目录
一.前言
今天我们来聊一聊数据结构的一部分——队列。今天我们主要涉及队列的基本概念结构,以及队列的基本实现。
二.正文
1.1队列
1.12队列的概念及结构
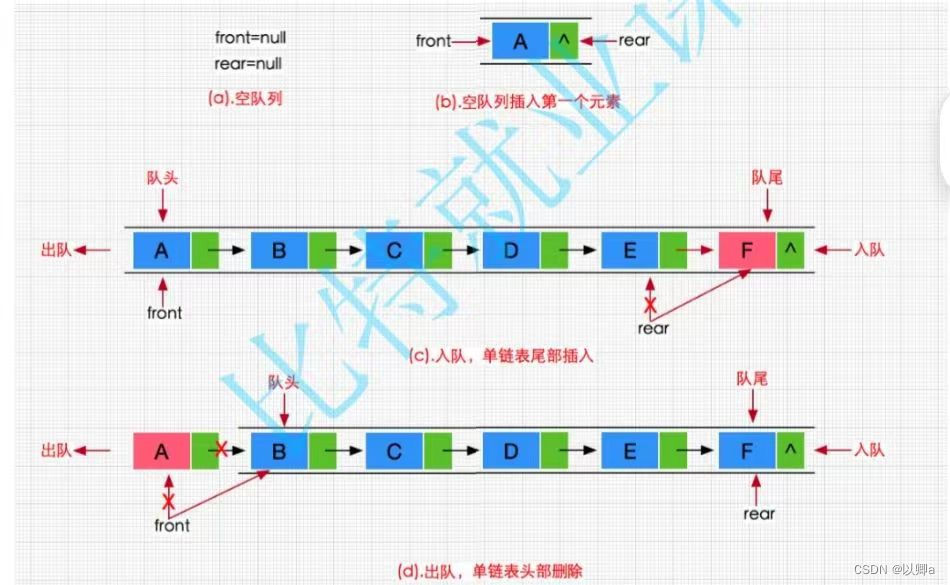
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out)
入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾
出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头
1.13队列的实现
队列也可以用数组和链表的结构实现,使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数组头上出数据,效率会比较低。 下面是我学习过程中老师的课件图表:
我们使用单链表实现队列的过程,就像我们之前所分享——单链表实现数据的增删查改
差不多。有兴趣的小伙伴可以了解一下:https://blog.csdn.net/yiqingaa/article/details/138206746?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
不过和单链表实现数据的增删查改不同的是,这里我们又多定义了一个结构体,用来存放链表的头/尾指针,以及节点个数。
这样设计的好处是:我们不需要使用二级指针,而且也不用传太多的参数。
struct Queue
{
QNode* phead;
QNode* ptail;
int size;
};其他的内容就没有过多改动。
Queue.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
typedef int QDataType;
struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType val;
};
typedef struct QueueNode QNode;
struct Queue
{
QNode* phead;
QNode* ptail;
int size;
};
typedef struct Queue Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* ps);//队列的初始化
void QueueDestroy(Queue* ps);//队列的销毁
void QueuePush(Queue* ps,QDataType x);//队尾插入数据
void QueuePop(Queue* ps);//对头删除数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* ps);//取队头数据
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* ps);//取队尾数据
int QueueSize(Queue* ps);//测量队列的元素个数
bool QueueEmoty(Queue* ps);//判断队列是否为空
Queue.c
#include"Queue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue* ps)//队列的初始化
{
assert(ps);
ps->ptail=ps->phead = NULL;
ps->size = 0;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* ps,QDataType x)//队尾的插入
{
assert(ps);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail!");
return;
}
newnode->next = NULL;
newnode->val = x;
if (ps->phead == NULL)
{
ps->phead = ps->ptail = newnode;
}
else
{
ps->ptail->next = newnode;
ps->ptail = newnode;
}
ps->size++;
}
void QueuePop(Queue* ps)//队头的删除
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size != 0);
if (ps->phead == ps->ptail)
{
ps->phead = ps->phead->next;
free(ps->ptail);
ps->ptail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* newhead = ps->phead;
ps->phead = ps->phead->next;
free(newhead);
newhead = NULL;
}
ps->size--;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* ps)//取出队头数据
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size != 0);
return ps->phead->val;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* ps)//取出队尾数据
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size != 0);
return ps->ptail->val;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* ps)//测量队列数据个数
{
assert(ps);
return ps->size;
}
bool QueueEmoty(Queue* ps)//判断队列是否为空
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->phead == NULL)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* ps)//销毁队列
{
assert(ps);
QNode* pcur = ps->phead;
QNode* pnext = pcur->next;
while (pnext)
{
free(pcur);
pcur = pnext;
pnext = pnext->next;
}
free(pcur);
ps->size = 0;
ps->phead = NULL;
ps->ptail = NULL;
}test.c
#include"Queue.h"
void test01()
{
Queue s;
QueueInit(&s);
QueuePush(&s,1);
QueuePush(&s,2);
QueuePush(&s,3);
QueuePush(&s,4);
QueueDestroy(&s);
//QueuePop(&s);
//QueuePop(&s);
//QueuePop(&s);
//QueuePop(&s);
printf("%d\n", QueueFront(&s));
printf("%d\n", QueueBack(&s));
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}值得注意的是:test.c只是我在测试函数功能时创建的。小伙伴们自行看看即可。
三.结言
文章到这里就结束了,觉得本文章对自己有用的小伙伴,能不能给个三连。
当然,如本文有些许错误,也请大捞们指正。























 902
902

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








