SPATIAL TRANSFORMER NETWORKS

在这个教程中,我们将学习利用视觉注意力机制(spatial transformer networks DeepMind paper )增强我们的网络。
Spatial transformer networks (以下简称 STN)是任何空间变换的可微注意力概括。STN 允许一个神经网络学习如何执行空间变换,从而可以增强模型的几何鲁棒性。例如,可以截取ROI,尺度变换,角度旋转或更多的放射变换等等。
STN 一个很重要的特性就是在可以插入到任意的CNN里,只需要少量的修改。
Loading the data
本节中,我们使用 MNIST 数据集,利用一个标准的卷积网络并且使用 STN 进行增强。
from six.moves import urllib
opener = urllib.request.build_opener()
opener.addheaders = [('User-agent', 'Mozilla/5.0')]
urllib.request.install_opener(opener)
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
datasets.MNIST(root='../../../datasets',
train=True,
download=True,
transform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))])),
batch_size=64,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=4)
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
datasets.MNIST(root='../../../datasets',
train=False,
download=True,
transform=transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))])),
batch_size=64,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=4)
Depicting spatial transformer networks
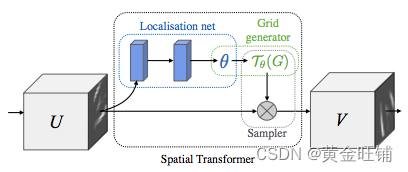
STN 主要有3个结构:
- Localisation net:是一个常规的 CNN,回归转换参数,转换的参数从来没有在数据集里学习过,网络自动学习空间变换信息从而可以增强全局的准确率;
- Grid generator:生成与输出图像中的每个像素对应的输入图像中的坐标网格。
- Sample:使用变换的参数并将其应用于输入图像。
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 10, kernel_size=5)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(10, 20, kernel_size=5)
self.conv2_drop = nn.Dropout2d()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(320, 50)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(50, 10)
# Spatial transformer localization-network
self.localization = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 8, kernel_size=7),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Conv2d(8, 10, kernel_size=5),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2),
nn.ReLU(True)
)
# Regressor for the 3 * 2 affine matrix
self.fc_loc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(10 * 3 * 3, 32),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Linear(32, 3 * 2)
)
# Initialize the weights/bias with identity transformation
self.fc_loc[2].weight.data.zero_()
self.fc_loc[2].bias.data.copy_(torch.tensor(
[1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0], dtype=torch.float))
# Spatial transformer network forward function
def stn(self, x):
xs = self.localization(x) # 特征提取
xs = xs.view(-1, 10 * 3 * 3) # feature map resize到对应的维度
theta = self.fc_loc(xs) # 局部网络 回归 参数 θ
theta = theta.view(-1, 2, 3) # 参数θ resize 到对应的维度
grid = F.affine_grid(theta, x.size()) # 对于 θ 计算输出对应的原图位置
x = F.grid_sample(x, grid) # 对原图进行 sample 得到目标输出
return x
def forward(self, x):
x = self.stn(x)
x = F.relu(F.max_pool2d(self.conv1(x), 2))
x = F.relu(F.max_pool2d(self.conv2_drop(self.conv2(x)), 2))
x = x.view(-1, 320)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.dropout(x, training=self.training)
x = self.fc2(x)
return F.log_softmax(x, dim=1)
model = Net().to(device=device)
Training the model
SGD 算法训练网络,网络以可监督的方式训练分类任务,同时自动学习 STN。
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
def train(epoch):
model.train()
for batch_idx, (data, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(data)
loss = F.nll_loss(output, target)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if batch_idx % 500 == 0:
print('Train Epoch: {} [{}/{} ({:.0f}%)]\tLoss: {:.6f}'.format(
epoch, batch_idx * len(data), len(train_loader.dataset),
100. * batch_idx / len(train_loader), loss.item()))
#
# A simple test procedure to measure the STN performances on MNIST.
#
def test():
with torch.no_grad():
model.eval()
test_loss = 0
correct = 0
for data, target in test_loader:
data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device)
output = model(data)
# sum up batch loss
test_loss += F.nll_loss(output, target, size_average=False).item()
# get the index of the max log-probability
pred = output.max(1, keepdim=True)[1]
correct += pred.eq(target.view_as(pred)).sum().item()
test_loss /= len(test_loader.dataset)
print('\nTest set: Average loss: {:.4f}, Accuracy: {}/{} ({:.0f}%)\n'
.format(test_loss, correct, len(test_loader.dataset),
100. * correct / len(test_loader.dataset)))
Visualizing the STN results
def convert_image_np(inp):
"""Convert a Tensor to numpy image."""
inp = inp.numpy().transpose((1, 2, 0))
mean = np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406])
std = np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
inp = std * inp + mean
inp = np.clip(inp, 0, 1)
return inp
# We want to visualize the output of the spatial transformers layer
# after the training, we visualize a batch of input images and
# the corresponding transformed batch using STN.
def visualize_stn():
with torch.no_grad():
# Get a batch of training data
data = next(iter(test_loader))[0].to(device)
input_tensor = data.cpu()
transformed_input_tensor = model.stn(data).cpu()
in_grid = convert_image_np(
torchvision.utils.make_grid(input_tensor))
out_grid = convert_image_np(
torchvision.utils.make_grid(transformed_input_tensor))
# Plot the results side-by-side
f, axarr = plt.subplots(1, 2)
axarr[0].imshow(in_grid)
axarr[0].set_title('Dataset Images')
axarr[1].imshow(out_grid)
axarr[1].set_title('Transformed Images')
for epoch in range(1, 20 + 1):
train(epoch)
test()
# Visualize the STN transformation on some input batch
visualize_stn()
plt.ioff()
plt.show()
























 645
645











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










