It's almost summer time, and that means that it's almost summer construction time! This year, the good people who are in charge of the roads on the tropical island paradise of Remote Island would like to repair and upgrade the various roads that lead between the various tourist attractions on the island.
The roads themselves are also rather interesting. Due to the strange customs of the island, the roads are arranged so that they never meet at intersections, but rather pass over or under each other using bridges and tunnels. In this way, each road runs between two specific tourist attractions, so that the tourists do not become irreparably lost.
Unfortunately, given the nature of the repairs and upgrades needed on each road, when the construction company works on a particular road, it is unusable in either direction. This could cause a problem if it becomes impossible to travel between two tourist attractions, even if the construction company works on only one road at any particular time.
So, the Road Department of Remote Island has decided to call upon your consulting services to help remedy this problem. It has been decided that new roads will have to be built between the various attractions in such a way that in the final configuration, if any one road is undergoing construction, it would still be possible to travel between any two tourist attractions using the remaining roads. Your task is to find the minimum number of new roads necessary.
The first line of input will consist of positive integers n and r, separated by a space, where 3 ≤ n ≤ 1000 is the number of tourist attractions on the island, and 2 ≤ r ≤ 1000 is the number of roads. The tourist attractions are conveniently labelled from 1 to n. Each of the following r lines will consist of two integers, vand w, separated by a space, indicating that a road exists between the attractions labelled v and w. Note that you may travel in either direction down each road, and any pair of tourist attractions will have at most one road directly between them. Also, you are assured that in the current configuration, it is possible to travel between any two tourist attractions.
One line, consisting of an integer, which gives the minimum number of roads that we need to add.
Sample Input 1 10 12 1 2 1 3 1 4 2 5 2 6 5 6 3 7 3 8 7 8 4 9 4 10 9 10 Sample Input 2 3 3 1 2 2 3 1 3
Output for Sample Input 1 2 Output for Sample Input 2 0
首先建立模型:
给定一个连通的无向图G,至少要添加几条边,才能使其变为双连通图。
模型很简单,正在施工的道路我们可以认为那条边被删除了。那么一个图G能够在删除任意一条边后,仍然是连通的,当且仅当图G至少为双连通的。
PS:不要问我为什么不是3-连通、4-连通...人家题目问“至少添加几条边”好不...
显然,当图G存在桥(割边)的时候,它必定不是双连通的。桥的两个端点必定分别属于图G的两个【边双连通分量】(注意不是点双连通分量),一旦删除了桥,这两个【边双连通分量】必定断开,图G就不连通了。但是如果在两个【边双连通分量】之间再添加一条边,桥就不再是桥了,这两个【边双连通分量】之间也就是双连通了。
那么如果图G有多个【边双连通分量】呢?至少应该添加多少条边,才能使得任意两个【边双连通分量】之间都是双连通(也就是图G是双连通的)?
这个问题就是本题的问题。要解决这个问题:
1、 首先要找出图G的所有【边双连通分量】。
Tarjan算法用来寻找图G的所有【边双连通分量】是最简单有效的方法,因为Tarjan算法在DFS过程中会对图G所有的结点都生成一个Low值,而由于题目已表明任意两个结点之间不会出现重边,因此Low值相同的两个结点必定在同一个【边双连通分量】中! (如果是有重边的话,那么不同的low值是可能是属于同一个边双连通分量的,这个时候就要通过其他方法去求解边双连通分量。不过这不是本题要讨论的)
2、 把每一个【边双连通分量】都看做一个点(即【缩点】)
也有人称【缩点】为【块】,都是一样的。其实缩点不是真的缩点,只要利用Low值对图G的点分类处理,就已经缩点了。
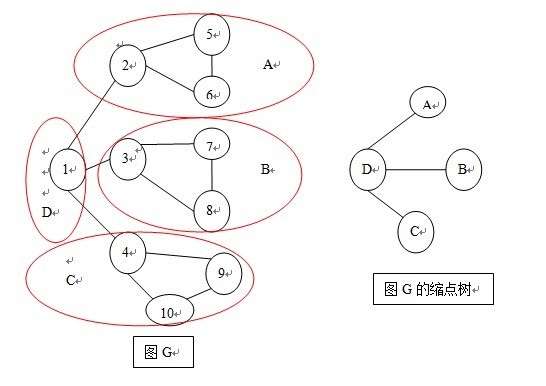
以样例1为例,样例1得到的图G为上左图,
其中Low[4]=Low[9]=Low[10]
Low[3]=Low[7]=Low[8]
Low[2]=Low[5]=Low[6]
Low[1]独自为政....
把Low值相同的点划分为一类,每一类就是一个【边双连通分量】,也就是【缩点】了,不难发现,连接【缩点】之间的边,都是图G的桥,那么我们就得到了上右图以缩点为结点,已桥为树边所构造成的树。
3、 问题再次被转化为“至少在缩点树上增加多少条树边,使得这棵树变为一个双连通图”。
首先知道一条等式:
若要使得任意一棵树,在增加若干条边后,变成一个双连通图,那么
至少增加的边数 =( 这棵树总度数为1的结点数 + 1 )/ 2
(证明就不证明了,自己画几棵树比划一下就知道了)
那么我们只需求缩点树中总度数为1的结点数(即叶子数)有多少就可以了。换而言之,我们只需求出所有缩点的度数,然后判断度数为1的缩点有几个,问题就解决了。
4、 求出所有缩点的度数的方法
两两枚举图G的直接连通的点,只要这两个点不在同一个【缩点】中,那么它们各自所在的【缩点】的度数都+1。注意由于图G时无向图,这样做会使得所有【缩点】的度数都是真实度数的2倍,必须除2后再判断叶子。
[点连通度与边连通度]
在一个无向连通图中,如果有一个顶点集合,删除这个顶点集合,以及这个集合中所有顶点相关联的边以后,原图变成多个连通块,就称这个点集为割点集合。一个图的点连通度的定义为,最小割点集合中的顶点数。
类似的,如果有一个边集合,删除这个边集合以后,原图变成多个连通块,就称这个点集为割边集合。一个图的边连通度的定义为,最小割边集合中的边数。
[双连通图、割点与桥]
如果一个无向连通图的点连通度大于1,则称该图是点双连通的(point biconnected),简称双连通或重连通。一个图有割点,当且仅当这个图的点连通度为1,则割点集合的唯一元素被称为割点(cut point),又叫关节点(articulation point)。
如果一个无向连通图的边连通度大于1,则称该图是边双连通的(edge biconnected),简称双连通或重连通。一个图有桥,当且仅当这个图的边连通度为1,则割边集合的唯一元素被称为桥(bridge),又叫关节边(articulation edge)。
可以看出,点双连通与边双连通都可以简称为双连通,它们之间是有着某种联系的,下文中提到的双连通,均既可指点双连通,又可指边双连通。
[双连通分支]
在图G的所有子图G'中,如果G'是双连通的,则称G'为双连通子图。如果一个双连通子图G'它不是任何一个双连通子图的真子集,则G'为极大双连通子图。双连通分支(biconnected component),或重连通分支,就是图的极大双连通子图。特殊的,点双连通分支又叫做块。
[求割点与桥]
该算法是R.Tarjan发明的。对图深度优先搜索,定义DFS(u)为u在搜索树(以下简称为树)中被遍历到的次序号。定义Low(u)为u或u的子树中能通过非父子边追溯到的最早的节点,即DFS序号最小的节点。根据定义,则有:
Low(u)=Min { DFS(u) DFS(v) (u,v)为后向边(返祖边) 等价于 DFS(v)<DFS(u)且v不为u的父亲节点 Low(v) (u,v)为树枝边(父子边) }
一个顶点u是割点,当且仅当满足(1)或(2) (1) u为树根,且u有多于一个子树。 (2) u不为树根,且满足存在(u,v)为树枝边(或称父子边,即u为v在搜索树中的父亲),使得DFS(u)<=Low(v)。
一条无向边(u,v)是桥,当且仅当(u,v)为树枝边,且满足DFS(u)<Low(v)。
[求双连通分支]
下面要分开讨论点双连通分支与边双连通分支的求法。
对于点双连通分支,实际上在求割点的过程中就能顺便把每个点双连通分支求出。建立一个栈,存储当前双连通分支,在搜索图时,每找到一条树枝边或后向边(非横叉边),就把这条边加入栈中。如果遇到某时满足DFS(u)<=Low(v),说明u是一个割点,同时把边从栈顶一个个取出,直到遇到了边(u,v),取出的这些边与其关联的点,组成一个点双连通分支。割点可以属于多个点双连通分支,其余点和每条边只属于且属于一个点双连通分支。
对于边双连通分支,求法更为简单。只需在求出所有的桥以后,把桥边删除,原图变成了多个连通块,则每个连通块就是一个边双连通分支。桥不属于任何一个边双连通分支,其余的边和每个顶点都属于且只属于一个边双连通分支。
[构造双连通图]
一个有桥的连通图,如何把它通过加边变成边双连通图?方法为首先求出所有的桥,然后删除这些桥边,剩下的每个连通块都是一个双连通子图。把每个双连通子图收缩为一个顶点,再把桥边加回来,最后的这个图一定是一棵树,边连通度为1。
统计出树中度为1的节点的个数,即为叶节点的个数,记为leaf。则至少在树上添加(leaf+1)/2条边,就能使树达到边二连通,所以至少添加的边数就是(leaf+1)/2。具体方法为,首先把两个最近公共祖先最远的两个叶节点之间连接一条边,这样可以把这两个点到祖先的路径上所有点收缩到一起,因为一个形成的环一定是双连通的。然后再找两个最近公共祖先最远的两个叶节点,这样一对一对找完,恰好是(leaf+1)/2次,把所有点收缩到了一起。
题意:一个连通的无向图,求至少需要添加几条边,救能保证删除任意一条边,图仍然是连通的。
思路:边的双连通图。其实就是要求至少添加几条边,可以使整个图成为一个边双连通图。用tarjan算法(求割点割边)求出low数组,这里可以简化,然 后依据“low相同的点在一个边连通分量中”,缩点之后构造成树(这里可以直接利用low[]数组,low[i]即为第i节点所在的连通分量的标号)。求 出树中出度为1的节点数left,答案即为(leaf+1)/2。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5000;
int vis[N], head[N], w[1010][1010], low[N], degree[N];
struct node
{
int to, next1;
} p[2*N+100];
int cnt, num;
void add(int u,int v)
{
p[cnt].to=v,p[cnt].next1=head[u];
head[u]=cnt++;
return ;
}
void dfs(int u,int fa)
{
vis[u]=1, low[u]=num++;
for(int i=head[u]; i!=-1; i=p[i].next1)
{
int v=p[i].to;
if(v==fa) continue;
if(!vis[v]) dfs(v,u);
low[u]=min(low[u],low[v]);
}
return ;
}
int tarjan(int n)
{
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
memset(low,0,sizeof(low));
memset(degree,0,sizeof(degree));
num=0;
dfs(1,-1);
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
for(int j=head[i]; j!=-1; j=p[j].next1)
{
int u=p[j].to;
if(low[u]!=low[i]) degree[low[i]]++;
}
}
int sum=0;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
if(degree[i]==1)sum++;
return (sum+1)/2;
}
int main()
{
int n, m,x, y;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
memset(w,0,sizeof(w));
for(int i=0; i<m; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
if(w[x][y]) continue;
w[x][y]=w[y][x]=1;
add(x,y); add(y,x);
}
printf("%d\n",tarjan(n));
return 0;
}






















 544
544

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








