推荐):让 dfs() / bfs() 返回面积(改void为int)
方案 2 :保留全局变量area,每次重置area(定义全局变量area,循环中每次重置area为0)
在遍历过程中,将访问过的陆地标记为“已访问”,避免重复计算。
遍历完成后,用一个变量维护全局最大值,每次更新当前岛屿面积的最大值。
最终,返回记录的最大面积即可。
3.深搜代码(例:方案二)
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt(); // 行数
int m = sc.nextInt(); // 列数
int[][] grid = new int[n][m];
// 读取矩阵
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
grid[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
Solution solution = new Solution();
// 力扣695. 岛屿的最大面积
System.out.println(solution.maxAreaOfIsland(grid));
}
}
class Solution {
// 四个方向:上、下、右、左
private static final int[][] DIRS = {{-1,0},{1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}};
private static int area;
public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[n][m];
int res = 0;
// 遍历整个矩阵
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
// 如果是陆地且未访问过,说明发现新岛屿
if (grid[i][j] == 1 && !visited[i][j]) {
area = 0; // 每次新的岛屿重置面积
dfs(grid, visited, i, j);
res = Math.max(res, area);
}
}
}
return res;
}
// 深度优先搜索,沉没当前岛屿
private void dfs(int[][] grid, boolean[][] visited, int x, int y) {
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
visited[x][y] = true; // 标记访问
area++;
for (int[] dir : DIRS) {
int nx = x + dir[0];
int ny = y + dir[1];
// 越界跳过
if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= n || ny >= m) continue;
// 递归访问未访问的陆地
if (grid[nx][ny] == 1 && !visited[nx][ny]) {
dfs(grid, visited, nx, ny);
}
}
}
}
4.广搜代码(例:方案一)
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt(); // 行数
int m = sc.nextInt(); // 列数
int[][] grid = new int[n][m];
// 读取矩阵
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
grid[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
Solution solution = new Solution();
// 力扣695. 岛屿的最大面积
System.out.println(solution.maxAreaOfIsland(grid));
}
}
class Solution {
// 四个方向:上、下、右、左
private static final int[][] DIRS = {{-1,0},{1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}};
public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[n][m];
int res = 0;
// 遍历整个矩阵
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
// 如果是陆地且未访问过,说明发现新岛屿
if (grid[i][j] == 1 && !visited[i][j]) {
// 返回岛屿面积
int area = bfs(grid, visited, i, j);
res = Math.max(res, area);
}
}
}
return res;
}
// 广度优先搜索(BFS)版 —— 用队列层层扩散
public static int bfs(int[][] grid, boolean[][] visited, int x, int y) {
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
int area = 0;
// 队列用于存储待访问的坐标
Queue<int[]> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(new int[]{x, y});
visited[x][y] = true; // 标记起点已访问
// 当队列不为空时,不断扩展四周的陆地
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
int[] cur = que.poll();
area++;
int curx = cur[0];
int cury = cur[1];
// 遍历四个方向(上、下、左、右)
for (int[] dir : DIRS) {
int nx = curx + dir[0];
int ny = cury + dir[1];
// 越界检查
if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= n || ny >= m) continue;
// 如果是陆地且未访问过,则入队
if (!visited[nx][ny] && grid[nx][ny] == 1) {
visited[nx][ny] = true; // 标记为已访问
que.offer(new int[]{nx, ny}); // 加入队列等待后续扩展
}
}
}
return area;
}
}
三、封闭岛屿问题(Medium)
1.对应题目
卡码网(ACM模式):101. 孤岛的总面积
LeetCode:1020. 飞地的数量
LeetCode:1254. 统计封闭岛屿的数目
本解题代码均按照求封闭岛屿总面积(卡码网101.孤岛的总面积)给出。
求封闭岛屿数目做法类似,此处不做讨论。
2.解题思路
这类题要求找出被水完全包围的“封闭岛屿”,即那些 不与边界相连 的陆地区域。
核心思路如下:
首先,我们要区分“开放岛屿”和“封闭岛屿”。凡是 与网格边界相连的陆地,都不可能是封闭岛屿。
因此,第一步可以先从边界出发,使用 DFS/BFS 将所有与边界相连的陆地全部标记掉。
接着,再次遍历整个网格:
-
每当遇到 未被访问的陆地节点(1),就说明这是一座封闭岛屿;
-
可以进一步计算其面积,或者仅计数 +1;
-
同时标记这块岛屿的所有陆地为海水(grid[x][y] = 0),避免重复统计。
最终,计数器 或总面积值 就是封闭岛屿的数量或面积。
3.深搜代码
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt(); // 行数
int m = sc.nextInt(); // 列数
int[][] grid = new int[n][m];
// 读取矩阵
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
grid[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
Solution solution = new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.closedIsland(grid));
}
}
class Solution {
// 四个方向:上、下、右、左
private static final int[][] DIRS = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
public int closedIsland(int[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (grid[i][0] == 1) {
dfs(grid, i, 0);
}
if (grid[i][m - 1] == 1) {
dfs(grid, i, m - 1);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (grid[0][i] == 1) {
dfs(grid, 0, i);
}
if (grid[n - 1][i] == 1) {
dfs(grid, n - 1, i);
}
}
int res = 0;
// 遍历整个矩阵
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
res++;
}
}
}
return res;
}
private void dfs(int[][] grid, int x, int y) {
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
grid[x][y] = 0; // 标记
for (int[] dir : DIRS) {
int nx = x + dir[0];
int ny = y + dir[1];
if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= n || ny >= m) continue;
if (grid[nx][ny] == 1) {
dfs(grid, nx, ny);
}
}
}
}
4.广搜代码
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt(); // 行数
int m = sc.nextInt(); // 列数
int[][] grid = new int[n][m];
// 读取矩阵
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
grid[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
Solution solution = new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.closedIsland(grid));
}
}
class Solution {
// 四个方向:上、下、右、左
private static final int[][] DIRS = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
public int closedIsland(int[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (grid[i][0] == 1) {
bfs(grid, i, 0);
}
if (grid[i][m - 1] == 1) {
bfs(grid, i, m - 1);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (grid[0][i] == 1) {
bfs(grid, 0, i);
}
if (grid[n - 1][i] == 1) {
bfs(grid, n - 1, i);
}
}
int res = 0;
// 遍历整个矩阵
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
res++;
}
}
}
return res;
}
public static void bfs(int[][] grid, int x, int y) {
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
// 队列用于存储待访问的坐标
Queue<int[]> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(new int[]{x, y});
grid[x][y] = 0; // 标记
// 当队列不为空时,不断扩展四周的陆地
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
int[] cur = que.poll();
int curx = cur[0];
int cury = cur[1];
for (int[] dir : DIRS) {
int nx = curx + dir[0];
int ny = cury + dir[1];
if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= n || ny >= m) continue;
if (grid[nx][ny] == 1) {
grid[nx][ny] = 0;
que.offer(new int[]{nx, ny}); // 加入队列等待后续扩展
}
}
}
}
}
四、太平洋大西洋水流问题(Medium)
1.对应题目
卡码网(ACM模式):103. 高山流水
LeetCode:417. 太平洋大西洋水流问题
本题所给代码输出格式与力扣保持一致(List<List< Integer >> res)
2.解题思路
题目要求水流只能从高度高的格子流向相邻高度 不高于自己的格子(上下左右四个方向)。
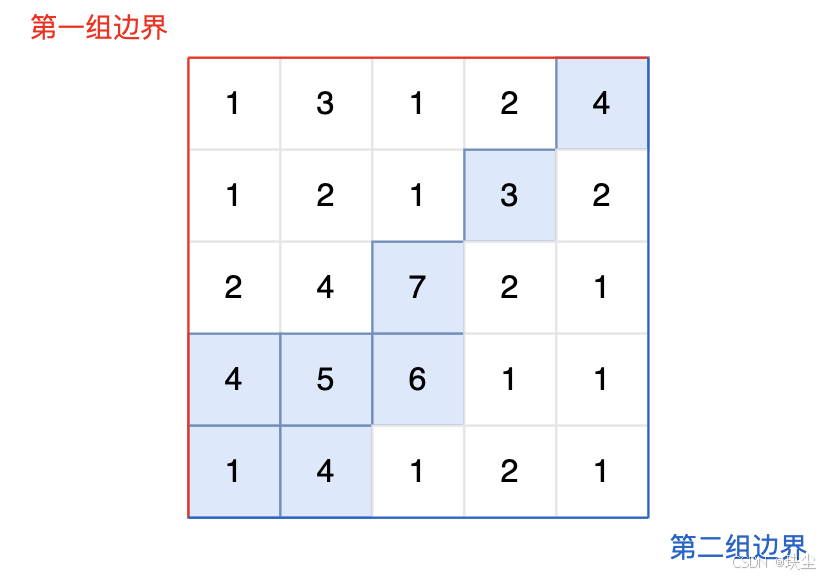
一个比较直观但低效的做法是:遍历每一个网格单元,然后分别判断该单元是否可以同时流向太平洋和大西洋。
这种方法看似简单,但代价很高:遍历每个节点需要一次 DFS/BFS,每次 DFS 的时间复杂度是 O(m x n),整个网格有 m x n 个节点,最终时间复杂度达到 O((m x n)^2),也就是四次方级别,效率非常低。
为了优化,我们可以换一个思路:从边界出发“逆向搜索”水流。
具体做法是:分别从太平洋和大西洋的边界节点出发,沿着高度递增或相等的方向遍历可到达的陆地,并把遍历过的节点标记起来。
最终,两个方向都被标记的节点,就是既能流向太平洋,又能流向大西洋的格子。
这种做法只需要对每个格子访问一次,时间复杂度大幅降低到 O(m x n),既直观又高效。
核心思路如下:
-
从边界出发,逆向搜索水流方向
- 将太平洋边界(左边界和上边界)作为起点,使用 DFS 或 BFS 遍历所有可以流向太平洋的格子,并标记这些格子;
- 将大西洋边界(右边界和下边界)作为起点,使用 DFS 或 BFS 遍历所有可以流向大西洋的格子,并标记这些格子。
-
判断同时可达的格子
- 遍历整个网格,找出那些 在太平洋可达集合和大西洋可达集合中都出现的格子,它们就是可以同时流向两个大洋的格子。
-
核心操作
- DFS/BFS 遍历过程中,只从当前格子流向 高度不低于当前格子的相邻格子,保证水流方向正确;
- 使用两个访问矩阵分别记录太平洋和大西洋的可达格子,避免重复遍历。
最终,将所有同时可达的格子坐标收集起来,返回结果即可。
3.深搜代码
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt(); // 行数
int m = sc.nextInt(); // 列数
int[][] grid = new int[n][m];
// 读取矩阵
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
grid[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
Solution solution = new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.pacificAtlantic(grid));
}
}
class Solution {
private static final int[][] DIRS = {{-1,0},{1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}};
public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] heights) {
int m = heights.length;
int n = heights[0].length;
boolean[][] pacific = new boolean[m][n];
boolean[][] atlantic = new boolean[m][n];
// 从左右两边开始 DFS
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
dfs(heights, pacific, i, 0); // 太平洋左边
dfs(heights, atlantic, i, n - 1); // 大西洋右边
}
// 从上下两边开始 DFS
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
dfs(heights, pacific, 0, j); // 太平洋上边
dfs(heights, atlantic, m - 1, j); // 大西洋下边
}
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j]) {
// System.out.println(i + " " + j);
res.add(Arrays.asList(i, j));
}
}
}
return res;
}
private void dfs(int[][] grid, boolean[][] visited, int x, int y) {
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
visited[x][y] = true;
for (int[] dir : DIRS) {
int nx = x + dir[0];
int ny = y + dir[1];
if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= m || ny >= n) continue;
// 反向流动条件:只能从低往高或相等流
if (!visited[nx][ny] && grid[nx][ny] >= grid[x][y]) {
dfs(grid, visited, nx, ny);
}
}
}
}
4.广搜代码
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt(); // 行数
int m = sc.nextInt(); // 列数
int[][] grid = new int[n][m];
// 读取矩阵
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
grid[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
Solution solution = new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.pacificAtlantic(grid));
}
}
class Solution {
private static final int[][] DIRS = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] heights) {
int m = heights.length;
int n = heights[0].length;
boolean[][] pacific = new boolean[m][n];
boolean[][] atlantic = new boolean[m][n];
// 从左右两边开始 DFS
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
bfs(heights, pacific, i, 0); // 太平洋左边
bfs(heights, atlantic, i, n - 1); // 大西洋右边
}
// 从上下两边开始 DFS
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
bfs(heights, pacific, 0, j); // 太平洋上边
bfs(heights, atlantic, m - 1, j); // 大西洋下边
}
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j]) {
// System.out.println(i + " " + j);
res.add(Arrays.asList(i, j));
}
}
}
return res;
}
private void bfs(int[][] grid, boolean[][] visited, int x, int y) {
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
// 队列用于存储待访问的坐标
Queue<int[]> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(new int[]{x, y});
visited[x][y] = true; // 标记起点已访问
// 当队列不为空时,不断扩展四周的陆地
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
int[] cur = que.poll();
int curx = cur[0];
int cury = cur[1];
// 遍历四个方向(上、下、左、右)
for (int[] dir : DIRS) {
int nx = curx + dir[0];
int ny = cury + dir[1];
if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= n || ny >= m) continue;
// 核心判断条件:只能逆流而上(下一个格子高度 >= 当前格子高度)
if (!visited[nx][ny] && grid[nx][ny] >= grid[curx][cury]) {
visited[nx][ny] = true; // 标记为已访问
que.offer(new int[]{nx, ny}); // 加入队列等待后续扩展
}
}
}
}
}
五、最大人工岛问题(Hard)
1.对应题目
卡码网(ACM模式):104. 建造最大岛屿
LeetCode:827. 最大人工岛
2.解题思路
这道题要求在一个由 0 和 1 组成的方阵中,最多将一个 0 改成 1,使得岛屿的面积最大。一个直接的思路是对每个 0 都尝试改成 1,然后重新计算整个矩阵中最大的岛屿面积。这样做的时间复杂度为 O(n⁴),因为每次都需要一次完整的 DFS 或 BFS 去计算岛屿面积,而矩阵又有 n² 个格子。这种方法在数据量较大时会超时。
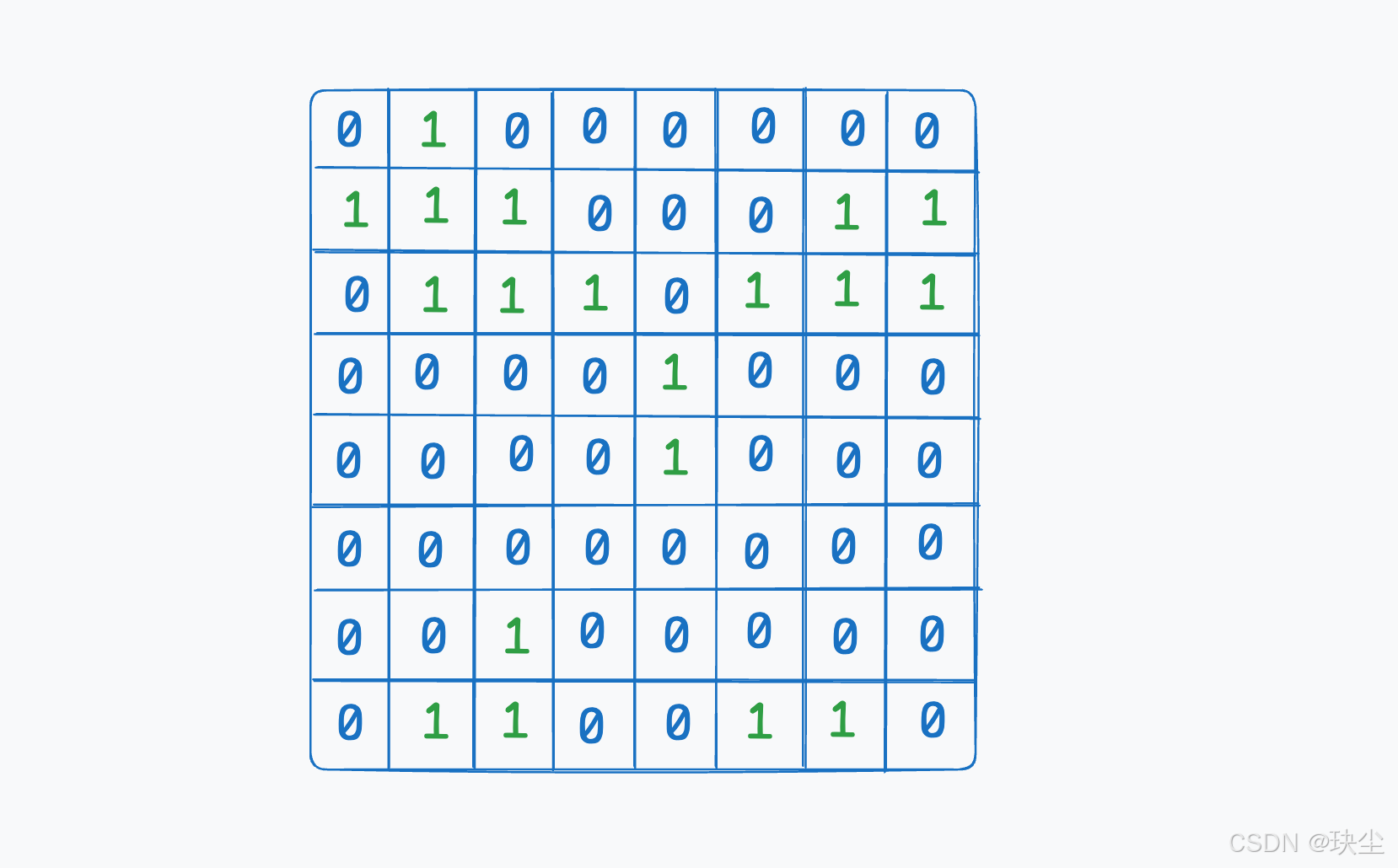
为了优化,我们可以换个角度思考。其实每个岛屿的面积是固定的,不需要重复计算。 因此,我们可以在一开始就遍历整个矩阵,用 DFS 或 BFS 把所有的岛屿都“编号”起来,并记录每个岛屿的面积。为了区分不同的岛屿,我们可以用 islandId 从 2 开始编号(因为矩阵中原本只有 0 和 1)。同时使用一个哈希表来保存 编号(key) 与 岛屿面积(value) 的映射关系。这样,每个格子所属的岛屿信息就被记录下来了。
// DFS 标记所有岛屿,并计算面积
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 0) isAllGrid = false;
if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1) {
count = 0;
dfs(grid, visited, i, j, mark);
gridNum.put(mark, count);
mark++; // 编号+1
}
}
}
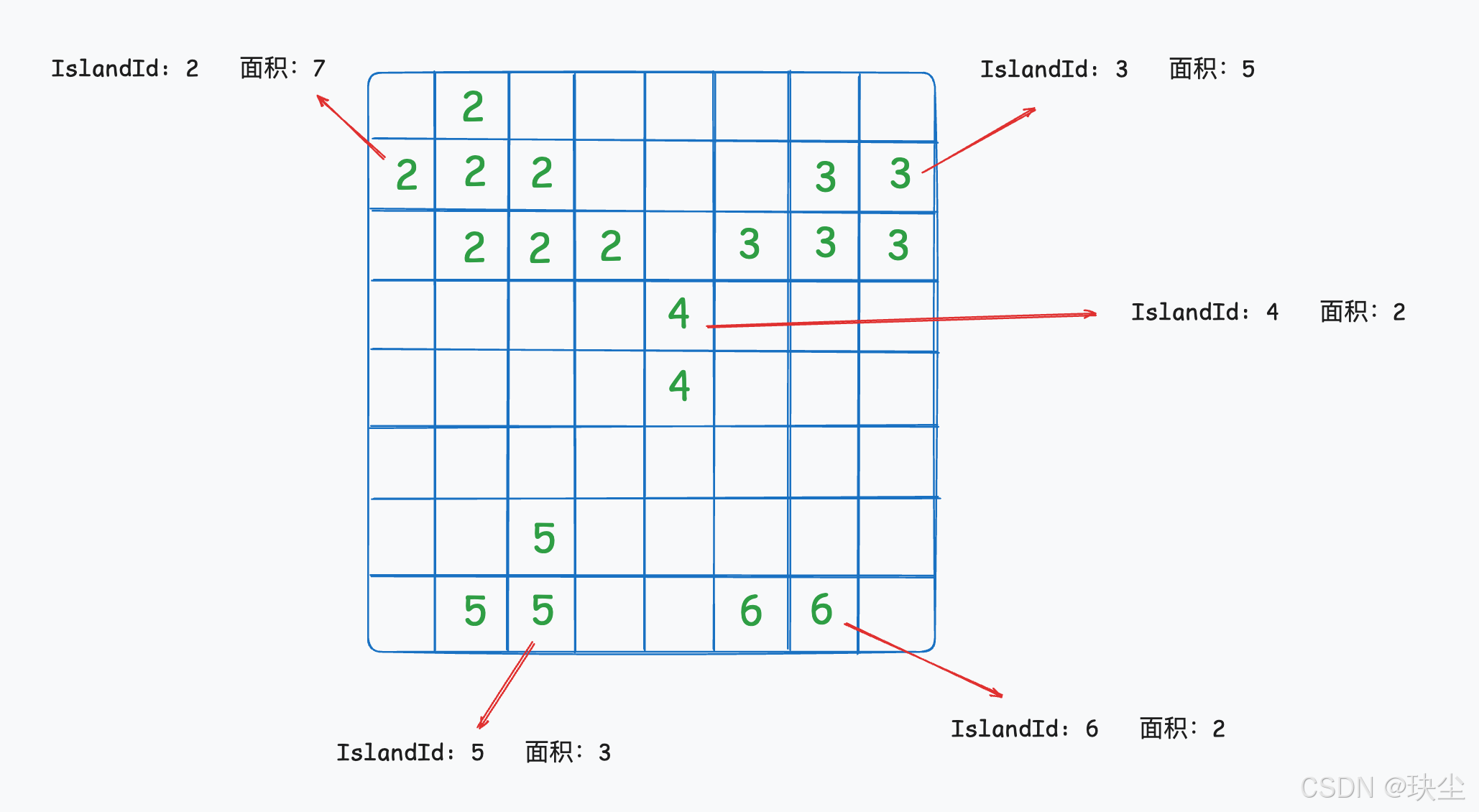
接下来,我们只需要再遍历一遍矩阵,找到每一个 0 的位置,查看它四个方向上相邻的格子。
如果相邻的格子属于不同的岛屿,就将这些岛屿的面积相加,再加上当前这个 0 自己的面积(即 +1),得到通过改变这个 0 所能形成的新岛屿的总面积。为了避免重复统计相同的岛屿,可以使用一个 Set 来去重。对所有的 0 都进行这样的计算,记录其中的最大值。
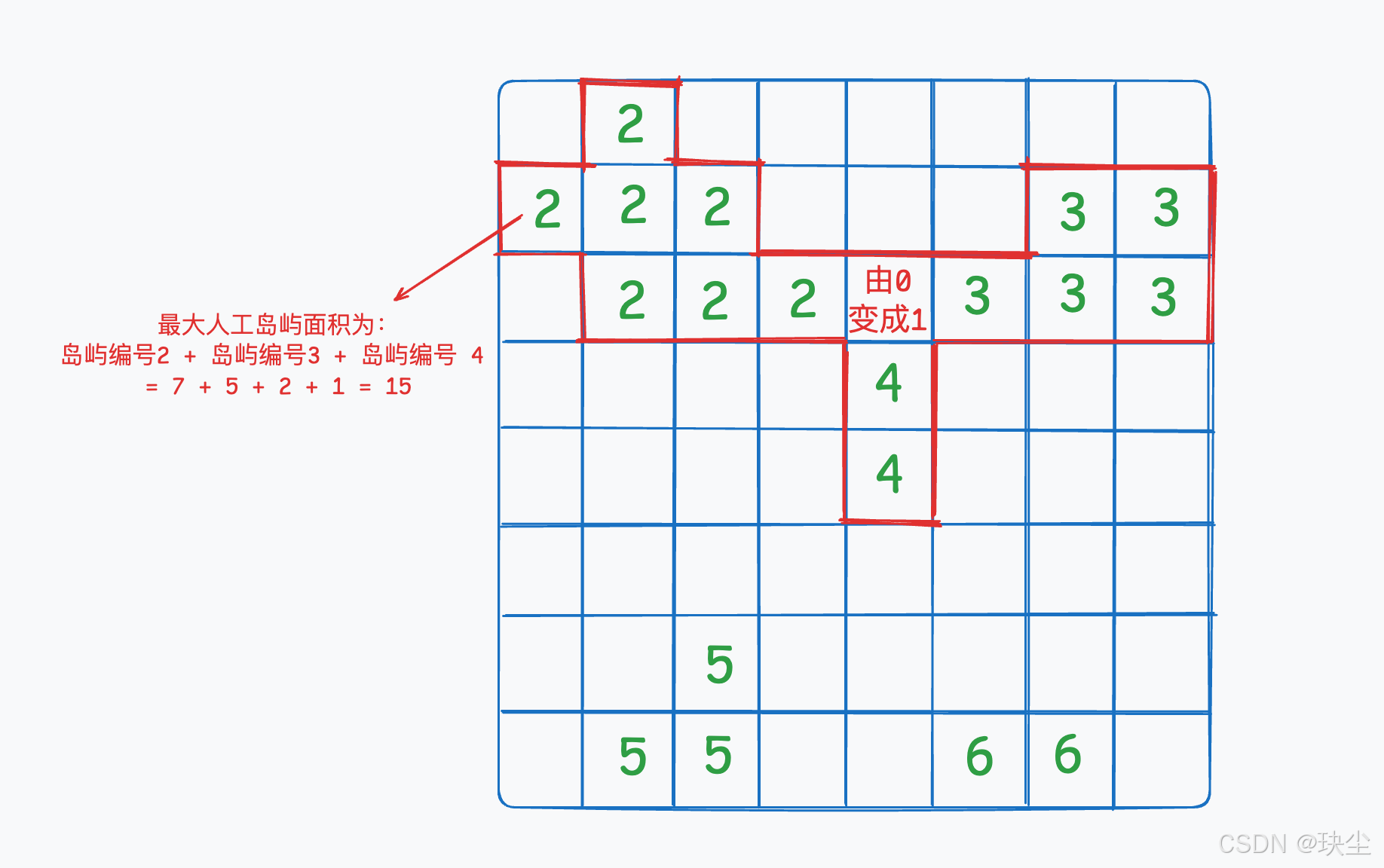
最后,还要考虑一些特殊情况:如果整个矩阵都是 1,那么结果就是矩阵的总面积;如果全是 0,则只能造出一个面积为 1 的岛屿。
通过这种方法,我们将原来的暴力枚举优化为 O(n²) 的时间复杂度。整个过程只需两次遍历矩阵,第一次标号并计算面积,第二次尝试合并相邻岛屿。这个思路本质上是通过 “空间换时间”,利用岛屿编号和面积缓存来避免重复搜索,同时也体现了图搜索中记忆化的思想。
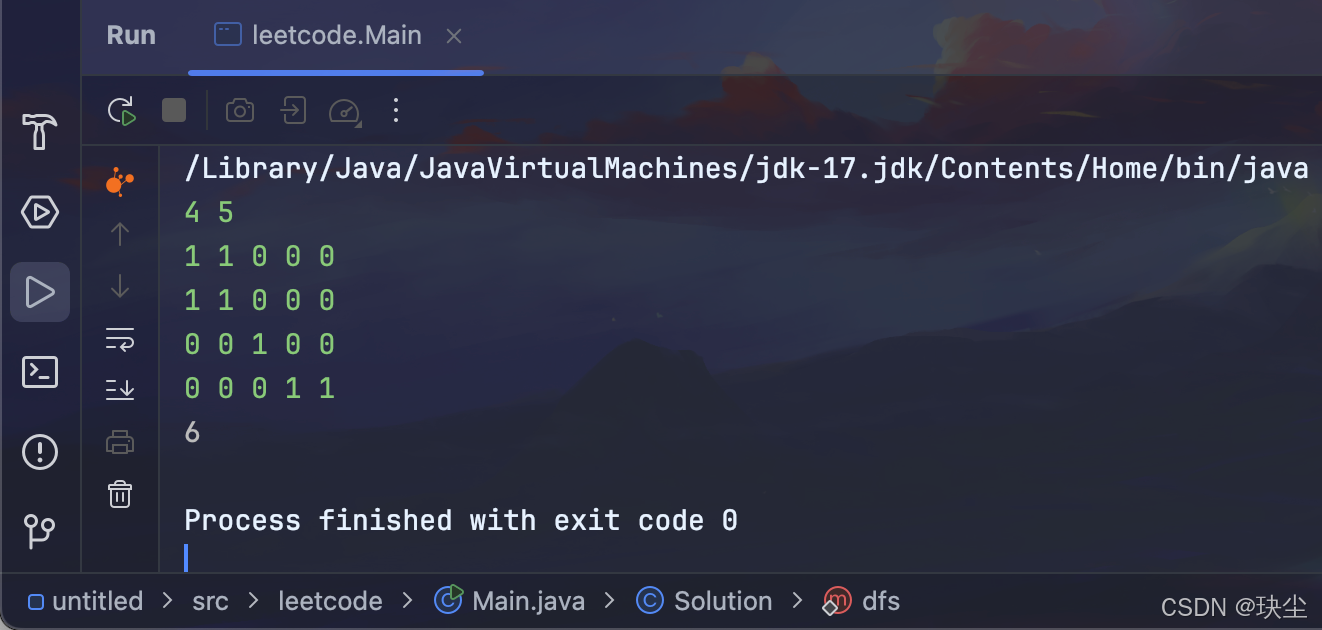
3.深搜代码
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int m = sc.nextInt();
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[][] grid = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
grid[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
Solution solution = new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.largestIsland(grid));
}
}
class Solution {
private static int count;
private static final int[][] DIRS = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};
public int largestIsland(int[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
boolean isAllGrid = true;
int mark = 2;
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[n][m];
Map<Integer, Integer> gridNum = new HashMap<>();
// DFS 标记所有岛屿,并计算面积
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 0) isAllGrid = false;
if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1) {
count = 0;
dfs(grid, visited, i, j, mark);
gridNum.put(mark, count);
mark++; // 编号+1
}
}
}
// 如果整张图全是陆地,直接返回全部面积
if (isAllGrid) return n * m;
// 尝试把某个 0 变成 1,计算连接后的最大面积
int result = 0;
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
int area = 1;
set.clear();
if (grid[i][j] == 0) {
for (int[] dir : DIRS) {
int nx = i + dir[0];
int ny = j + dir[1];
if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= n || ny >= m) continue;
int id = grid[nx][ny];
if (set.contains(id)) continue;
area += gridNum.getOrDefault(id, 0);
set.add(id);
}
result = Math.max(result, area);
}
}
}
return result;
}
private static void dfs(int[][] grid, boolean[][] visited, int x, int y, int mark) {
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
visited[x][y] = true;
grid[x][y] = mark; // 给陆地打上岛屿编号
count++;
for (int[] d : DIRS) {
int nx = x + d[0];
int ny = y + d[1];
if (nx < 0 || nx >= n || ny < 0 || ny >= m) continue;
if(!visited[nx][ny] && grid[nx][ny] == 1) {
dfs(grid, visited, nx, ny, mark);
}
}
}
}
4.广搜代码
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int m = sc.nextInt();
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[][] grid = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
grid[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
Solution solution = new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.largestIsland(grid));
}
}
class Solution {
private static int count;
private static final int[][] DIRS = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};
public int largestIsland(int[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
boolean isAllGrid = true;
int mark = 2;
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[n][m];
Map<Integer, Integer> gridNum = new HashMap<>();
// BFS 标记所有岛屿,并计算面积
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 0) isAllGrid = false;
if (!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j] == 1) {
count = 0;
bfs(grid, visited, i, j, mark);
gridNum.put(mark, count);
mark++; // 编号+1
}
}
}
// 如果整张图全是陆地,直接返回全部面积
if (isAllGrid) return n * m;
// 尝试把某个 0 变成 1,计算连接后的最大面积
int result = 0;
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
int area = 1;
set.clear();
if (grid[i][j] == 0) {
for (int[] dir : DIRS) {
int nx = i + dir[0];
int ny = j + dir[1];
if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= n || ny >= m) continue;
int id = grid[nx][ny];
if (set.contains(id)) continue;
area += gridNum.getOrDefault(id, 0);
set.add(id);
}
result = Math.max(result, area);
}
}
}
return result;
}
private void bfs(int[][] grid, boolean[][] visited, int x, int y, int mark) {
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
Queue<int[]> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(new int[]{x, y});
visited[x][y] = true;
grid[x][y] = mark;
count++;
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
int[] cur = que.poll();
int curx = cur[0];
int cury = cur[1];
for (int[] dir : DIRS) {
int nx = curx + dir[0];
int ny = cury + dir[1];
if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= n || ny >= m) continue;
if (!visited[nx][ny] && grid[nx][ny] == 1) {
visited[nx][ny] = true;
grid[nx][ny] = mark;
count++;
que.offer(new int[]{nx, ny});
}
}
}
}
}
六、岛屿周长问题(Easy)
1.对应题目
卡码网(ACM模式):106. 海岸线计算
LeetCode:463. 岛屿的周长
2. 解题思路
虽然大多数岛屿类问题都需要用到 DFS 或 BFS 来进行遍历,但这道题并不需要。为了打破思维定势,这道题正是一个考察模拟与计数逻辑的经典例子。
这里我们可以从两种角度来思考:
解法一:边界判断法
-
我们遍历整个网格,当遇到陆地格子(值为 1)时,检查它的上下左右四个方向。
-
如果某个方向越界或该方向是水域(值为 0),就说明这一侧形成了一条岛屿边界。
-
我们将每个陆地格子对外暴露的边数累加起来,最终得到整个岛屿的周长。
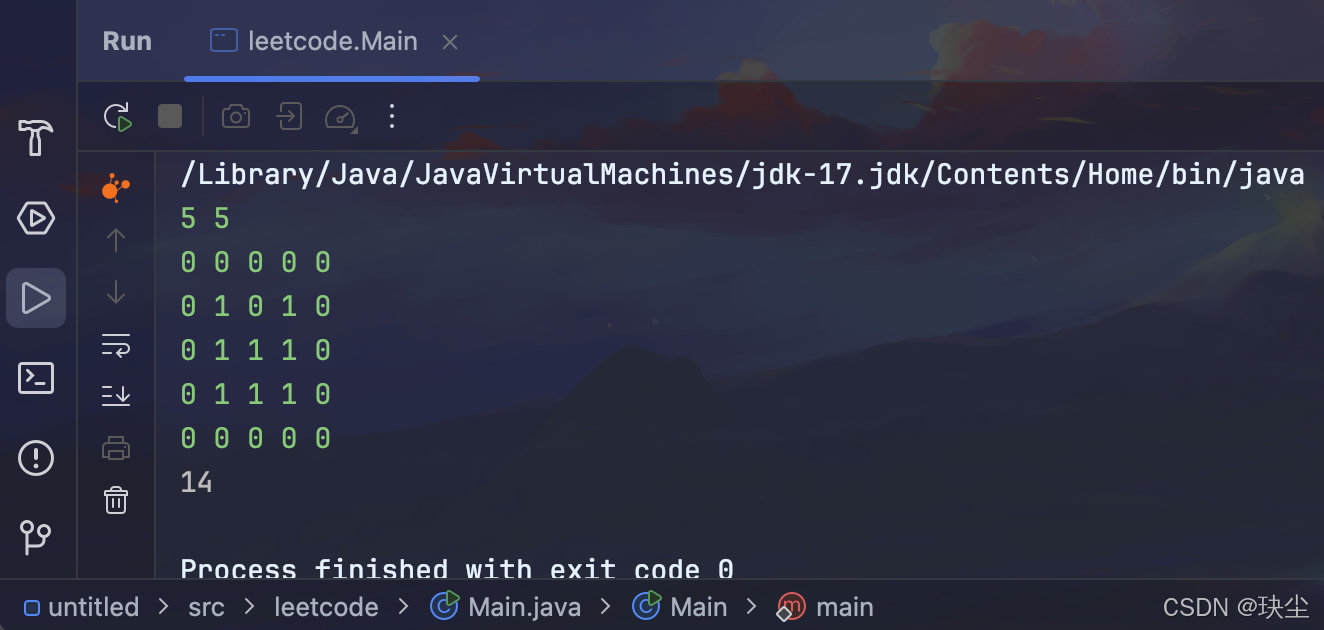
解法二:相邻消边法
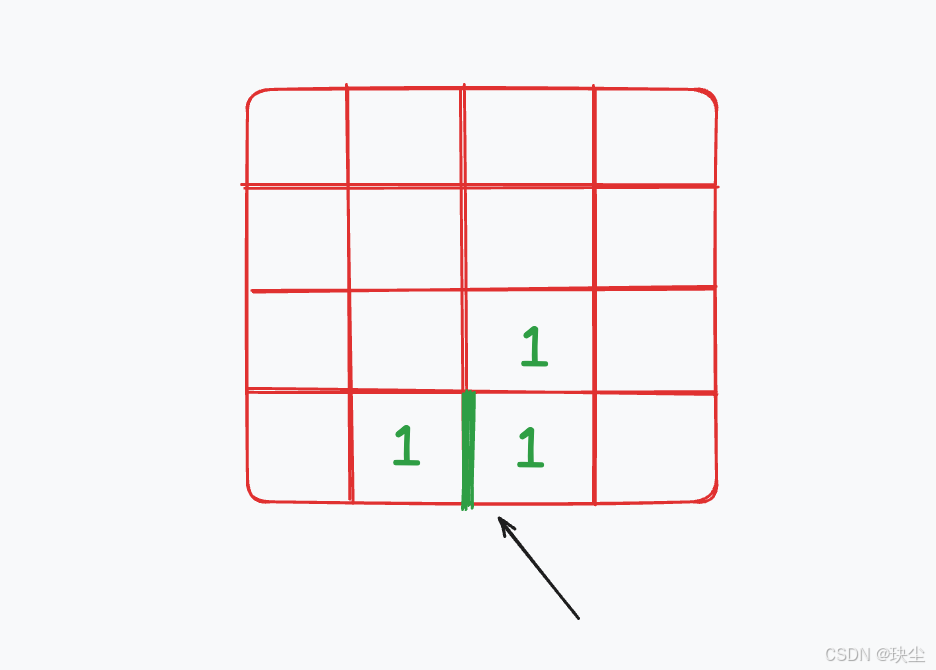
换个角度看,每块陆地本身有 4 条边,如果我们直接把所有陆地格子的边数相加,得到的就是“未合并”的总边数。
但是,如果两块陆地相邻,它们会共享一条边,这条边在两次统计中都被算进去了,因此需要减去 2。
我们可以先统计陆地的总数量 count,再统计相邻陆地对的数量 cover,最终结果为:
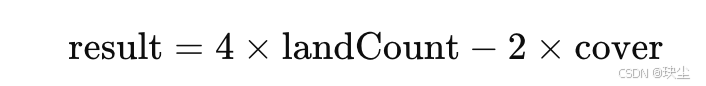
3.解法一代码
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
private static final int[][] DIRS = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int m = sc.nextInt();
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[][] grid = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
grid[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
System.out.println(islandPerimeter(grid));
}
public static int islandPerimeter(int[][] grid) {
// 遍历上下左右四个方向,碰到边界或者水就++
int res = 0;
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
for (int[] dir : DIRS) {
int nx = i + dir[0];
int ny = j + dir[1];
if (nx < 0 || ny < 0 || nx >= n || ny >= m || grid[nx][ny] == 0) {
res++;
}
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
4.解法二代码
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int m = sc.nextInt();
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[][] grid = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
grid[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
Solution solution = new Solution();
System.out.println(solution.islandPerimeter(grid));
}
}
class Solution {
public static int islandPerimeter(int[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length;
int m = grid[0].length;
int count = 0; // 陆地数量
int cover = 0; // 相邻陆地对数量(共享边)
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
count++;
// 统计下边相邻的陆地
if (i + 1 < n && grid[i + 1][j] == 1) cover++;
// 统计右边相邻的陆地
if (j + 1 < m && grid[i][j + 1] == 1) cover++;
}
}
}
// 每块陆地有4条边,每一对相邻陆地共享2条边
return count * 4 - cover * 2;
}
}
小结
写到这里,整个“岛屿系列”也算告一段落了。回过头看,这类题虽然换了各种花样——有的让我们数岛屿、有的让我们求最大面积、有的让我们算周长——但核心思路其实是一脉相承的。它们都在考察我们对网格遍历的掌握:怎么去“走”完整个地图、怎么处理访问标记、怎么避免重复、又如何把问题拆解成一个个独立的小块。
在这个过程中,DFS、BFS这些看似抽象的算法工具,慢慢从“背公式”变成了“手中武器”。你会发现,算法并不只是枯燥的技巧,而是一种思考问题的方式——看到复杂的局面,能先找规律、再拆结构、最后下手实现。
也许刚开始写岛屿题的时候,你还会觉得有点绕、有点烦,但当你真正理解那种“陆地连成片”的逻辑后,就会发现它其实挺有意思的——每一次递归、每一次搜索,都是在让程序一点点“看清世界的边界”。
岛屿题写多了,算法思维也就渐渐清晰了。也许这就是刷题最有成就感的地方:
不是你记住了多少套路,而是有一天,你突然意识到——原来自己真的会思考问题了。 🌊✨





















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








