(一)通俗解释:
①X1,X2就是我们的两个特征(年龄,工资)
Y是银行最终会借给我们多少钱
②找到最合适的一条线(想象一个高维)来,最好的拟合我们的数据点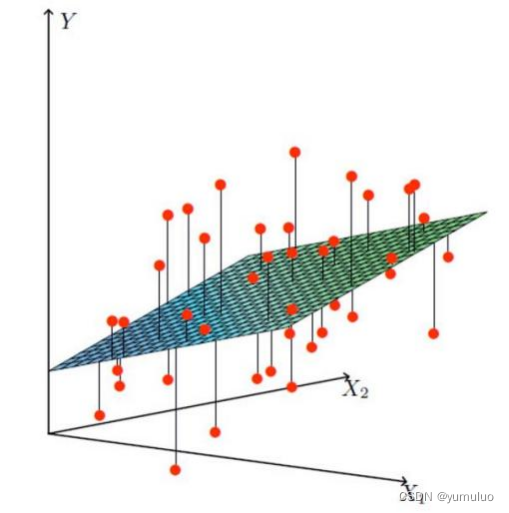
(二) 数学来了:
1.假设θ1是年龄的参数,θ2是工资的参数
2.拟合的平面:(θ0是偏置顶)
3.整合:
(三)误差:
1.真实值和预测值之间肯定是要存在差异的
(用 来表示该误差)
2.对于每个样本
(四)误差:
1.预测值与误差:
2.由于误差服从高斯分布:
3.合并二式:
附上代码:
import numpy as np
from utils.features import prepare_for_training
class LinearRegression:
def __init__(self,data,labels,polynomial_degree = 0,sinusoid_degree = 0,normalize_data=True):
"""
1.对数据进行预处理操作
2.先得到所有的特征个数
3.初始化参数矩阵
"""
(data_processed,
features_mean,
features_deviation) = prepare_for_training(data, polynomial_degree, sinusoid_degree,normalize_data=True)
self.data = data_processed
self.labels = labels
self.features_mean = features_mean
self.features_deviation = features_deviation
self.polynomial_degree = polynomial_degree
self.sinusoid_degree = sinusoid_degree
self.normalize_data = normalize_data
num_features = self.data.shape[1]
self.theta = np.zeros((num_features,1))
def train(self,alpha,num_iterations = 500):
"""
训练模块,执行梯度下降
"""
cost_history = self.gradient_descent(alpha,num_iterations)
return self.theta,cost_history
def gradient_descent(self,alpha,num_iterations):
"""
实际迭代模块,会迭代num_iterations次
"""
cost_history = []
for _ in range(num_iterations):
self.gradient_step(alpha)
cost_history.append(self.cost_function(self.data,self.labels))
return cost_history
def gradient_step(self,alpha):
"""
梯度下降参数更新计算方法,注意是矩阵运算
"""
num_examples = self.data.shape[0]
prediction = LinearRegression.hypothesis(self.data,self.theta)
delta = prediction - self.labels
theta = self.theta
theta = theta - alpha*(1/num_examples)*(np.dot(delta.T,self.data)).T
self.theta = theta
def cost_function(self,data,labels):
"""
损失计算方法
"""
num_examples = data.shape[0]
delta = LinearRegression.hypothesis(self.data,self.theta) - labels
cost = (1/2)*np.dot(delta.T,delta)/num_examples
return cost[0][0]
@staticmethod
def hypothesis(data,theta):
predictions = np.dot(data,theta)
return predictions
def get_cost(self,data,labels):
data_processed = prepare_for_training(data,
self.polynomial_degree,
self.sinusoid_degree,
self.normalize_data
)[0]
return self.cost_function(data_processed,labels)
def predict(self,data):
"""
用训练的参数模型,与预测得到回归值结果
"""
data_processed = prepare_for_training(data,
self.polynomial_degree,
self.sinusoid_degree,
self.normalize_data
)[0]
predictions = LinearRegression.hypothesis(data_processed,self.theta)
return predictions





















 1715
1715











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








