文件夹操作
例8-1 利用 os 列出当前目录的绝对路径,及其下的所有子目录、所有文件。
代码示例:
import os
os.path.abspath('.')
os.path.abspath('..')
os.listdir()
os.listdir('e:\\')
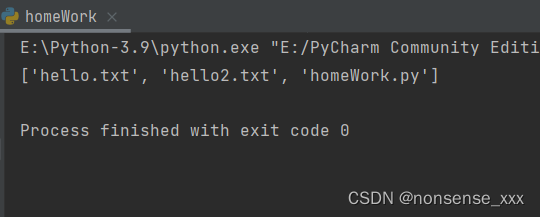
y = [f for f in os.listdir(r'.\\') if f.endswith(('.py', '.txt'))]
print(y)运行结果:
例8-2 利用os.path创建目录、创建多级目录,判断目录、文件是否存在。
代码示例:
import os
os.mkdir('d:\\test')
os.makedirs('d:\\Python\\test')
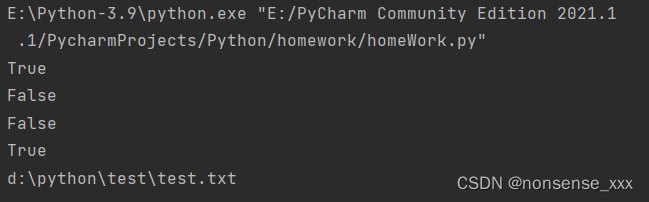
print(os.path.isdir('d:\\Python\\test'))
print(os.path.isfile(r'd:\\Python\\test\test.txt'))
print(os.path.exists(r'd:\\Python\\test\test.txt'))
print(os.path.exists(r'd:\\Python\\test'))
print(os.path.join('d:\\python\\test', 'test.txt'))运行结果:
例8-3 利用shutil复制、移动目录及文件。
代码示例:
import os
import shutil
os.chdir("d:\\Python\\test")
shutil.copyfile("test.txt", "d:\\test_copy.txt")
shutil.move("test.txt", "d:\\test_copy.txt")
os.remove("d:\\test_copy.txt")
shutil.copytree("d:\\Python\\test", "d:\\newdir")运行结果:

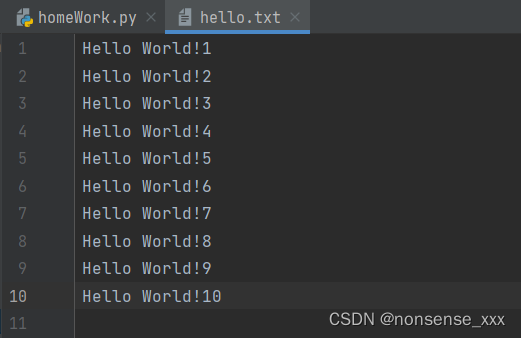
课堂练习 : 向hello.txt中写入10行“Hello World! 行号”
代码示例:
f=open("hello.txt","w+")
for i in range(1,11):
f.write("Hello World!"+str(i)+"\n")
c=f.readlines(10)
for s in c:
print(s)运行结果:
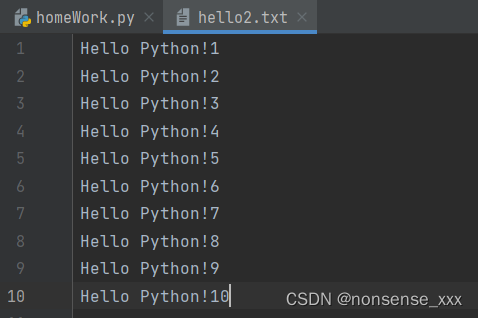
课堂练习 : 将hello.txt中的字符串“World”全部替换成字符串“Python”,并将结果存入hello2.txt
代码示例:
f1=open("hello.txt","r")
f2=open("hello2.txt","w")
for s in f1.readlines():
f2.write(s.replace("World","Python"))
f1.close()
f2.close()运行结果:
读写文本案例
例8-4 向文本文件中写入内容,然后再读出。用w 模式打开文件时,若文件不存在,则会自动创建它。另外,w 模式打开时,会立即清空文件原有内容。
代码示例:
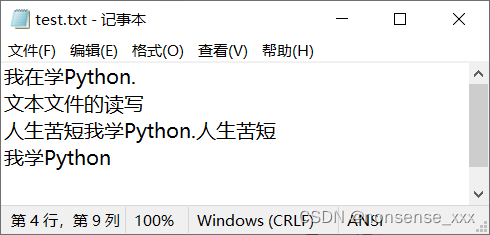
s1 = '我在学Python.\n文本文件的读写\n'
s2 = ['人生苦短', '我学Python.']
s3 = ['人生苦短\n', '我学Python\n']
with open('d://test.txt', 'w') as fp:
fp.write(s1)
fp.writelines(s2)
fp.writelines(s3)
with open('d:/test.txt') as fp:
print(fp.read())运行结果:

例8-5 如果想保留原文件内容,只是在文件末尾添加,可用a模式打开文件。此时,若文件不存在,也会自动创建它。
代码示例:
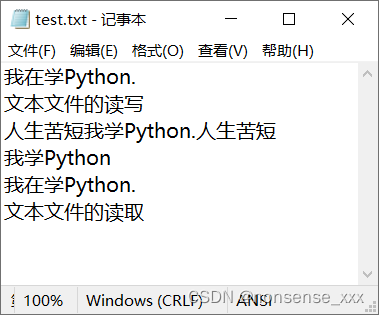
s = '我在学Python.\n文本文件的读取\n'
with open('d:/test.txt', 'a+') as fp:
fp.write(s)
with open('d:/test.txt') as fp:
r = fp.readlines()
print(type(r))运行结果:
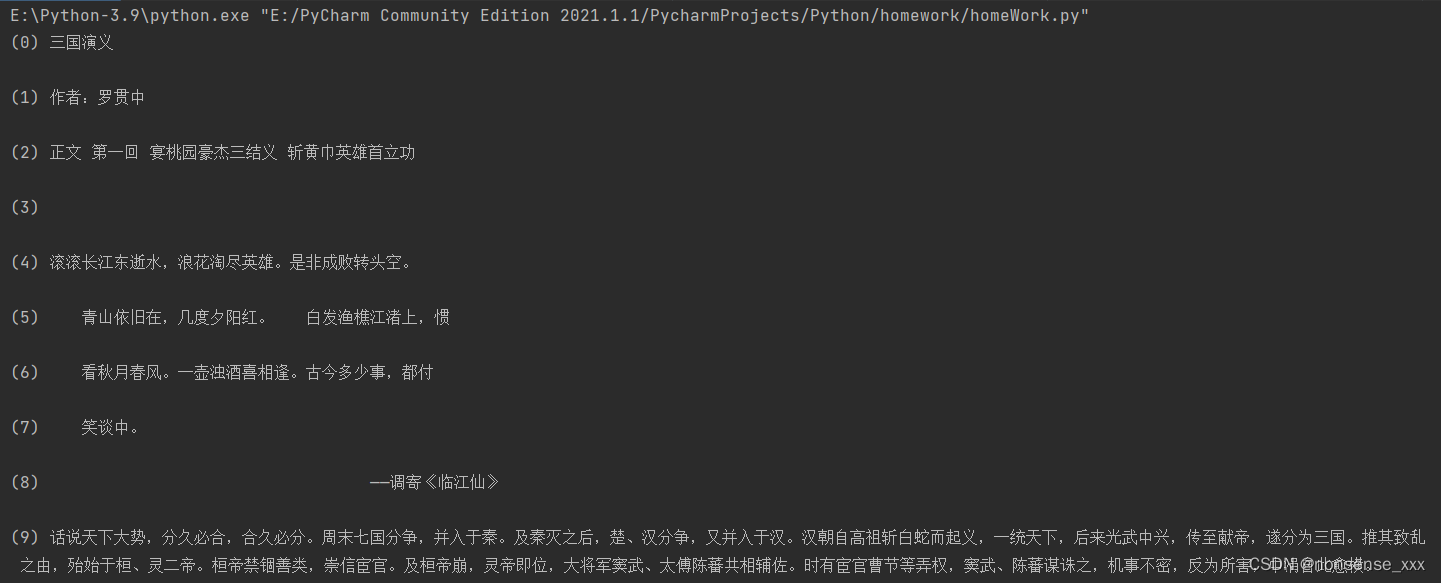
例8-6 用readline()或readlines()遍历并输出文本文件的内容。
代码示例:
j = 0
with open('./三国演义.txt', encoding='gb18030') as fp:
while j < 10:
line = fp.readline()
print("(" + str(j) + ")", line)
j += 1运行结果:
例8-7 编写程序,将d盘根目录下所有文本文件中,含有字符串“密码”的所有文件名,写入到一个文件中。
代码示例:
import os
y = [f for f in os.listdir('d:\\') if f.endswith(('.txt',))]
x = []
for f in y:
with open('d:\\' + f, encoding='gb18030') as fp:
for line in fp:
if '密码' in line:
x.append(f)
break
f = open('d:\\myTest.txt', 'a+', encoding='gb18030')
f.writelines(x)
f.close()运行结果:
使用open()读写二进制文件
例8-8 将MySQL 8.0数据库文件 smstock.ibd写入到新文件smstock_new.ibd中
代码示例:
with open('./smstock.ibd', 'rb') as f:
s = f.readline()
print(s)
with open('./smstock_new.ibd', 'wb+') as fp:
fp.write(s)
print('MySQL 数据库文件,读写成功!')运行结果:
例8-9 将图片文件“格利高里·派克.jpg”写入到新文件“格利高里_new.jpg”
代码示例:
with open('./格利高里·派克.jpg','rb') as fp:
data = fp.read()
print(type(data))
print(data)
with open('./格利高里_new.jpg','wb+') as fp:
fp.write(data)
print("图片文件,读写成功!")运行结果:
使用pickle模块读写dat文件
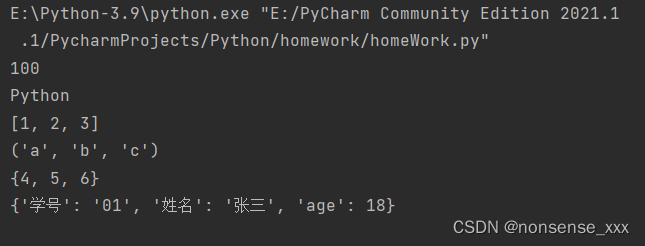
例8-10 使用pickle的dump()方法序列化数据,并写入dat二进制文件中
代码示例:
import pickle
x = [1, 2, 3];
y = ('a', 'b', 'c');
z = {4, 5, 6}
d = {'学号': '01', '姓名': '张三', 'age': 18}
data = (100, 'Python', x, y, z, d)
with open('d:\\test_pickle.dat', 'wb') as f:
try:
for d in data:
pickle.dump(d, f)
print('写dat文件成功。')
except:
print('写dat文件失败。')运行结果:
例8-11 使用pickle的load()方法反序列化数据,并输出dat二进制文件内容。
代码示例:
import pickle
with open('d:/test_pickle.dat', 'rb') as f:
end = False
while not end:
try:
x = pickle.load(f)
print(x)
except:
end = True运行结果:
使用xlrd、openpyxl 模块读Excel 文件
例8-15 读取“年度新生人口和死亡人口.xls”的内容。该文件收录了1949-2016年期间,我国部分地区新生人口、死亡人口、净增人口数据。
代码示例:
import xlrd
wb = xlrd.open_workbook("./年度新生人口和死亡人口.xls")
sheet = wb.sheet_by_index(0) # 通过索引获取表格
for i in range(sheet.nrows): # 按行数迭代
row = sheet.row_values(i) # 获取第 i行,返回列表
print(row)运行结果:

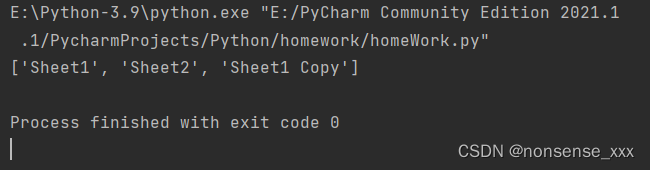
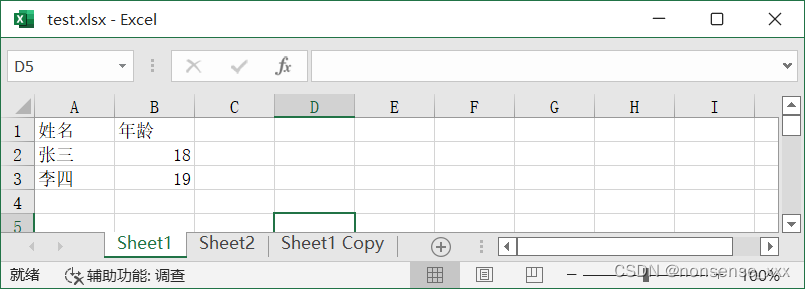
例8-16 用 openpyxl 库创建 xlsx 文件,并写入数据。
代码示例:
import openpyxl
wb = openpyxl.Workbook()
ws1 = wb.active
ws1.title = 'Sheet1'
ws1['A1'] = '姓名'
ws1['B1'] = '年龄'
ws1.append(['张三', 18])
ws1.append(['李四', 19])
ws2 = wb.create_sheet('Sheet2')
ws3 = wb.copy_worksheet(wb['Sheet1'])
print(wb.sheetnames) # 打印所有表名
wb.save('d:\\test.xlsx')运行结果:






















 34
34











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








