在软件开发过程中,总是需要用到面向对象编程,设计模式是软件开发中比较重要的思想。虽然总体而言有23种设计模式,但一般都是各设计模式搭配起来用的,设计模式之间也有一些共通点。
这次我使用工厂方法模式和策略模式对几种常用的排序算法进行封装,使用这两种模式配合可以较好地遵守开放-封闭原则,后续如果有新的排序算法加入,只需增加新的算法类和算法工厂类即可,不用修改原来的算法结构,提高了维护性和升级性。
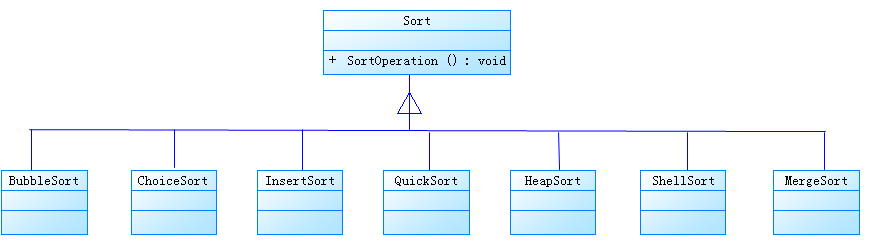
策略模式:定义了算法家族,分别封装起来,让他们之间可以互相替换,此模式让模式的变化,不会影响到使用算法的客户。
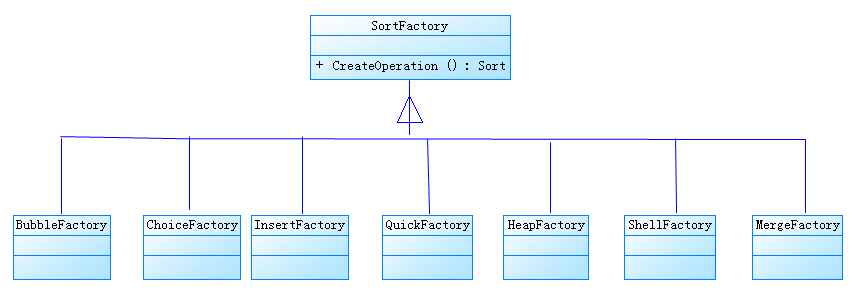
工厂方法模式:定义一个用于创建对象的接口,让子类决定实例化哪一个类。工厂方法是一个类的实例化延迟到子类。
排序算法策略模式类图如下:
排序算法工厂模式类图如下:
代码及注释如下:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Sort
{
public:
virtual void SortOperation(int src[], int len){}
virtual void SortOperation(int src[], int low, int high){}
};
class BubbleSort :public Sort
{
public:
void SortOperation(int src[], int len)
{
int i, j;
bool flag = true;
for (i = 0; i < len && flag == true; i++)
{
flag = false;
for (j = len - 2; j >= i; j--)
{
if (src[j] > src[j + 1])
{
swap(src[j], src[j + 1]);
flag = true;
}
}
}
}
};
class SelectSort :public Sort
{
public:
void SortOperation(int src[], int len)
{
int i, j, min;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
min = i;
for (j = i + 1; j < len; j++)
{
if (src[j] < src[min])
min = j;
}
if (i != min)
{
swap(src[i], src[min]);
}
}
}
};
class InsertSort :public Sort
{
public:
void SortOperation(int src[], int len)
{
int i, j, temp;
for (i = 1; i < len; i++)
{
if (src[i] < src[i - 1])
{
temp = src[i];
for (j = i - 1; src[j] > temp; j--)
{
src[j + 1] = src[j];
}
src[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
};
class QuickSort :public Sort
{
public:
int Partition(int src[], int low, int high)
{
int pivotkey;
pivotkey = src[low];
while (low < high)
{
while (low < high&&src[high] >= pivotkey)
high--;
swap(src[low], src[high]);
while (low < high&&src[low] <= pivotkey)
low++;
swap(src[low], src[high]);
}
return low;
}
void SortOperation(int src[], int low, int high)
{
int Pivot;
if (low < high)
{
Pivot = Partition(src, low, high);
SortOperation(src, low, Pivot - 1);
SortOperation(src, Pivot + 1, high);
}
}
};
class HeadSort :public Sort
{
public:
void HeapRebuild(int src[], int root, int size)
{
int LeftChild = 2 * root + 1;
if (LeftChild <= size - 1)
{
int RightChild = LeftChild + 1;
if (RightChild <= size - 1)
{
if (src[LeftChild] < src[RightChild])
{
LeftChild = RightChild;
}
}
if (src[root]<src[LeftChild])
{
swap(src[LeftChild], src[root]);
HeapRebuild(src, LeftChild, size);
}
}
}
void SortOperation(int src[], int len)
{
for (int i = len - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
HeapRebuild(src, i, len);
}
int last = len - 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= len; i++, last--)
{
swap(src[0], src[last]);
HeapRebuild(src, 0, last);
}
}
};
class ShellSort :public Sort
{
public:
void SortOperation(int src[],int len)
{
int i, j, k;
int temp;
for (i = len / 2; i > 0; i /= 2)
{
for (j = i; j < len; j++)
{
temp = src[j];
for (k = j - i; k >= 0 && temp < src[k]; k -= i)
{
src[k + i] = src[k];
}
src[k + i] = temp;
}
}
}
};
class MergeSort :public Sort
{
public:
void Merge(int *data, int p, int q, int r)
{
int leftnum, rightnum, i, j, k;
int *left = NULL, *right = NULL;
leftnum = q - p + 1;
rightnum = r - q;
left = new int[sizeof(int)*(leftnum)];
right = new int[sizeof(int)*(rightnum)];
for (i = 0; i < leftnum; i++)
{
left[i] = data[p + i];
}
for (j = 0; j < rightnum; j++)
{
right[j] = data[q + 1 + j];
}
i = 0;
j = 0;
k = p;
while (i<leftnum&&j<rightnum)
{
if (left[i] <= right[j])
{
data[k] = left[i];
k++;
i++;
}
else
{
data[k] = right[j];
k++;
j++;
}
}
while (i < leftnum)
{
data[k] = left[i];
k++;
i++;
}
while (j < rightnum)
{
data[k] = right[j];
k++;
j++;
}
}
void MSort(int SR[], int s, int t)
{
int m;
if (s<t)
{
m = (s + t) / 2;
MSort(SR, s, m);
MSort(SR, m + 1, t);
Merge(SR, s, m, t);
}
}
void SortOperation(int src[], int len)
{
MSort(src, 0, len - 1);
}
};
class SortFactory
{
public:
virtual Sort *CreateOperation() = 0;
};
class BubbleFactory :public SortFactory
{
public:
Sort *CreateOperation()
{
return new BubbleSort();
}
};
class SelectFactory :public SortFactory
{
public:
Sort *CreateOperation()
{
return new SelectSort();
}
};
class InsertFactory :public SortFactory
{
public:
Sort *CreateOperation()
{
return new InsertSort();
}
};
class QuickFactory :public SortFactory
{
public:
Sort *CreateOperation()
{
return new QuickSort();
}
};
class HeadFactory :public SortFactory
{
public:
Sort *CreateOperation()
{
return new HeadSort();
}
};
class ShellFactory :public SortFactory
{
public:
Sort *CreateOperation()
{
return new ShellSort();
}
};
class MergeFactory :public SortFactory
{
public:
Sort *CreateOperation()
{
return new MergeSort();
}
};
int main()
{
cout << "排序前:"<< endl;
int a[] = { 1, 3, 4, 8, 2, 10, 25, 111, 0, 16 };
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
cout << a[i] << endl;
SortFactory *bubble = new BubbleFactory();
Sort* bubblesort = bubble->CreateOperation();
bubblesort->SortOperation(a, 10);
cout << "```````````````````````````" << endl;
cout << "排序后:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
cout << a[i] << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}

























 431
431











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








