一、标定原理
机器人手眼标定分为eye in hand与eye to hand两种。介绍之前进行变量定义说明:
{b}: base基坐标系
{g}: gripper夹具坐标系
{t}: target标定板坐标系
{c}: camera相机坐标系
1、眼在手上(eye in hand)
眼在手上,相机固定在机器人上。
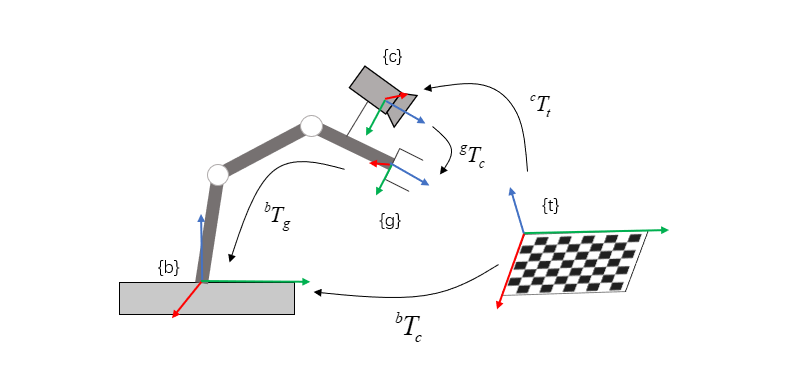
图1. eye in hand示意图

由以上两公式得:
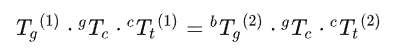
经变换得:
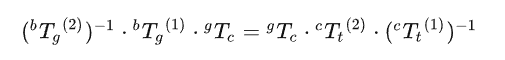
可得:
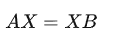
求解X即标定 :
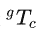
2、眼在手外(eye to hand)
眼在在手外,相机固定在机器人外。
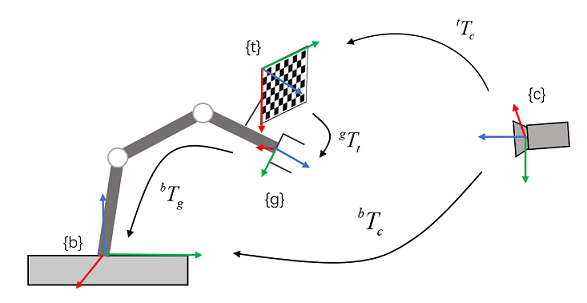
图2. eye to hand示意图

由以上两公式可得:
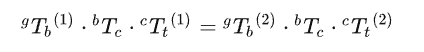
经变换得:
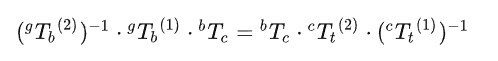
可得:
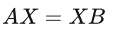
求解X即标定:
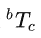
二 、标定步骤
将标定板固定至机械臂末端;
在位置1采集标定板图像,并记录机械臂在位置1下的位置与姿态;
在位置2采集标定板图像,并记录机械臂在位置2下的位置与姿态;
移动机械臂更换不同位置,采集25-40张图像,并记录机械臂在每个位置下的位姿;
相机标定,获取25-40组Tt_c ;
位姿读取,获取25-40组Tb_g ;
根据5,6调用标定接口,获取Tc_b 。
三、标定代码
import os
import cv2
import xlrd2
from math import *
import numpy as np
class Calibration:
def __init__(self):
self.K = np.array([[2.54565632e+03, 0.00000000e+00, 9.68119560e+02],
[0.00000000e+00, 2.54565632e+03, 5.31897821e+02],
[0.00000000e+00, 0.00000000e+00, 1.00000000e+00]], dtype=np.float64)
self.distortion = np.array([[-0.2557898, 0.81056366, 0.0, 0.0, -8.39153683]])
self.target_x_number = 12
self.target_y_number = 8
self.target_cell_size = 40
def angle2rotation(self, x, y, z):
Rx = np.array([[1, 0, 0], [0, cos(x), -sin(x)], [0, sin(x), cos(x)]])
Ry = np.array([[cos(y), 0, sin(y)], [0, 1, 0], [-sin(y), 0, cos(y)]])
Rz = np.array([[cos(z), -sin(z), 0], [sin(z), cos(z), 0], [0, 0, 1]])
R = Rz @ Ry @ Rx
return R
def gripper2base(self, x, y, z, tx, ty, tz):
thetaX = x / 180 * pi
thetaY = y / 180 * pi
thetaZ = z / 180 * pi
R_gripper2base = self.angle2rotation(thetaX, thetaY, thetaZ)
T_gripper2base = np.array([[tx], [ty], [tz]])
Matrix_gripper2base = np.column_stack([R_gripper2base, T_gripper2base])
Matrix_gripper2base = np.row_stack((Matrix_gripper2base, np.array([0, 0, 0, 1])))
R_gripper2base = Matrix_gripper2base[:3, :3]
T_gripper2base = Matrix_gripper2base[:3, 3].reshape((3, 1))
return R_gripper2base, T_gripper2base
def target2camera(self, img):
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, corners = cv2.findChessboardCorners(gray, (self.target_x_number, self.target_y_number), None)
corner_points = np.zeros((2, corners.shape[0]), dtype=np.float64)
for i in range(corners.shape[0]):
corner_points[:, i] = corners[i, 0, :]
object_points = np.zeros((3, self.target_x_number * self.target_y_number), dtype=np.float64)
count = 0
for i in range(self.target_y_number):
for j in range(self.target_x_number):
object_points[:2, count] = np.array(
[(self.target_x_number - j - 1) * self.target_cell_size,
(self.target_y_number - i - 1) * self.target_cell_size])
count += 1
retval, rvec, tvec = cv2.solvePnP(object_points.T, corner_points.T, self.K, distCoeffs=distortion)
Matrix_target2camera = np.column_stack(((cv2.Rodrigues(rvec))[0], tvec))
Matrix_target2camera = np.row_stack((Matrix_target2camera, np.array([0, 0, 0, 1])))
R_target2camera = Matrix_target2camera[:3, :3]
T_target2camera = Matrix_target2camera[:3, 3].reshape((3, 1))
return R_target2camera, T_target2camera
def process(self, img_path, pose_path):
image_list = []
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(img_path):
if files:
for file in files:
image_name = os.path.join(root, file)
image_list.append(image_name)
R_target2camera_list = []
T_target2camera_list = []
for img_path in image_list:
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
R_target2camera, T_target2camera = self.target2camera(img)
R_target2camera_list.append(R_target2camera)
T_target2camera_list.append(T_target2camera)
R_gripper2base_list = []
T_gripper2base_list = []
data = xlrd2.open_workbook(pose_path)
table = data.sheets()[0]
for row in range(table.nrows):
x = table.cell_value(row, 0)
y = table.cell_value(row, 1)
z = table.cell_value(row, 2)
tx = table.cell_value(row, 3)
ty = table.cell_value(row, 4)
tz = table.cell_value(row, 5)
R_gripper2base, T_gripper2base = self.gripper2base(x, y, z, tx, ty, tz)
R_gripper2base_list.append(R_gripper2base)
T_gripper2base_list.append(T_gripper2base)
R_camera2base, T_camera2base = cv2.calibrateHandEye(R_gripper2base_list, T_gripper2base_list,
R_target2camera_list, T_target2camera_list)
return R_camera2base, T_camera2base, R_gripper2base_list, T_gripper2base_list, R_target2camera_list, T_target2camera_list
def check_result(self, R_cb, T_cb, R_gb, T_gb, R_tc, T_tc):
for i in range(len(R_gb)):
RT_gripper2base = np.column_stack((R_gb[i], T_gb[i]))
RT_gripper2base = np.row_stack((RT_gripper2base, np.array([0, 0, 0, 1])))
RT_base2gripper = np.linalg.inv(RT_gripper2base)
print(RT_base2gripper)
RT_camera_to_base = np.column_stack((R_cb, T_cb))
RT_camera_to_base = np.row_stack((RT_camera_to_base, np.array([0, 0, 0, 1])))
print(RT_camera_to_base)
RT_target_to_camera = np.column_stack((R_tc[i], T_tc[i]))
RT_target_to_camera = np.row_stack((RT_target_to_camera, np.array([0, 0, 0, 1])))
RT_camera2target = np.linalg.inv(RT_target_to_camera)
print(RT_camera2target)
RT_target_to_gripper = RT_base2gripper @ RT_camera_to_base @ RT_camera2target
print("第{}次验证结果为:".format(i))
print(RT_target_to_gripper)
print('')
if __name__ == "__main__":
image_path = r"D\code\img"
pose_path = r"D\code\pose.xlsx"
calibrator = Calibration()
R_cb, T_cb, R_gb, T_gb, R_tc, T_tc = calibrator.process(image_path, pose_path)
calibrator.check_result(R_cb, T_cb, R_gb, T_gb, R_tc, T_tc)





















 1106
1106











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








