| Time Limit: 2000MS | Memory Limit: 30000K | |
| Total Submissions: 11960 | Accepted: 4244 | |
| Case Time Limit: 1000MS | ||
Description
Input
* Line 2+M: A single integer, K. 1 <= K <= 10,000
* Lines 3+M..2+M+K: Each line corresponds to a distance query and contains the indices of two farms.
Output
Sample Input
7 6 1 6 13 E 6 3 9 E 3 5 7 S 4 1 3 N 2 4 20 W 4 7 2 S 3 1 6 1 4 2 6
Sample Output
13 336
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> using namespace std; const int N = 400000; struct node { int to, next, cost; } G1[N]; struct edge { int to, next, indx; } G2[N]; int par[N], head1[N], head2[N], visit[N]; int cnt1, cnt2; void add1(int u,int v,int c); void add2(int u,int v,int c); void init(); int n, m; typedef long long LL; LL dist[N], res[N]; int ser(int u); void tarjan(int u); int main() { while(scanf("%d %d", &n, &m)!=EOF) { init(); cnt1=0, cnt2=0; for(int i=0; i<m; i++) { int x, y, cost; char c; scanf("%d %d %d %c",&x, &y, &cost,&c); add1(x, y, cost); add1(y, x, cost); } int k; scanf("%d", &k); for(int i=0; i<k; i++) { int x, y; scanf("%d %d",&x, &y); add2(x, y, i); add2(y, x, i); } dist[1]=0; tarjan(1); for(int i=0; i<k; i++) { printf("%I64d\n",res[i]); } } return 0; } void add1(int u,int v,int c) { G1[cnt1].to=v; G1[cnt1].cost=c; G1[cnt1].next=head1[u]; head1[u]=cnt1++; return ; } void add2(int u,int v,int c) { G2[cnt2].to=v; G2[cnt2].indx=c; G2[cnt2].next=head2[u]; head2[u]=cnt2++; return ; } void init() { for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) { par[i]=i; } memset(head1,-1,sizeof(head1)); memset(head2,-1,sizeof(head2)); memset(visit,0,sizeof(visit)); return ; } void tarjan(int u) { visit[u]=1; for(int i=head1[u]; i!=-1; i=G1[i].next) { int v=G1[i].to; if(!visit[v]) { dist[v]=dist[u]+G1[i].cost; tarjan(v); par[v]=u; } } for(int i=head2[u]; i!=-1; i=G2[i].next) { int v=G2[i].to; if(visit[v]) { res[G2[i].indx]=dist[v]+dist[u]-2*dist[ser(v)]; } } return ; } int ser(int u) { int l=u, r=u, j; while(l!=par[l]) l=par[l]; while(r!=l) j=par[r], par[r]=l, r=j;//路径压缩 return l; }
下面为转载的链式前向星知识
我们首先来看一下什么是前向星.
前向星是一种特殊的边集数组,我们把边集数组中的每一条边按照起点从小到大排序,如果起点相同就按照终点从小到大排序,
并记录下以某个点为起点的所有边在数组中的起始位置和存储长度,那么前向星就构造好了.
用len[i]来记录所有以i为起点的边在数组中的存储长度.
用head[i]记录以i为边集在数组中的第一个存储位置.
那么对于下图:
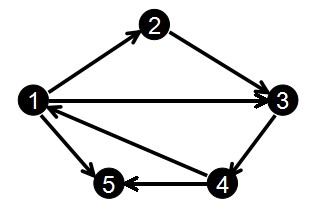
我们输入边的顺序为:
1 2
2 3
3 4
1 3
4 1
1 5
4 5
那么排完序后就得到:
编号: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
起点u: 1 1 1 2 3 4 4
终点v: 2 3 5 3 4 1 5
得到:
head[1] = 1 len[1] = 3
head[2] = 4 len[2] = 1
head[3] = 5 len[3] = 1
head[4] = 6 len[4] = 2
但是利用前向星会有排序操作,如果用快排时间至少为O(nlog(n))
如果用链式前向星,就可以避免排序.
我们建立边结构体为:
struct Edge
{
int next;
int to;
int w;
};
其中edge[i].to表示第i条边的终点,edge[i].next表示与第i条边同起点的下一条边的存储位置,edge[i].w为边权值.
另外还有一个数组head[],它是用来表示以i为起点的第一条边存储的位置,实际上你会发现这里的第一条边存储的位置其实
在以i为起点的所有边的最后输入的那个编号.
head[]数组一般初始化为-1,对于加边的add函数是这样的:
初始化cnt = 0,这样,现在我们还是按照上面的图和输入来模拟一下:
edge[0].to = 2; edge[0].next = -1; head[1] = 0;
edge[1].to = 3; edge[1].next = -1; head[2] = 1;
edge[2].to = 4; edge[2],next = -1; head[3] = 2;
edge[3].to = 3; edge[3].next = 0; head[1] = 3;
edge[4].to = 1; edge[4].next = -1; head[4] = 4;
edge[5].to = 5; edge[5].next = 3; head[1] = 5;
edge[6].to = 5; edge[6].next = 4; head[4] = 6;
很明显,head[i]保存的是以i为起点的所有边中编号最大的那个,而把这个当作顶点i的第一条起始边的位置.
这样在遍历时是倒着遍历的,也就是说与输入顺序是相反的,不过这样不影响结果的正确性.
比如以上图为例,以节点1为起点的边有3条,它们的编号分别是0,3,5 而head[1] = 5
我们在遍历以u节点为起始位置的所有边的时候是这样的:
for(int i=head[u];~i;i=edge[i].next)
那么就是说先遍历编号为5的边,也就是head[1],然后就是edge[5].next,也就是编号3的边,然后继续edge[3].next,也
就是编号0的边,可以看出是逆序的.






















 889
889

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








