关于js中的offsetWidth、clientWidth、scrollWidth等一系列属性及其方法一直都傻傻分不清,这里就来总结一下这些方法的用法和含义。
注: 三长短,两位置:offsetWidth、clientWidth、scrollWidth、offsetTop、scrollTop可以通过元素(element)载体使用:
- 元素:可以使用offsetWidth、clientWidth、scrollWidth、offsetTop(相对哪个元素的高度)、scrollTop
- elem.属性:offsetWidth、clientWidth、scrollWidth、offsetTop、scrollTop
- document.属性 :offsetWidth、clientWidth、scrollTop
- window:
- 可以使用innerWidth和innerHeight;
- scrollY:返回文档在垂直方向已滚动的像素值。
备注:pageYOffset 属性是 scrollY 属性的别名,兼容性写法参考如下:https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/window/scrollY#%E5%A4%87%E6%B3%A8
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
#stander {
width: 100px;
height: 20px;
background-color: black;
}
#target {
/* box-sizing: border-box; */
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
border: 10px solid green;
padding: 5px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="stander"></div>
<div id="target">
</div>
<script>
const target = document.querySelector('#target');
console.log('offsetWidth', target.offsetWidth);
console.log('clientWidth', target.clientWidth);
console.log('offsetLeft', target.offsetLeft);
</script>
</body>
<script>
/*
******************************元素视图属性开始******************************************
* 三长宽 两位置
* offsetWidth: 水平方向 width + 左右padding + 左右border
* offsetHeight: 垂直方向 height + 上下padding + 上下border
*
* clientWidth: 水平方向 width + 左右padding
* clientHeight: 垂直方向 height + 上下padding
*
* scrollWidth: 元素内容真实的宽度,内容不超出盒子高度时为盒子的clientWidth
* scrollHeight: 元素内容真实的高度,内容不超出盒子高度时为盒子的clientHeight
*
* offsetTop: 获取当前元素到 定位父节点 的top方向的距离
* offsetLeft: 获取当前元素到 定位父节点 的left方向的距离
*
* scrollTop 注意:这个属性应该是作用在父元素的属性
* scrollLeft 注意:这个属性应该是作用在父元素的属性
*
*******************************元素视图属性结束******************************************
*
******************************Document文档视图开始****************************************
*
*
* document.documentElement.offsetHeight 获取整个文档的高度(包含body的margin)
* document.body.offsetHeight 获取整个文档的高度(不包含body的margin)
*
* document.documentElement.clientWidth 浏览器窗口可视区宽度(不包括浏览器控制台、菜单栏、工具栏、滚动条)
* document.documentElement.clientHeight 浏览器窗口可视区高度(不包括浏览器控制台、菜单栏、工具栏、滚动条)
* document.documentElement.scrollTop 返回文档的滚动top方向的距离(当窗口发生滚动时值改变)注意:这个属性应该是作用在父元素的属性
* document.documentElement.scrollLeft 返回文档的滚动left方向的距离(当窗口发生滚动时值改变)注意:这个属性应该是作用在父元素的属性
*
*
*********************************Document文档视图结束*******************************************
*
*********** Window视图属性(低版本IE浏览器[<IE9]不支持) 【自测包含滚动条,但网络教程都说不包含???】
*
*
* innerWidth 浏览器窗口可视区宽度(不包括浏览器控制台、菜单栏、工具栏)
* innerHeight 浏览器窗口可视区高度(不包括浏览器控制台、菜单栏、工具栏)
* window.scrollY 返回文档在垂直方向已滚动的像素值。 参考链接:https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/window/scrollY
*
* ***** Window视图属性结束**********************************************************************
*
*
*
*
****** 元素方法
* 1. getBoundingClientRect() 获取元素到body
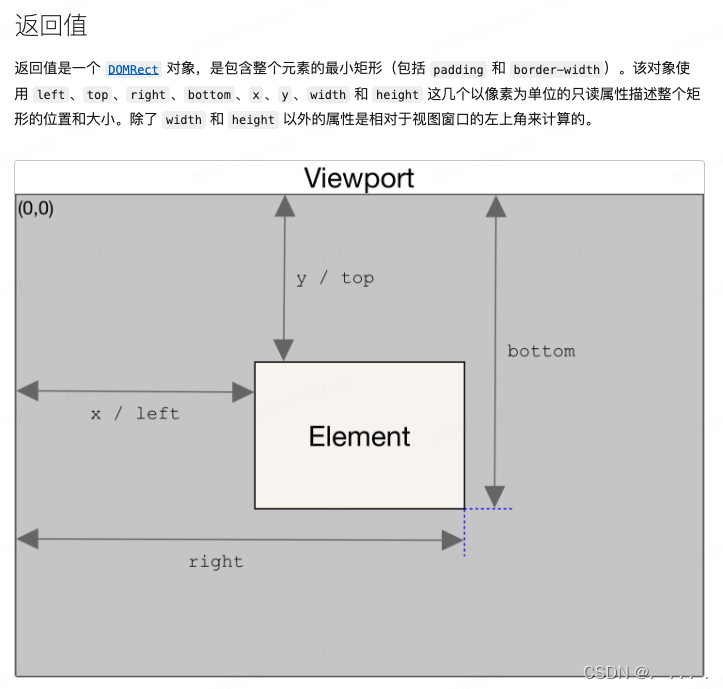
* bottom: 元素底边(包括border)到可视区最顶部的距离
* left: 元素最左边(不包括border)到可视区最左边的距离
* right: 元素最右边(包括border)到可视区最左边的距离
* top: 元素顶边(不包括border)到可视区最顶部的距离
* height: 元素的offsetHeight
* width: 元素的offsetWidth
* x: 元素左上角的x坐标
* y: 元素左上角的y坐标
*
* 2. scrollIntoView() 让元素滚动到可视区
*
* ***** 元素方法结束
*
*/
</script>
</html>

offsetWidth 和 clientWidth的区别:
offsetWidth 和 clientWidth 都是 DOM 元素上的属性,它们返回元素的宽度值,但是它们计算宽度的方式和包含的内容有所不同。
以下是 offsetWidth 和 clientWidth 之间的主要区别:
offsetWidth:
offsetWidth返回元素的完整宽度,包括元素的宽度(width)、内边距(padding)、边框(border)和滚动条(如果存在且渲染的话)。- 它是一个只读属性,返回的值是整数,单位是像素(px)。
offsetWidth包含元素的可见和不可见部分(例如,如果元素有滚动条,滚动条的宽度也会被计算在内)。
clientWidth:
clientWidth返回元素的可视宽度,包括元素的宽度(width)和内边距(padding),但不包括边框(border)、外边距(margin)和滚动条。- 同样,它也是一个只读属性,返回值是整数,单位是像素(px)。
clientWidth只计算元素内部可用于内容显示的宽度,因此它不包括滚动条宽度,即使元素实际上有一个滚动条。
例子:
假设你有一个元素,其样式如下:
element {
width: 200px; /* 宽度 */
padding: 10px; /* 内边距 */
border: 5px solid black; /* 边框 */
margin: 20px; /* 外边距 */
overflow: scroll; /* 有滚动条 */
}
clientWidth将返回200px(宽度)+10px(左内边距)+10px(右内边距)=220px。offsetWidth将返回200px(宽度)+10px(左内边距)+10px(右内边距)+5px(左边框)+5px(右边框)+ 滚动条宽度(如果可见的话),结果可能是230px或者更多,取决于滚动条的宽度。
在实际应用中,选择哪一个属性取决于你需要测量或使用宽度的上下文。如果你需要知道元素的总宽度(包括边框和滚动条),使用 offsetWidth。如果你只关心元素内部可用于内容的宽度(不包括边框和滚动条),使用 clientWidth。
有关scroll,滚动的是父窗口
测试demo如下:
结果是打印11
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
}
#main {
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
max-height: 200px;
background-color: #ccc;
vertical-align: middle;
overflow: auto;
}
#content {
width: 100px;
height: 1000px;
background-color: antiquewhite;
margin: 0 auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="main">
<div id="content">
</div>
</div>
<script>
const main = document.querySelector('#main');
const content = document.querySelector('#content');
main.addEventListener('scroll', () => {
console.log(11)
})
content.addEventListener('scroll', () => {
console.log(22)
})
</script>
</body>
</html>

有关 element.getBoundingClientRect()
通过该方法可以动态计算某个元素到另一个元素的距离。
例如:
const element = document.getElementById('yourElementId');
const bodyRect = document.body.getBoundingClientRect();
const elementRect = element.getBoundingClientRect();
const offsetTop = elementRect.top - bodyRect.top;
注意: top和bottom都是到视图顶部的距离。
HTMLElement.offsetParent
注意:offsetParent属性返回的是一个元素。
HTMLElement.offsetParent 是一个只读属性,返回一个指向最近的(指包含层级上的最近)包含该元素的定位元素或者最近的 table,td,th,body元素。当元素的 style.display 设置为 “none” 时,offsetParent 返回 null。offsetParent 很有用,因为 offsetTop 和 offsetLeft 都是相对于其内边距边界的。

























 470
470

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










