前言
公司新接的一个项目,需要JAVA Modbus串口通信驱动一个设备运行,
一、Modbus是什么?
Modbus是一种串行通信协议,是Modicon公司(现在的施耐德电气Schneider Electric)于1979年为使用可编程逻辑控制器(PLC)通信而发表。Modbus已经成为工业领域通信协议的业界标准(De facto),并且现在是工业电子设备之间常用的连接方式。
Modbus协议是一个master/slave架构的协议。有一个节点是master节点,其他使用Modbus协议参与通信的节点是slave节点。每一个slave设备都有一个唯一的地址。在串行和MB+网络中,只有被指定为主节点的节点可以启动一个命令(在以太网上,任何一个设备都能发送一个Modbus命令,但是通常也只有一个主节点设备启动指令)。
二、使用步骤
1.需要的资源

2.引入资源
后台引入jar,我这里是个maven项目,我是把这几个jar作为本地jar引入的,在pom中直接插入以下内容
<dependency>
<groupId>com.serotonin</groupId>
<artifactId>modbus4j</artifactId>
<version>3.0.5</version>
<scope>system</scope>
<systemPath>${project.basedir}/src/main/resources/lib/modbus4j-3.0.5.jar</systemPath>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.RXTXcomm</groupId>
<artifactId>RXTXcomm</artifactId>
<version>3.0.5</version>
<scope>system</scope>
<systemPath>${project.basedir}/src/main/resources/lib/RXTXcomm.jar</systemPath>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.scream3r</groupId>
<artifactId>jssc</artifactId>
<version>2.8.0</version>
<scope>system</scope>
<systemPath>${project.basedir}/src/main/resources/lib/jssc-2.8.0.jar</systemPath>
</dependency>
resources目录下新建lib放入jar包

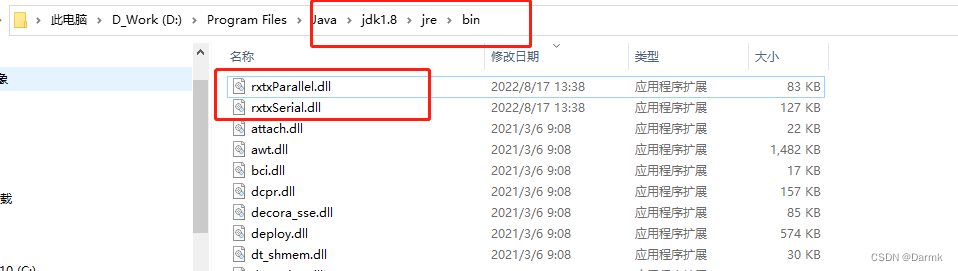
将 rxtxParallel.dll,rxtxSerial.dll放到JDK安装目录 jre/bin 下
3.新建代码
将这三个类直接放到项目中
SerialInputStream.java
package com.sower.pv.utils;
/*
* To change this template, choose Tools | Templates
* and open the template in the editor.
*/
import jssc.SerialPort;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* Class that wraps a {@link SerialPort} to provide {@link InputStream}
* functionality. This stream also provides support for performing blocking
* reads with timeouts.
* <br>
* It is instantiated by passing the constructor a {@link SerialPort} instance.
* Do not create multiple streams for the same serial port unless you implement
* your own synchronization.
*
* @author Charles Hache <chalz@member.fsf.org>
*
* Attribution: https://github.com/therealchalz/java-simple-serial-connector
*
*/
public class SerialInputStream extends InputStream {
private SerialPort serialPort;
private int defaultTimeout = 0;
/**
* Instantiates a SerialInputStream for the given {@link SerialPort} Do not
* create multiple streams for the same serial port unless you implement
* your own synchronization.
*
* @param sp The serial port to stream.
*/
public SerialInputStream(SerialPort sp) {
serialPort = sp;
}
/**
* Set the default timeout (ms) of this SerialInputStream. This affects
* subsequent calls to {@link #read()}, {@link #(int[])}, and
* {@link #(int[], int, int)} The default timeout can be 'unset'
* by setting it to 0.
*
* @param time The timeout in milliseconds.
*/
public void setTimeout(int time) {
defaultTimeout = time;
}
/**
* Reads the next byte from the port. If the timeout of this stream has been
* set, then this method blocks until data is available or until the timeout
* has been hit. If the timeout is not set or has been set to 0, then this
* method blocks indefinitely.
*/
@Override
public int read() throws IOException {
return read(defaultTimeout);
}
/**
* The same contract as {@link #read()}, except overrides this stream's
* default timeout with the given timeout in milliseconds.
*
* @param timeout The timeout in milliseconds.
* @return The read byte.
* @throws IOException On serial port error or timeout
*/
public int read(int timeout) throws IOException {
byte[] buf = new byte[1];
try {
if (timeout > 0) {
buf = serialPort.readBytes(1, timeout);
} else {
buf = serialPort.readBytes(1);
}
return buf[0];
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IOException(e);
}
}
/**
* Non-blocking read of up to buf.length bytes from the stream. This call
* behaves as read(buf, 0, buf.length) would.
*
* @param buf The buffer to fill.
* @return The number of bytes read, which can be 0.
* @throws IOException on error.
*/
@Override
public int read(byte[] buf) throws IOException {
return read(buf, 0, buf.length);
}
/**
* Non-blocking read of up to length bytes from the stream. This method
* returns what is immediately available in the input buffer.
*
* @param buf The buffer to fill.
* @param offset The offset into the buffer to start copying data.
* @param length The maximum number of bytes to read.
* @return The actual number of bytes read, which can be 0.
* @throws IOException on error.
*/
@Override
public int read(byte[] buf, int offset, int length) throws IOException {
if (buf.length < offset + length) {
length = buf.length - offset;
}
int available = this.available();
if (available > length) {
available = length;
}
try {
byte[] readBuf = serialPort.readBytes(available);
// System.arraycopy(readBuf, 0, buf, offset, length);
System.arraycopy(readBuf, 0, buf, offset, readBuf.length);
return readBuf.length;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IOException(e);
}
}
/**
* Blocks until buf.length bytes are read, an error occurs, or the default
* timeout is hit (if specified). This behaves as blockingRead(buf, 0,
* buf.length) would.
*
* @param buf The buffer to fill with data.
* @return The number of bytes read.
* @throws IOException On error or timeout.
*/
public int blockingRead(byte[] buf) throws IOException {
return blockingRead(buf, 0, buf.length, defaultTimeout);
}
/**
* The same contract as {@link #blockingRead(byte[])} except overrides this
* stream's default timeout with the given one.
*
* @param buf The buffer to fill.
* @param timeout The timeout in milliseconds.
* @return The number of bytes read.
* @throws IOException On error or timeout.
*/
public int blockingRead(byte[] buf, int timeout) throws IOException {
return blockingRead(buf, 0, buf.length, timeout);
}
/**
* Blocks until length bytes are read, an error occurs, or the default
* timeout is hit (if specified). Saves the data into the given buffer at
* the specified offset. If the stream's timeout is not set, behaves as
* {@link #read(byte[], int, int)} would.
*
* @param buf The buffer to fill.
* @param offset The offset in buffer to save the data.
* @param length The number of bytes to read.
* @return the number of bytes read.
* @throws IOException on error or timeout.
*/
public int blockingRead(byte[] buf, int offset, int length) throws IOException {
return blockingRead(buf, offset, length, defaultTimeout);
}
/**
* The same contract as {@link #blockingRead(byte[], int, int)} except
* overrides this stream's default timeout with the given one.
*
* @param buf The buffer to fill.
* @param offset Offset in the buffer to start saving data.
* @param length The number of bytes to read.
* @param timeout The timeout in milliseconds.
* @return The number of bytes read.
* @throws IOException On error or timeout.
*/
public int blockingRead(byte[] buf, int offset, int length, int timeout) throws IOException {
if (buf.length < offset + length) {
throw new IOException("Not enough buffer space for serial data");
}
if (timeout < 1) {
return read(buf, offset, length);
}
try {
byte[] readBuf = serialPort.readBytes(length, timeout);
System.arraycopy(readBuf, 0, buf, offset, length);
return readBuf.length;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IOException(e);
}
}
@Override
public int available() throws IOException {
int ret;
try {
ret = serialPort.getInputBufferBytesCount();
if (ret >= 0) {
return ret;
}
throw new IOException("Error checking available bytes from the serial port.");
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IOException("Error checking available bytes from the serial port.");
}
}
}
SerialOutputStream.java
package com.sower.pv.utils;
/**
*
* Copyright (c) 2009-2020 Freedomotic Team http://www.freedomotic-iot.com
*
* This file is part of Freedomotic
*
* This Program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under
* the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software
* Foundation; either version 2, or (at your option) any later version.
*
* This Program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
* ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS
* FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more
* details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with
* Freedomotic; see the file COPYING. If not, see
* <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
*/
import jssc.SerialPort;
import jssc.SerialPortException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
/**
* Class that wraps a {@link SerialPort} to provide {@link OutputStream}
* functionality.
* <br>
* It is instantiated by passing the constructor a {@link SerialPort} instance.
* Do not create multiple streams for the same serial port unless you implement
* your own synchronization.
*
* @author Charles Hache <chalz@member.fsf.org>
*
* Attribution: https://github.com/therealchalz/java-simple-serial-connector
*
*/
public class SerialOutputStream extends OutputStream {
SerialPort serialPort;
/**
* Instantiates a SerialOutputStream for the given {@link SerialPort} Do not
* create multiple streams for the same serial port unless you implement
* your own synchronization.
*
* @param sp The serial port to stream.
*/
public SerialOutputStream(SerialPort sp) {
serialPort = sp;
}
@Override
public void write(int b) throws IOException {
try {
serialPort.writeInt(b);
} catch (SerialPortException e) {
throw new IOException(e);
}
}
@Override
public void write(byte[] b) throws IOException {
write(b, 0, b.length);
}
@Override
public void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException {
byte[] buffer = new byte[len];
System.arraycopy(b, off, buffer, 0, len);
try {
serialPort.writeBytes(buffer);
} catch (SerialPortException e) {
throw new IOException(e);
}
}
}
SerialPortWrapperImpl.java
package com.sower.pv.utils;
/**
*
* Copyright (c) 2009-2020 Freedomotic Team http://www.freedomotic-iot.com
*
* This file is part of Freedomotic
*
* This Program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under
* the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software
* Foundation; either version 2, or (at your option) any later version.
*
* This Program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
* ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS
* FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more
* details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with
* Freedomotic; see the file COPYING. If not, see
* <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
*/
import com.serotonin.modbus4j.serial.SerialPortWrapper;
import jssc.SerialPort;
import jssc.SerialPortException;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
/**
*
*/
public class SerialPortWrapperImpl implements SerialPortWrapper {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(com.sower.pv.utils.SerialPortWrapperImpl.class);
private SerialPort port;
private String commPortId;
private int baudRate;
private int dataBits;
private int stopBits;
private int parity;
private int flowControlIn;
private int flowControlOut;
public SerialPortWrapperImpl(String commPortId, int baudRate, int dataBits, int stopBits, int parity, int flowControlIn,
int flowControlOut) {
this.commPortId = commPortId;
this.baudRate = baudRate;
this.dataBits = dataBits;
this.stopBits = stopBits;
this.parity = parity;
this.flowControlIn = flowControlIn;
this.flowControlOut = flowControlOut;
port = new SerialPort(this.commPortId);
}
@Override
public void close() throws Exception {
port.closePort();
//listeners.forEach(PortConnectionListener::closed);
LOG.debug("Serial port {} closed", port.getPortName());
}
@Override
public void open() {
try {
port.openPort();
port.setParams(this.getBaudRate(), this.getDataBits(), this.getStopBits(), this.getParity());
port.setFlowControlMode(this.getFlowControlIn() | this.getFlowControlOut());
//listeners.forEach(PortConnectionListener::opened);
LOG.debug("Serial port {} opened", port.getPortName());
} catch (SerialPortException ex) {
LOG.error("Error opening port : {} for {} ", port.getPortName(), ex);
}
}
@Override
public InputStream getInputStream() {
return new SerialInputStream(port);
}
@Override
public OutputStream getOutputStream() {
return new SerialOutputStream(port);
}
@Override
public int getBaudRate() {
return baudRate;
//return SerialPort.BAUDRATE_9600;
}
// @Override
// public int getFlowControlIn() {
// return flowControlIn;
// //return SerialPort.FLOWCONTROL_NONE;
// }
//
// @Override
// public int getFlowControlOut() {
// return flowControlOut;
// //return SerialPort.FLOWCONTROL_NONE;
// }
public int getFlowControlIn() {
return flowControlIn;
}
public int getFlowControlOut() {
return flowControlOut;
}
@Override
public int getDataBits() {
return dataBits;
//return SerialPort.DATABITS_8;
}
@Override
public int getStopBits() {
return stopBits;
//return SerialPort.STOPBITS_1;
}
@Override
public int getParity() {
return parity;
//return SerialPort.PARITY_NONE;
}
}
调用例子,运行main方法,我这里是更改线圈的指令
package com.sower.pv.utils;
import com.serotonin.modbus4j.ModbusFactory;
import com.serotonin.modbus4j.ModbusMaster;
import com.serotonin.modbus4j.exception.ModbusInitException;
import com.serotonin.modbus4j.exception.ModbusTransportException;
import com.serotonin.modbus4j.msg.*;
import com.serotonin.modbus4j.serial.SerialPortWrapper;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 通过串口解析MODBUS协议
* @author yaohj
*/
public class CollectionMain {
// 设定MODBUS网络上从站地址
private final static int SLAVE_ADDRESS = 68;
//串行波特率
private final static int BAUD_RATE = 9600;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SerialPortWrapper serialParameters = new
SerialPortWrapperImpl("COM3", BAUD_RATE, 8, 1, 0, 0, 0);
/* 创建ModbusFactory工厂实例 */
ModbusFactory modbusFactory = new ModbusFactory();
/* 创建ModbusMaster实例 */
ModbusMaster master = modbusFactory.createRtuMaster(serialParameters);
/* 初始化 */
try {
master.init();
// readHoldingRegistersTest(master, SLAVE_ADDRESS, 99, 24);
try {
writeCoil(master,SLAVE_ADDRESS,1,true);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
readCoilTest(master,SLAVE_ADDRESS,2,1);
} catch (ModbusInitException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
master.destroy();
}
}
/**
* 读保持寄存器上的内容
* @param master 主站
* @param slaveId 从站地址
* @param start 起始地址的偏移量
* @param len 待读寄存器的个数
*/
private static void readHoldingRegistersTest(ModbusMaster master, int slaveId, int start, int len) {
try {
ReadHoldingRegistersRequest request = new ReadHoldingRegistersRequest(slaveId, start, len);
ReadHoldingRegistersResponse response = (ReadHoldingRegistersResponse)master.send(request);
if (response.isException()) {
System.out.println("Exception response: message=" + response.getExceptionMessage());
} else {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(response.getShortData()));
short[] list = response.getShortData();
for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
System.out.print(list[i] + " ");
}
}
} catch (ModbusTransportException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void readCoilTest(ModbusMaster master, int slaveId, int start, int len) {
try {
ReadCoilsRequest request=new ReadCoilsRequest(slaveId,start,len);
ReadCoilsResponse response=(ReadCoilsResponse) master.send(request);
if (response.isException()) {
System.out.println("Exception response: message=" + response.getExceptionMessage());
} else {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(response.getShortData()));
System.out.println(response.getData()[0]);
short[] list = response.getShortData();
for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
System.out.print(list[i] + " ===");
}
}
} catch (ModbusTransportException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void writeCoil(ModbusMaster master, int slaveId, int offset, boolean value) throws Exception{
WriteCoilRequest request=new WriteCoilRequest(slaveId,offset,value);
// ByteQueue queue = new ByteQueue();
WriteCoilResponse response=(WriteCoilResponse) master.send(request);
// WriteRegisterResponse response = (WriteRegisterResponse) master.send(request);
if (response.isException()){
System.out.println("写线圈错误,错误信息是" + response.getExceptionMessage());
}else{
System.out.println("写线圈指令发送成功!");
}
}
}
总结
以上就是今天要讲的内容,本文仅仅简单介绍了Java Modbus RTU串口通信。


























 1029
1029

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








