文章目录
选择排序
- 选择排序包括简单选择排序
- 堆排序
简单选择排序
-
和bubbleSort和相似
-
但是更加直观
-
设待排序列分为A/B区
- A区保存已经拍好的元素,这些元素全局有序(都处于
最终有序位置)上 - B区保存待排序元素
- A区保存已经拍好的元素,这些元素全局有序(都处于
-
每一趟排序都会为A区增加一个元素,相应的B区中的元素就减少一个
- 从B区计算出/确定出要加入A区的下一个元素的过程是越来越快
- 比较的次数越来越少
- 从B区计算出/确定出要加入A区的下一个元素的过程是越来越快
-
L[0] L[1] L[2] … L[i] … L[n-1] -
初始情况下,A区元素为0个
-
B区包含序列所有元素
-
第一趟排序开始,要计算出B区中的最小值min(1),将其调整到A区
- 可以表现为将L[0]用min(1)交换
- 那么B区的元素范围从L[1]~L[n-1]
-
第二趟开始
- 计算L[1]~L[n-1]中的最小元素min(2)
- 将它和L[1]交换位置,
-
…
-
直到B区中只剩下一个元素,排序结束
计算min(i)
-
设第i趟排序要计算的最小值为min(i)
-
设待排序区B的元素为B[i]~B[n-1]
-
假设
to_min=i-
to_min的值是单调不增的(或递减的) -
现在范围j=i+1,i+2,…,n-1内试图找到比初始值min(i)更小的元素,进行迭代更新
-
for (int j=i+1,j<n,j++){ if(B(min)>B[j]) { to_min=j } } -
当循环走完,就确定区间B的真正最小值min
-
-
交换
-
主要在于交换不是每次都是必须的,有时候,计算出来的min位置就是初始值位置,那么就不交换🎈
-
if(min!=i){ // swap(L[min],L[i]); swap(L,i,min)//交换数组L的L[i],L[min]两个元素 } -
经过上面的追加判断再交换,选择排序的元素移动次数可以尽可能少,
- 但是不优化的话,一定是3(n-1)
- 优化后可能少于这个数(但最坏情况下还是3(n-1)次)
- 每趟排序可能交换1次,也可能不交换
- 设swap需要移动3次元素
-
参考代码SelectSort
def swap(l, i, j):
#python支持成组赋值
l[i], l[j] = l[j], l[i]
def selectionSort(l):
"""简单选择排序,传入一个待排序列表即可完成排序(调用之)
Parameters
----------
l : list
需要排序的列表
Returns
-------
list
sorted list !
"""
for i in range(len(l)):
to_min=i
j=i+1#初始化变量指针(循环变量)
while(j<len(l)):
if(l[to_min]>l[j]):
to_min=j
j+=1
if(i!=to_min):
swap(l,i,to_min)
# l[to_min],l[i]=l[i],l[to_min]
print("sorted res:",l)
return l
性能分析
- 简单选择排序的一个好处在于移动元素的次数比较少
- 但是比较的次数和序列的长度有关却和顺序无关
- 无论如何都得比较 ∑ i = 1 n − 1 = n ( n − 1 ) 2 \sum\limits_{i=1}^{n-1}=\frac{n(n-1)}{2} i=1∑n−1=2n(n−1)次
稳定性
- 由于选择排序中调用了swap来交换待排序区的首元素wx和最小元素wm,有潜在的跳跃,可能导致不稳定
- 也就是,wx可能被换到wm的位置,而wx和wm中交换之前可能还存在若干个和wx相等的元素
- 比如2,2,1
- 第一趟排序,第L[0]=2和L[2]=1发生交换,导致前面的2被交换到后面去
- 得到1,2,2已经是最终结果的样子
堆排序
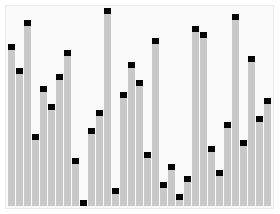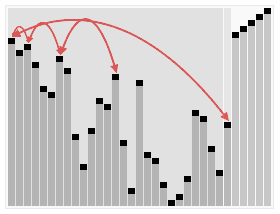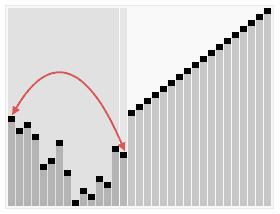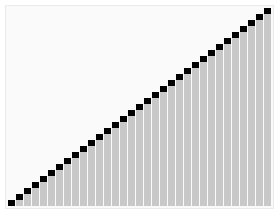
ref
-
In computer science, heapsort is a comparison-based sorting algorithm.
-
Heapsort can be thought of as an improved selection sort:
-
like selection sort, heapsort divides its input into a sorted and an unsorted region,
-
and it iteratively shrinks the unsorted region by extracting the largest element from it and inserting it into the sorted region.
-
Unlike selection sort, heapsort does not waste time with a linear-time scan of the unsorted region; rather, heap sort maintains the unsorted region in a heap data structure to more quickly find the largest element in each step.[1]
-
Although somewhat slower in practice on most machines than a well-implemented quicksort, it has the advantage of a more favorable worst-case O(n log n) runtime.
- 尽管在大多数机器上的实践中,它比实现良好的快速排序要慢一些
- 但是它的有点在于具有最好的渐进性能(最坏情况下,待排序序列问题规模很大)
-
Heapsort is an in-place algorithm, but it is not a stable sort.
- 堆排序也是原地排序,不稳定
-
堆排序简史
- Heapsort was invented by J. W. J. Williams in 1964.[2]
- This was also the birth of the heap, presented already by Williams as a useful data structure in its own right.[3] In the same year, Robert W. Floyd published an improved version that could sort an array in-place, continuing his earlier research into the treesort algorithm.[3]
堆(Heap)
- 堆是一个近似完全二叉树的结构,并同时满足堆的性质:
- 即子节点的键值或索引总是小于(或者大于)它的父节点
- 若是满足以下特性,即可称为堆:(更具体的划分)
- 给定堆中任意节点P和C,若P是C的母节点,那么P的值会小于等于(或大于等于)C的值
- 若母节点的值恒小于等于子节点的值,此堆称为最小堆(min heap);
- 反之,若母节点的值恒大于等于子节点的值,此堆称为最大堆(max heap)。
- 在堆中最顶端的那一个节点,称作根节点(root node),根节点本身没有母节点(parent node)
- 给定堆中任意节点P和C,若P是C的母节点,那么P的值会小于等于(或大于等于)C的值
存储堆
- 经常的,我们把堆用数组来存储
- 根据完全二叉树的性质:
-
第
i
个结点的孩子结点编号为
2
i
或者
2
i
+
1
,
而双亲结点则是
f
l
o
o
r
(
i
2
)
第i个结点的孩子结点编号为2i或者2i+1,而双亲结点则是floor(\frac{i}{2})
第i个结点的孩子结点编号为2i或者2i+1,而双亲结点则是floor(2i)
- 当然只有在结点i具有对应孩子/双亲是,以上的公式才是有效的
-
第
i
个结点的孩子结点编号为
2
i
或者
2
i
+
1
,
而双亲结点则是
f
l
o
o
r
(
i
2
)
第i个结点的孩子结点编号为2i或者2i+1,而双亲结点则是floor(\frac{i}{2})
第i个结点的孩子结点编号为2i或者2i+1,而双亲结点则是floor(2i)
- 根据堆的定义,可以发现,堆的任意一个分支结点作为根结点的子树,也是一个堆
- 简单的将,堆中的结点x总是大等于它的所有层孩子结点(后代)
- 这一点在调整堆的时候是一条重要性质,确保我们自底向上的调整是有效的
- 简单的将,堆中的结点x总是大等于它的所有层孩子结点(后代)
大根堆(max-heap)
-
n
个关键字序列
L
[
1
,
⋯
,
n
]
n个关键字序列L[1,\cdots,n]
n个关键字序列L[1,⋯,n]称为大根堆或者大顶堆(max-Heap)的条件包括:
-
L
(
i
)
⩾
L
(
2
i
)
且
L
(
i
)
⩾
L
(
2
i
+
1
)
L(i)\geqslant L(2i)且L(i) \geqslant L(2i+1)
L(i)⩾L(2i)且L(i)⩾L(2i+1)
- 更加优雅的写法: L ( i ) ⩾ m a x ( L ( 2 i ) , L ( 2 i + 1 ) ) L(i)\geqslant max(L(2i),L(2i+1)) L(i)⩾max(L(2i),L(2i+1))
-
L
(
i
)
⩾
L
(
2
i
)
且
L
(
i
)
⩾
L
(
2
i
+
1
)
L(i)\geqslant L(2i)且L(i) \geqslant L(2i+1)
L(i)⩾L(2i)且L(i)⩾L(2i+1)
- [外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-beh00mZe-1665624168544)(D:\repos\blogs\neep\408\ds\SortAlogrithms\assets\image-20221011184231272.png)]
- A max-heap viewed as (a) a binary tree and (b) an array. The number within the circle
at each node in the tree is the value stored at that node. The number above a node is the corresponding
index in the array. Above and below the array are lines showing parent-child relationships; parents
are always to the left of their children. The tree has height three; the node at index 4 (with value 8)
has height one.
- A max-heap viewed as (a) a binary tree and (b) an array. The number within the circle
小根堆(min-heap)
-
n
个关键字序列
L
[
1
,
⋯
,
n
]
n个关键字序列L[1,\cdots,n]
n个关键字序列L[1,⋯,n]称为小根堆(Heap)的条件包括:
- L ( i ) ⩽ m i n ( L ( 2 i ) , L ( 2 i + 1 ) ) L(i)\leqslant min(L(2i),L(2i+1)) L(i)⩽min(L(2i),L(2i+1))
对比完全二叉查找树
- 完全二叉查找树CBST中
- 结点i的和它的孩子结点间的关系(假设有两个孩子)
- L ( 2 i ) ⩽ L ( i ) ⩽ L ( 2 i + 1 ) L(2i)\leqslant L(i)\leqslant L(2i+1) L(2i)⩽L(i)⩽L(2i+1)
- 这是最明显的区别
排序过程
-
The heapsort algorithm can be divided into two parts.
-
In the first step
- a heap is built out of the data (see Binary heap § Building a heap).
- The heap is often placed in an array with the layout of a complete binary tree.
- The complete binary tree maps the binary tree structure into the array indices;
- each array index represents a node;
- the index of the node’s parent, left child branch, or right child branch are simple expressions.
- For a zero-based array, the root node is stored at index 0; if
iis the index of the current node, then
iParent(i) = floor((i-1) / 2) 向下取整. iLeftChild(i) = 2*i + 1 iRightChild(i) = 2*i + 2 -
In the second step,
- a sorted array is created by repeatedly removing the largest element from the heap (the root of the heap), and inserting it into the array.
- The heap is updated after each removal to maintain the heap property.
- Once all objects have been removed from the heap, the result is a sorted array.
-
Heapsort can be performed in place.
- The array can be split into two parts,
- the sorted array and
- the heap.
- The storage of heaps as arrays is diagrammed here.
- The heap’s invariant is preserved after each extraction, so the only cost is that of extraction.
- 堆的不变量在每次提取后都会保留下来,因此唯一的代价就是提取。
- The heap’s invariant is preserved after each extraction, so the only cost is that of extraction.
- The array can be split into two parts,
-
若以升序排序说明,把数组转换成最大堆(Max-Heap Heap),这是一种满足最大堆性质(Max-Heap Property)的二叉树:对于除了根之外的每个节点i, A[parent(i)] ≥ A[i]。
重复从最大堆取出数值最大的结点(把根结点和最后一个结点交换,把交换后的最后一个结点移出堆),并让残余的堆维持最大堆性质。
主要问题
- 建堆
- 建堆的过程可以理解为不断调整堆的过程
- 维护堆
i级堆的调整(自顶向下)
- 首先分析,调整堆的函数Heapify的工作环境/条件
- heapify函数被设计为,能够解决结点i的两个孩子 i . l i.l i.l和 i . R i.R i.R都是某个堆的根结点的情况
- 这种情况下,执行自顶向下的调整,当孩子的
m
a
x
(
i
.
l
.
k
e
y
,
i
.
r
.
k
e
y
)
>
i
.
k
e
y
max(i.l.key,i.r.key)> i.key
max(i.l.key,i.r.key)>i.key
- 或者说 m a x N o d e . k e y = m a x ( i . k e y , i . l . k e y , r . k e y ) > i . k e y maxNode.key=max(i.key,i.l.key,r.key)>i.key maxNode.key=max(i.key,i.l.key,r.key)>i.key的时候,最大值是i的某个孩子
- 较大的孩子就是maxNode,将其和i调换位置
- 如果i还是比它新的孩子结点(中的某个或全部)来的小,则继续上述的交换操作
- 直到满足堆的性质位置(最终一定会满足,因为最坏的情况是结点i沉到堆底了)
- 至于结点i的兄弟那边的子树则完全没有关系
- 当被调整的堆满足某些条件的时候,执行一次HeapAdjust,就可以使得以某个结点首的序列满足堆的性质
- 能处理这类情况的heapfiy足以应对maxHeap弹出最大元素(heapTop)或者说和堆底最后一个未排序元素交换位置)后执行的调整维护堆性质的操作
- 那么能不能处理其他问题
- 可以,只要正确处理调用关系,可以用来建立堆
- 但是一次调用肯定不行
- 可以,只要正确处理调用关系,可以用来建立堆
堆的调整算法(HeapAdjust/Heapify)
-
heapify:
-
对于大根堆,我们也叫max-heapify
-
In order to maintain the max-heap property, we call the procedure MAX-HEAPIFY.
- Its inputs are an array A and an index i into the array.
- When it is called, MAX-HEAPIFY assumes that the binary trees rooted at LEFT(i) and RIGHT(i) are max-
heaps - but that A[i] might be smaller than its children, thus violating the max-heap property.
- MAX-HEAPIFY lets the value at A[i] “float down” in the max-heap so that the subtree rooted at index i obeys the max-heap property.
-
-
现在,我们来实现这个堆的调整算法(使得它具有执行一次调整的能力)
def heapify(l, k=1, end=0):
"""由于完全二叉树的结点的双亲孩子结点编号计算公式依赖于编号的非0性
因此,这里的起点k必须是非0的
我们的数组第一个位置要空出来,(可以充当备份被筛选元素🎒)
Parameters
----------
l : 需要调整(heapify的序列)
🎈🎈不是任何序列都可以一次性就可以调整成功,
但是最坏的情况下,也只需要最多有限次调整就可以将任意的序列调整成堆
如果将一个序列理解成:非堆区A+堆区B,在序列中B区是后一个区域,通过反复调整,B区逐渐扩大
A区逐渐减小,直到B区包含了全序列的所有元素,那么建堆就完成了
除非是在堆排序中的弹出堆定(交换)引起的被破坏这类的情况,才可以一次调用就修复堆的性质
k : int, optional
_description_, by default 1
end : int, optional
对序列中的前end个元素(有意义的关键字)进行heapify调整, by default 0,如果不传值,那么内部会默认计算全部全l序列的长度
如果传值,那么将以传入的非0值为准
那么每次调用的heapify的范围是l[k]~l[end]
对于大根堆升序排序,默认总是让k=1即可,但是
end在heapSort中调用来调整堆的时候,取值从堆的最后一个分支结点编号逐渐减小2
Returns
-------
list
heapified list
"""
end= len(l)-1 if end==0 else end
# print("heapify len:",end)
bak_k = l[k]
i = 2 * k #左孩子节点
while (i <= end):
if (i < end): #如果结点i存在左右节点(都有)避免后续访问越界
#判断到底是左孩子大还是右孩子大
bigger_child_index = i #不是必须的,但是含义更加清晰
if (l[i] < l[i + 1]): #如果是右孩子大,那么将i更新为i+1;否则保持i不变(默认左孩子大)
bigger_child_index = i + 1
i += 1
#到此处,我们已经可以保证,此时的i指向的是是结点k的较大的孩子(下标)
# 现在再判断这个大孩子和他们的根结点bak_k到底谁比较大
if (bak_k >= l[i]):
#发现根结点k不比两个孩子小,不需进一步调整,结束
#这里我们用bak_k这一备份值,是因为后续我们要更新k,所以用bak_k才是正确的
break
else: #孩子结点根结点大,需要调整
l[k] = l[i] #将l[i]覆盖掉l[k]
# 更新k=i
k = i #令k接替/指向较大孩子的位置,以便执行下一轮比较
# 另外,我们手动模拟的时候可能习惯交换i和k
#在代码里面也可以交换,但是本实现中没有必要,
# 因为我们有l[k]的备份bak_k,因此不需要可以保存l[k]的值
#可以到最后确定下来被筛选的结点要沉到哪个具体位置,在执行赋值即可
#继续判断下一轮,看bak_k中的值要放在哪里
i *= 2
#放在else内部应该也可以(因为执行的效果是要么都执行,要么都不执行)
#循环结束,bak_k的元素可以被赋值给l[k],完成调整(最终位置)
l[k] = bak_k
return l
建堆操作/堆的插入操作(自底向上)
-
如果知道排序二叉树的建立,那么容易从空树到一棵完整树的构建过程
- BST的构造比较简单
- Heap的构造比较不那么直白
-
构造堆过程示一个自底向上的过程
- 这个自底向上的构造过程中调用的却是自顶向下的heapify
- 也就是,自底向上中嵌套着自顶向下
- 我们不妨称从乱序序列开始构造堆的过程称为大调整bigHeapify或者BuildHeap
- 假设,一个有maxHeap,最大值为R,现在要加入一个结点,值很大(比如Z),Z>R
- 如果是最好的情况,根本不需要调整堆
- 如果从上往下调整,无从调起
- 而从下往上,我们可以逐步的将Z结点往上调整到根结点
- 这个自底向上的构造过程中调用的却是自顶向下的heapify
-
事实上,堆的调整函数可以用来构建堆(通过正确的方式调用)
- 相当于从一个特殊的堆(空堆)开始插入结点调整
- 或者也可以理解为,一个完全混乱的序列,我们希望:
- 通过合理的组织heapify的调用,使得这个序列能够被调整到是完全符合堆的性质
-
以大根堆为例,假设此时大根堆有结点n个
-
我们从大根堆的最后一个分支结点 f l o o r ( n 2 ) floor(\frac{n}{2}) floor(2n)作为子树开始向前调整
-
调整堆的次序:(第i个) i的取值 备注 1 k = f l o o r ( n 2 ) k=floor(\frac{n}{2}) k=floor(2n) 基本式k用来简化取整表达式的书写 2 2 2 k − 1 k-1 k−1 3 k − 2 k-2 k−2 … k 1 最后一次调整,整个结构将彻底符合堆的要求
-
构造堆算法BuildHeap
-
以构造大根堆为例
-
def buildHeap(l): len_l = len(l) i = len_l // 2 # 从最后一个分支结点开始往前面反复的调整(heapify) while (i): heapify(l, k=i) #print(l) i -= 1 return l
堆排序算法(HeapSort)
def heapSort(l):
print("build heap:")
buildHeap(l)
print(l)
len_l = len(l)
for i in range(len_l-1, 1, -1):
print("i=%d,l[i]=%d,l[1]=%d" % (i, l[i],l[1]))
#l[1]表示maxHeapTop堆顶元素(最大元素)
l[i], l[1] = l[1], l[i]
# print("after swap:",l)
heapify(l,1,len_l=i-1)
# print("after heapify maintained🎈🎈",i,l)
print("")
# print_layers2(l)
return l
调用/测试上述函数
# 测试函数功能
def test_print_layers(l):
print(print_layers(l))
def test_reserve_head_with(l):
print(reserve_head_with(l))
def test_heapify(l):
res_heapify=heapify(l1,k=1,len_l=6)
print("beautfy the result(remove the meaningless header -1 OR None):🎈",res_heapify[1:])
def test_buildHeap(l):
print(buildHeap(l)[1:])
def test_heapSort(l):
reserve_head_with(l)
print("res🎇🎇:",heapSort(l)[1:])
if __name__ == "__main__":
# main()
l = [ 53, 17, 78, 9, 45, 65, 87, 32]
l1 = [-1, 53, 45, 65, 32, 17, 9, 78, 87]
test_heapSort(l)
堆排序性能
- 堆排序是具有最好的渐近性能之一的比较排序
- 最好/最坏/平均情况下:时间复杂度都为 O ( n log 2 n ) O(n\log_2 n) O(nlog2n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
- 仅使用了常数个辅助单元
- 其他操作的性能
- 调整堆(heapify)
- 调整堆的时间复杂度为堆的高度h所决定的
- 即O(h)
- h = f l o o r ( log 2 n ) + 1 h=floor(\log_2 n)+1 h=floor(log2n)+1
- 调整堆的时间复杂度为堆的高度h所决定的
- 建堆
- 时间复杂度为O(n)
- 调整堆(heapify)
稳定性
- 由于heapify调整堆的时候,对于
p.l.key==p.r.key可能将左孩子调整上去,就导致不稳定- 例如1,2,2经过heapify得到2,1,2,最后一个元素处于最终有序位置,下一次heapify仅对前两个元素进行
- 再对2,1进行heapify,弹出堆顶2(1,2,交换位置),得到最终序列1,2,2这里原序列的第一个2处在有序序列的最后位置
代码参考
选择排序法_实数排序: (升序版)
结构梳理版
/* 选择排序法_实数排序: (升序版)
有助于增强理解的特征:最大比较区间的次数为n-1次 ;最小长度比较区间比较的次数为1次.*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include "d:/repos/cpp/ConsoleApps/c_codes/libs/common_funcs.c"
// 找出min_loc 到j位置范围内最小㢝的数组索引(采用这种方案的话,每趟排序最多也只需要执行一次交换操作)
int update_min_loc(float *a, int *min_loc_addr, int j)
{
int min_loc = *min_loc_addr;
if (a[min_loc] > a[j])
{
*min_loc_addr = j;
}
return *min_loc_addr;
}
// 在需要的时候交换start_loc和j两个位置上的元素,确保start_loc上的元素是较小的一方!
int set_minor_elem(float *a, int start_loc, int j)
{
int min_loc = start_loc;
if (a[min_loc] > a[j])
{
swap_float_pointer(a + j, a + min_loc);
}
return min_loc;
}
// 确保位置i上的元素在[i~n]范围内是最小的
void set_next_most(float *a, int n, int i)
{
int min_loc = i;
/* 找到最小元素所在位置,这里比较边界是将左边界收缩,而右边界不变. */
/*指出比较范围和比较对象
比较范围:起始元素向后收缩;最终元素保持不变
*/
/*每一趟:外重循环从LHS∈[0,n-2]中选定一个LHS,
内重循环控制该趟排序的一系列比较中,使RHS∈[LHS+1,n-1]全部依次与该趟指定的这个LHS作比较 */
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
/* 参数i是固定的,而参数j在递增 */
update_min_loc(a, &min_loc, j);
}
/* 判断:必要时交换元素 */
/* 最终的得到的min_loc和初始值i比较,看是否变化了,当然,也可不比较直接交换. */
if (min_loc != i)
{
swap_float_pointer(a + i, a + min_loc);
}
}
// 确保位置i上的元素在[i~n]范围内是最小的
void set_next_most_v2(float *a, int n, int i)
{
/*每一趟:外重循环从LHS∈[0,n-2]中选定一个LHS,
内重循环控制该趟排序的一系列比较中,使RHS∈[LHS+1,n-1]全部依次与该趟指定的这个LHS作比较 */
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
{
set_minor_elem(a, i, j);
}
}
void select_sort(float *a, int n)
/* 在内部计数数组的元素个数要求传入的数组有做结尾处理/规整的初始化,干脆就调用该函数之前计数下元素个数 */
{
/*LHS表示关系表达式的左边;RHS表示关系表达式的右边;
选中排序:每趟排序共用同一个LHS;单趟排序中:*/
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
// set_next_most(a, n, i);
set_next_most_v2(a, n, i);
}
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
float l[7] = {5, 2, 8, 0, 4, 3, 2};
int n = 7;
select_sort(l, n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
printf("%.0f,", l[i]);
}
return 0;
}
一体化版
/* 选择排序法_实数排序: (升序版)
有助于增强理解的特征:最大比较区间的次数为n-1次 ;最小长度比较区间比较的次数为1次.*/
void sort_select_float(float *a,int n_elements)
/* 在内部计数数组的元素个数要求传入的数组有做结尾处理/规整的初始化,干脆就调用该函数之前计数下元素个数 */
{
int min = 0 ;
int j = 0;
float temp = 0;
/*LHS表示关系表达式的左边;RHS表示关系表达式的右边;
选中排序:每趟排序共用同一个LHS;单趟排序中:*/
for(int i = 0;i < n_elements - 1;i++)
{
min = i;
/* 找到最小元素所在位置,这里比较边界是将左边界收缩,而右边界不变. */
/*指出比较范围和比较对象*/
/*每一趟:外重循环从LHS∈[0,n-2]中选定一个LHS,
内重循环控制该趟排序的一系列比较中,使RHS∈[LHS+1,n-1]全部依次与该趟指定的这个LHS作比较 */
for( j = i+1 ; j < n_elements ;j++)
{
if(a[min] > a[j])
{
min = j;
}
}
/* 交换元素 */
if(min != i)/* 最终的得到的min和初始值i比较,看是否变化了,当然,也可不比较直接交换. */
{
/* 注意不是a[i]和a[j]交换(bubble才这样.) */
temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[min];
a[min] = temp;
//printf("%f ",a[i]);
}
/*监视每一趟的排序结果.
for(int i = 0;i < n_elements - 1;i++) printf("%f ",a[i]);
printf("\n\n"); */
}
}




















 180
180











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








