RefineNet发布于2016年,早于PSPnet。
《RefineNet: Multi-Path Refinement Networks for High-Resolution Semantic Segmentation》
RefineNet
论文思想
- 作者认为,下采样和池化等操作将图像缩小到32倍以后丢失了许多细节特征,而在以前的论文中,主要使用反卷积的操作(像Unet中)来恢复一些特征,但是这种恢复的方法不能准确恢复很多重要的特征。
- 一些低级的特征对于物体的边界和细节预测十分重要,在DeepLab中,主要依靠空洞卷积来实现,但是这种方法往往需要大量的计算和大量的GPU内存资源,其次,作者认为空洞卷积操作会丢失一些细节特征。
- 像FCN中,利用中间层的特征来恢复图像信息,生成高分辨率的预测图,作者先是肯定了这种思路,然后提出了他的观点:就是这种简单的融合缺乏空间位置信息。
- 基于以上3点,作者引入了他的RefineNet。利用各个级别的特征图,通过多层特征来生成高分辨率图像。用一个多路的细化网络,同时所有的组件都遵循残差结构。
- 提出了Chained Residual Pooling结构用于从一个大图像区域中捕捉背景上下文。
模型结构
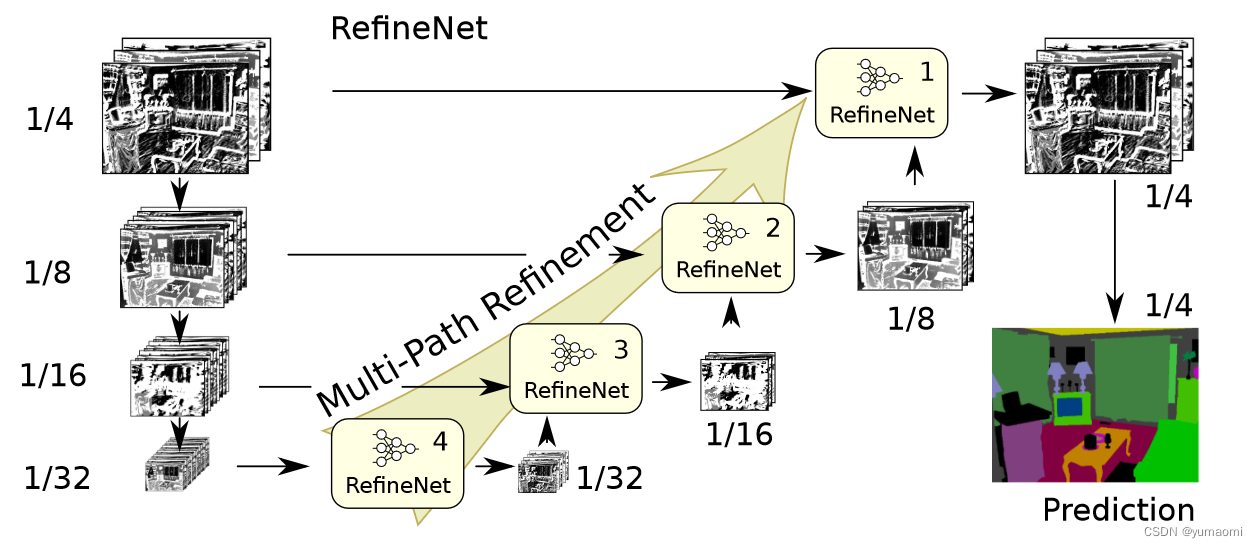

作者将每一层的特征图输入到一个RefineNet结构中,再与上采样的特征图进行融合,通过这种多路的特征提取、特征融合,来提升模型的分割效果。
一个RefineNet由三个组件构成,分别为RCU(Residual Conv Unit)、Multi-resolution Fusion、Chained Residual Pooling。所有的组件都遵循了残差结构。
其中Chained Residual Pooling被设置用来捕捉全局的上下文信息。比较有意思的是,图2 d中,上采样过程每次学习到的都是上一层的残差结果,而不是相加后再输入去学习,作者认为这种一级一级的残差学习可以帮助模型学习到较好的残差校正结果。
模型复现
Resnet101部分
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion: int = 4
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride = 1, downsample = None, groups = 1,
base_width = 64, dilation = 1, norm_layer = None):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
if norm_layer is None:
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
if groups != 1 or base_width != 64:
raise ValueError("BasicBlock only supports groups=1 and base_width=64")
if dilation > 1:
raise NotImplementedError("Dilation > 1 not supported in BasicBlock")
# Both self.conv1 and self.downsample layers downsample the input when stride != 1
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes ,kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
padding=dilation,groups=groups, bias=False,dilation=dilation)
self.bn1 = norm_layer(planes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes ,kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
padding=dilation,groups=groups, bias=False,dilation=dilation)
self.bn2 = norm_layer(planes)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
expansion = 4
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample= None,
groups = 1, base_width = 64, dilation = 1, norm_layer = None,):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
if norm_layer is None:
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
width = int(planes * (base_width / 64.0)) * groups
# Both self.conv2 and self.downsample layers downsample the input when stride != 1
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, width, kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = norm_layer(width)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(width, width, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, bias=False, padding=dilation, dilation=dilation)
self.bn2 = norm_layer(width)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(width, planes * self.expansion, kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False)
self.bn3 = norm_layer(planes * self.expansion)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class ResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(
self,block, layers,num_classes = 1000, zero_init_residual = False, groups = 1,
width_per_group = 64, replace_stride_with_dilation = None, norm_layer = None):
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
if norm_layer is None:
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
self._norm_layer = norm_layer
self.inplanes = 64
self.dilation = 1
if replace_stride_with_dilation is None:
# each element in the tuple indicates if we should replace
# the 2x2 stride with a dilated convolution instead
replace_stride_with_dilation = [False, False, False]
if len(replace_stride_with_dilation) != 3:
raise ValueError(
"replace_stride_with_dilation should be None "
f"or a 3-element tuple, got {replace_stride_with_dilation}"
)
self.groups = groups
self.base_width = width_per_group
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, self.inplanes, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False)
self.bn1 = norm_layer(self.inplanes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0])
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layers[1], stride=2, dilate=replace_stride_with_dilation[0])
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, layers[2], stride=2, dilate=replace_stride_with_dilation[1])
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, layers[3], stride=2, dilate=replace_stride_with_dilation[2])
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode="fan_out", nonlinearity="relu")
elif isinstance(m, (nn.BatchNorm2d, nn.GroupNorm)):
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
# Zero-initialize the last BN in each residual branch,
# so that the residual branch starts with zeros, and each residual block behaves like an identity.
# This improves the model by 0.2~0.3% according to https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.02677
if zero_init_residual:
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, Bottleneck):
nn.init.constant_(m.bn3.weight, 0) # type: ignore[arg-type]
elif isinstance(m, BasicBlock):
nn.init.constant_(m.bn2.weight, 0) # type: ignore[arg-type]
def _make_layer(
self,
block,
planes,
blocks,
stride = 1,
dilate = False,
):
norm_layer = self._norm_layer
downsample = None
previous_dilation = self.dilation
if dilate:
self.dilation *= stride
stride = stride
if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
norm_layer(planes * block.expansion))
layers = []
layers.append(
block(
self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample, self.groups, self.base_width, previous_dilation, norm_layer
)
)
self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
for _ in range(1, blocks):
layers.append(
block(
self.inplanes,
planes,
groups=self.groups,
base_width=self.base_width,
dilation=self.dilation,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
)
)
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def _forward_impl(self, x):
outs = []
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
outs.append(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
outs.append(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
outs.append(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
outs.append(x)
return outs
def forward(self, x) :
return self._forward_impl(x)
def _resnet(block, layers, pretrained_path = None, **kwargs,):
model = ResNet(block, layers, **kwargs)
if pretrained_path is not None:
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(pretrained_path), strict=False)
return model
def resnet50(pretrained_path=None, **kwargs):
return ResNet._resnet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3],pretrained_path,**kwargs)
def resnet101(pretrained_path=None, **kwargs):
return ResNet._resnet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3],pretrained_path,**kwargs)RefineNet部分
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class ResidualConvUnit(nn.ModuleList):
def __init__(self, in_channels):
super(ResidualConvUnit, self).__init__()
for i in range(4):
self.append(
nn.Sequential(
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels//(2**(3 - i)) , in_channels//(2**(3 - i)) , 3, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels//(2**(3 - i)) ),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels//(2**(3 - i)) , in_channels//(2**(3 - i)) , 3, padding=1, bias=False),
)
)
def forward(self, x):
outs = []
for index, module in enumerate(self):
x1 = module(x[index])
x1 = x[index] + x1
outs.append(x1)
return outs
def un_pool(input, scale):
return F.interpolate(input, scale_factor=scale, mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
class MultiResolutionFusion(nn.ModuleList):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, scale_factors = [1,2,4,8]):
super(MultiResolutionFusion, self).__init__()
self.scale_factors = scale_factors
for index, scale in enumerate(scale_factors):
self.append(
nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels//2** (len(scale_factors)-index-1), out_channels, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
)
)
def forward(self, x):
outputs = []
for index, module in enumerate(self):
xi = module(x[index])
xi = un_pool(xi, scale=self.scale_factors[index])
outputs.append(xi)
return outputs[0] + outputs[1] + outputs[2] + outputs[3]
class ChainedResidualPool(nn.ModuleList):
def __init__(self, in_channels, blocks=4):
super(ChainedResidualPool, self).__init__()
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.blocks = blocks
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
for i in range(blocks):
self.append(
nn.Sequential(
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, in_channels,kernel_size=3, padding=1, stride=1, bias=False),
)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.relu(x)
path = x
for index, CRP in enumerate(self):
path = CRP(path)
x = x + path
return x
class RefineNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes):
super(RefineNet, self).__init__()
self.backbone = ResNet.resnet101()
self.final = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(256, 128, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(128, num_classes, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False),
)
self.ResidualConvUnit = ResidualConvUnit(2048)
self.MultiResolutionFusion = MultiResolutionFusion(2048, 256)
self.ChainedResidualPool = ChainedResidualPool(256)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.backbone(x)
x = self.ResidualConvUnit(x)
x = self.MultiResolutionFusion(x)
x = self.ChainedResidualPool(x)
x = un_pool(x, scale=4)
x = self.final(x)
return x数据集
数据集使用Camvid数据集。见CamVid数据集的创建和使用-pytorch。
# 导入库
import os
os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = '0'
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch import optim
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader, random_split
from tqdm import tqdm
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
import os.path as osp
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import albumentations as A
from albumentations.pytorch.transforms import ToTensorV2
torch.manual_seed(17)
# 自定义数据集CamVidDataset
class CamVidDataset(torch.utils.data.Dataset):
"""CamVid Dataset. Read images, apply augmentation and preprocessing transformations.
Args:
images_dir (str): path to images folder
masks_dir (str): path to segmentation masks folder
class_values (list): values of classes to extract from segmentation mask
augmentation (albumentations.Compose): data transfromation pipeline
(e.g. flip, scale, etc.)
preprocessing (albumentations.Compose): data preprocessing
(e.g. noralization, shape manipulation, etc.)
"""
def __init__(self, images_dir, masks_dir):
self.transform = A.Compose([
A.Resize(224, 224),
A.HorizontalFlip(),
A.VerticalFlip(),
A.Normalize(),
ToTensorV2(),
])
self.ids = os.listdir(images_dir)
self.images_fps = [os.path.join(images_dir, image_id) for image_id in self.ids]
self.masks_fps = [os.path.join(masks_dir, image_id) for image_id in self.ids]
def __getitem__(self, i):
# read data
image = np.array(Image.open(self.images_fps[i]).convert('RGB'))
mask = np.array( Image.open(self.masks_fps[i]).convert('RGB'))
image = self.transform(image=image,mask=mask)
return image['image'], image['mask'][:,:,0]
def __len__(self):
return len(self.ids)
# 设置数据集路径
DATA_DIR = r'dataset\camvid' # 根据自己的路径来设置
x_train_dir = os.path.join(DATA_DIR, 'train_images')
y_train_dir = os.path.join(DATA_DIR, 'train_labels')
x_valid_dir = os.path.join(DATA_DIR, 'valid_images')
y_valid_dir = os.path.join(DATA_DIR, 'valid_labels')
train_dataset = CamVidDataset(
x_train_dir,
y_train_dir,
)
val_dataset = CamVidDataset(
x_valid_dir,
y_valid_dir,
)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=32, shuffle=True,drop_last=True)
val_loader = DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=32, shuffle=True,drop_last=True)模型训练
model = RefineNet(num_classes=33).cuda()
#model.load_state_dict(torch.load(r"checkpoints/resnet101-5d3b4d8f.pth"),strict=False)
from d2l import torch as d2l
from tqdm import tqdm
import pandas as pd
#损失函数选用多分类交叉熵损失函数
lossf = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(ignore_index=255)
#选用adam优化器来训练
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(),lr=0.1)
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size=50, gamma=0.1, last_epoch=-1)
#训练50轮
epochs_num = 50
def train_ch13(net, train_iter, test_iter, loss, trainer, num_epochs,scheduler,
devices=d2l.try_all_gpus()):
timer, num_batches = d2l.Timer(), len(train_iter)
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epoch', xlim=[1, num_epochs], ylim=[0, 1],
legend=['train loss', 'train acc', 'test acc'])
net = nn.DataParallel(net, device_ids=devices).to(devices[0])
loss_list = []
train_acc_list = []
test_acc_list = []
epochs_list = []
time_list = []
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
# Sum of training loss, sum of training accuracy, no. of examples,
# no. of predictions
metric = d2l.Accumulator(4)
for i, (features, labels) in enumerate(train_iter):
timer.start()
l, acc = d2l.train_batch_ch13(
net, features, labels.long(), loss, trainer, devices)
metric.add(l, acc, labels.shape[0], labels.numel())
timer.stop()
if (i + 1) % (num_batches // 5) == 0 or i == num_batches - 1:
animator.add(epoch + (i + 1) / num_batches,
(metric[0] / metric[2], metric[1] / metric[3],
None))
test_acc = d2l.evaluate_accuracy_gpu(net, test_iter)
animator.add(epoch + 1, (None, None, test_acc))
scheduler.step()
print(f"epoch {epoch+1} --- loss {metric[0] / metric[2]:.3f} --- train acc {metric[1] / metric[3]:.3f} --- test acc {test_acc:.3f} --- cost time {timer.sum()}")
#---------保存训练数据---------------
df = pd.DataFrame()
loss_list.append(metric[0] / metric[2])
train_acc_list.append(metric[1] / metric[3])
test_acc_list.append(test_acc)
epochs_list.append(epoch+1)
time_list.append(timer.sum())
df['epoch'] = epochs_list
df['loss'] = loss_list
df['train_acc'] = train_acc_list
df['test_acc'] = test_acc_list
df['time'] = time_list
df.to_excel("savefile/RefineNet_camvid1.xlsx")
#----------------保存模型-------------------
if np.mod(epoch+1, 5) == 0:
torch.save(model.state_dict(), f'checkpoints/RefineNet_{epoch+1}.pth')
开始训练
train_ch13(model, train_loader, val_loader, lossf, optimizer, epochs_num,scheduler)训练结果

























 4303
4303











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










