实验目的及要求:
(1)进程调度是处理机管理的核心内容。
(2)通过本实验可以加深理解有关进程控制块、进程队列的概念,并体会和了解优先数和时间片轮转调度算法的具体实施办法。
(3)本实验要求用C语言编写和调试一个简单的进程调度程序。
实验内容
(1)设计进程控制块PCB表结构,分别适用于优先数调度算法和循环轮转调度算法。
(2)建立进程就绪队列。对算法编制子程序。
(3)编制进程调度算法:①高优先权调度;②循环轮转调度
这里分析高优先权算法
代码部分:
#include "stdio.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <conio.h>
#define getpch(type) (type*)malloc(sizeof(type))
#define NULL 0
struct pcb { /* 定义进程控制块PCB */
char name[10];
char state;
int super;
int ntime;
int rtime;
struct pcb* link;
}*ready=NULL,*p; //ready ,p 为全局变量;
typedef struct pcb PCB;
void sort() /* 建立对进程进行优先级排列函数*/
{
PCB *first, *second;
int insert=0;
// 如果优先级最大,则插入队首,否则比较优先级插入适当位置。
if((ready==NULL)||((p->super)>(ready->super))) /*优先级最大者,插入队首*/
{
p->link=ready;
ready=p;
}
else /* 进程比较优先级,插入适当的位置中*/
{
first=ready;
second=first->link;
while(second!=NULL)
{
if((p->super)>(second->super)) /*若插入进程比当前进程优先数大*/
{ /*插入到当前进程前面*/
p->link=second;
first->link=p;
second=NULL; /*结束循环*/
insert=1;
}
else /* 若插入进程比当前进程优先数小,则first指针和second指针后移,继续比较。*/
{
first=first->link;
second=second->link;
}
}
if(insert==0) first->link=p; /*插入进程优先数最低,则插入到队尾*/
}
}
void input() /* 建立进程控制块函数*/
{
int i,num;
//clrscr(); /*清屏*/
printf("\n 请输入进程数量:");
scanf("%d",&num);
for(i=0;i<num;i++)
{
printf("\n 进程号No.%d:\n",i);
p=getpch(PCB);
printf("\n 输入进程名:");
scanf("%s",p->name);
printf("\n 输入进程优先数:");
scanf("%d",&p->super);
printf("\n 输入进程运行时间:");
scanf("%d",&p->ntime);
printf("\n");
p->rtime=0;p->state='w';
p->link=NULL;
sort(); /* 调用sort函数,将创建的进程插入到就绪队列中*/
}
}
int space() /*统计就绪队列长度*/
{
int l=0; PCB* pr=ready;
while(pr!=NULL)
{
l++;
pr=pr->link;
}
return(l);
}
void disp(PCB * pr) /*建立进程显示函数,用于显示当前进程*/
{
printf("\n qname \t state \t super \t ndtime \t runtime \n");
printf("|%s\t",pr->name);
printf("|%c\t",pr->state);
printf("|%d\t",pr->super);
printf("|%d\t",pr->ntime);
printf("|%d\t",pr->rtime);
printf("\n");
}
void check() /* 建立进程查看函数 */
{
PCB* pr;
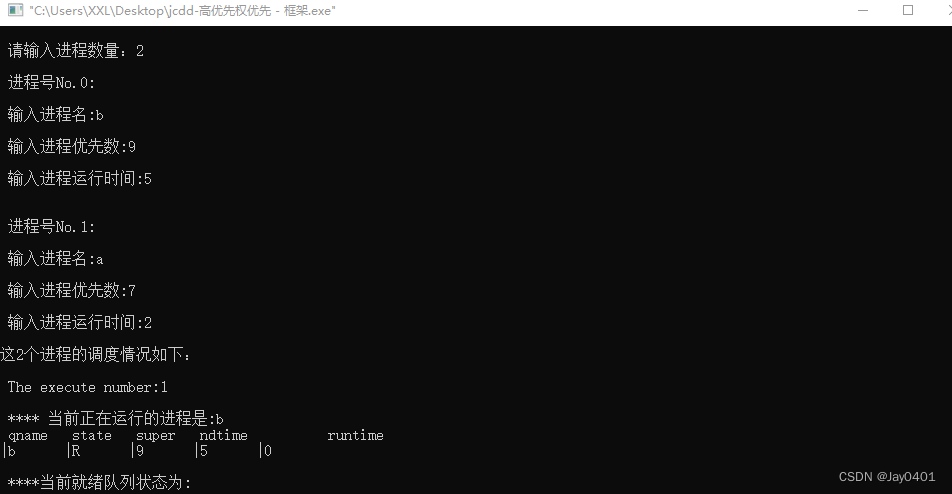
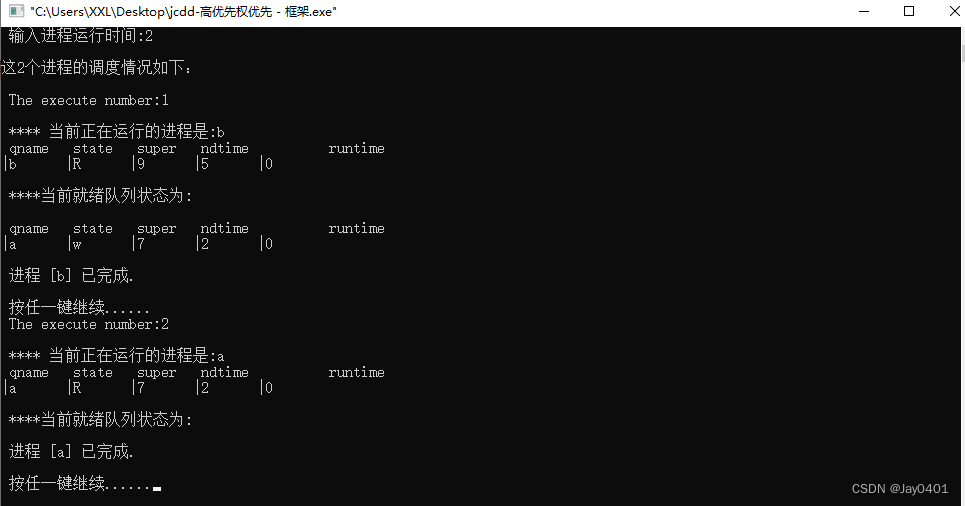
printf("\n **** 当前正在运行的进程是:%s",p->name); /*显示当前运行进程*/
disp(p);
pr=ready;
printf("\n ****当前就绪队列状态为:\n"); /*显示就绪队列状态*/
while(pr!=NULL)
{
disp(pr);
pr=pr->link;
}
}
void destroy() /*建立进程撤消函数(进程运行结束,撤消进程)*/
{
printf("\n 进程 [%s] 已完成.\n",p->name);
free(p);
}
void running() /*执行进程后撤销*/
{
(p->rtime)=p->ntime;
destroy(); /* 调用destroy函数*/
}
int main() /*主函数*/
{
int len,h=0;
char ch;
input();/* 调用建立进程控制块函数,创建就绪队列*/
len=space(); /* 获取就绪队列长度*/
printf("这%d个进程的调度情况如下:\n",len) ;
while((len!=0)&&(ready!=NULL))
{
//ch=getchar();
h++;
printf("\n The execute number:%d \n",h);
p=ready; /* 从就绪队列取出队首进程*/
ready=p->link;
p->link=NULL;
p->state='R';
check(); /* 调用进程查看函数,查看当前要运行的进程信息和就绪队列信息*/
running();
printf("\n 按任一键继续......");
ch=getchar();
}
printf("\n\n 所有进程已经完成.\n");
//ch=getchar();
}





















 1471
1471











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








