0 项目说明
**基于 U-Net 网络的遥感图像语义分割 **
提示:适合用于课程设计或毕业设计,工作量达标,源码开放
实验训练使用 Anaconda 版 Python 3.7 下的 TensorFlow-GPU1.8
后期图像生成由于 GPU 显存限制,使用 TensorFlow 的 CPU 版本进行计算预测图计算。
1 研究目的
U-Net 是一种由全卷积神经网络启发的对称结构网络,在医疗影像分割领域取得了很好的效果。 此次研究尝试使用 U-Net 网络在对多光谱遥感影像数据集上进行训练,尝试使用卷积神经网络自动分割出建筑,希望能够得到一种自动分割遥感影像的简便方法。
2 研究方法
首先提出了一种基于遥感图像类别比率的交叉熵损失函数——类别平衡交叉熵。并与应用于医疗图像分割的 U-Net 相结合,将其应用于遥感图像语义分割。
在 Inria Aerial Image Labeling Dataset 训练数据集上分别使用交叉熵损失函数和类别平衡交叉熵损失函数进行训练,得到两个训练好的卷积神经网络。再利用这两个网络在 Inria Aerial Image Labeling Dataset 测试数据集上生成预测图像进行比对。
3 研究结论
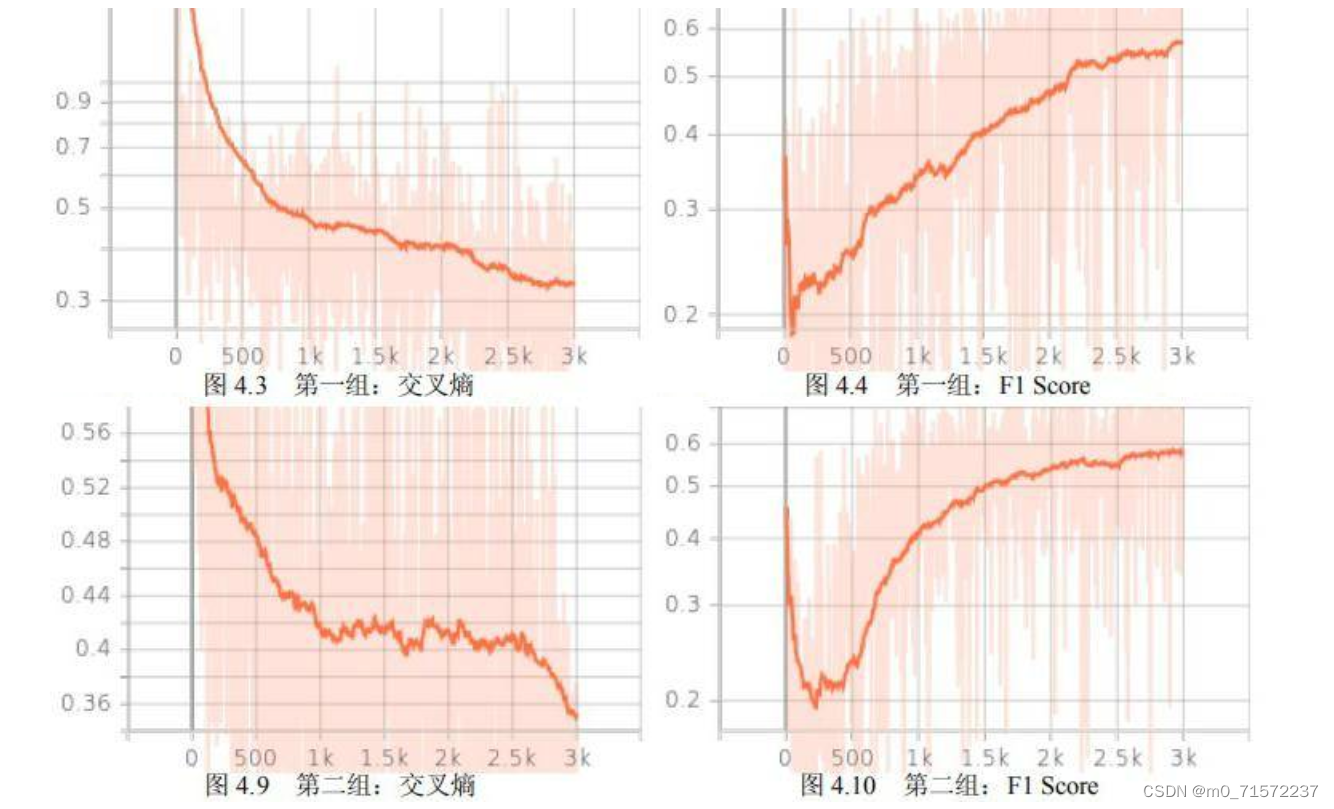
两种方法在正确率和交叉熵上没有太大差别,以交叉熵作为损失函数略优于以类别平衡交叉熵方法。但是这两种方法在F1 Score 上有较大差别。交叉熵的 F1 Score 为 0.47,类别平衡交叉熵的F1 Score 为 0.51,类别平衡交叉熵较交叉熵提高了 8.5%。
4 论文目录
第一章 绪论
1.1 研究背景与意义
1.2 国内外研究现状
1.2.1 语义分割研究现状
1.2.2 将深度学习应用于遥感图像分割现状
1.3 本文的主要工作
1.4 论文章节安排
第二章 背景知识
2.1 全卷积网络
2.2 使用全连接网络进行精准分割
2.2.1 线性结构网络
2.2.2 对称结构网络
第三章 实验设计
3.1 数据集选择及处理
3.2 图像处理流程设计
3.2.1 网络结构
3.2.2 卷积核初始化方案
3.2.3 输出图像恢复及优化
3.3 损失设计
3.3.1 交叉熵
3.3.2 带权重的交叉熵
3.3.3 类别平衡交叉熵
3.4 结果评估
3.5 具体实现
3.5.1 实验平台
3.5.2 模型实现
第四章 实验
4.1 网络初始化设计
4.2 实验结果
4.2.1 第一组:交叉熵
4.2.2 第二组:类别平衡交叉熵
4.2.3 结果分析
4.3 典型错误
4.3.1 建筑过大
4.3.2 错认
4.3.3 树木和光影
4.4 最终结果
第五章 总结和展望
5.1 全文总结
5.2 未来展望
致谢
参考文献
5 项目源码
from glob import glob
from PIL import Image
from os import path, makedirs
import numpy as np
from itertools import count, cycle
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s %(message)s')
color_class_dict = {(0,): 1, (255,): 0}
n_class = len(list(color_class_dict.keys()))
def name_generator(file_path, ex_name=None, cycle_num=None):
if len(file_path.split('.')) == 2: # file_path带扩展名
true_file_name = path.basename(file_path).split('.')[-2]
true_file_type = path.basename(file_path).split('.')[-1]
else: # file_path不带拓展名
true_file_name = path.basename(file_path)
true_file_type = None
if not ex_name:
true_file_type = None
elif ex_name is not None:
true_file_type = ex_name
if cycle_num is not None:
for i in cycle(range(cycle_num)):
if true_file_type is not None:
yield true_file_name + '_' + str(i) + '.' + true_file_type
else:
yield true_file_name + '_' + str(i)
else:
for i in count(0):
if true_file_type is not None:
yield true_file_name + '_' + str(i) + '.' + true_file_type
else:
yield true_file_name + '_' + str(i)
def resize_image(image_path, new_width, new_height, save_dir=None):
image = Image.open(image_path)
image = image.resize((new_width, new_height))
if save_dir is not None:
file_name = path.basename(image_path)
image.save(path.join(save_dir, file_name))
else:
image.save(image_path)
def split_image(image_path,
split_width,
split_height,
save_dir,
save_as_img=False):
# 按下面顺序分割:
# 1 2 3
# 4 5 6
image = Image.open(image_path)
image_width, image_height = image.size
if image_width % split_width or image_height % split_height:
raise ValueError('该图像大小为:{}x{};不能被等分为{}x{}的图像'.format(
image_width, image_height, split_width, split_height))
new_name = name_generator(image_path, ex_name=False)
for i in range(0, image_height, split_height):
for j in range(0, image_width, split_width):
cutting_box = (j, i, j + split_width, i + split_height)
slice_of_image = image.crop(cutting_box)
if save_as_img:
slice_of_image.save(
path.join(save_dir,
next(new_name) + '.png'))
else:
slice_of_image = np.array(slice_of_image)
np.save(path.join(save_dir, next(new_name)), slice_of_image)
def glut_image(image_list, glut_cols, glut_rows, image_width, image_height,
save_path):
glutted_image = Image.new(
'RGB', (image_width * glut_cols, image_height * glut_rows))
k = 0
for i in range(glut_rows):
for j in range(glut_cols):
# 判断image_list是不是字符串
# paste_it = Image.open(image_list[k])
paste_it = image_list[k]
glutted_image.paste(paste_it, (j * image_width, i * image_height))
k += 1
glutted_image.save(save_path)
def color_to_class(image_path, save_path=None):
raw_image = np.load(image_path)
raw_image = np.reshape(raw_image,
(raw_image.shape[0], raw_image.shape[1], -1))
[rows, cols, _] = raw_image.shape
classed_image = np.zeros((rows, cols, n_class))
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(cols):
classed_image[i, j, color_class_dict[tuple(raw_image[i, j])]] = 1
if save_path is not None:
np.save(path.join(save_path,
path.basename(image_path).split('.')[-2]),
classed_image)
else:
return classed_image
def output_map_to_class(output_map):
most_possible_label = np.argmax(output_map, 2)
classed_image = np.zeros(shape=output_map.shape)
[rows, cols] = most_possible_label.shape
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(cols):
classed_image[i, j, most_possible_label[i, j]] = 1
return classed_image
def class_to_color(classed_image):
reverse_color_class_dict = dict(
zip(color_class_dict.values(), color_class_dict.keys()))
colored_image = np.zeros(shape=(classed_image.shape[0],
classed_image.shape[1],
len(list(color_class_dict.keys())[0])))
for i in range(classed_image.shape[0]):
for j in range(classed_image.shape[1]):
for k in range(n_class):
if classed_image[i][j][k] == 1:
colored_image[i][j] = reverse_color_class_dict[k]
return colored_image
6 最后
**项目分享: ** https://gitee.com/asoonis/htw




















 997
997











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








