一:定义:
Strategy:Define a family of algorithms, encapsulate each one, and make them interchangeable. Strategy lets the algorithm vary independently from clients that use it.
二:引入
假设现在要设计一个贩卖各类书籍的电子商务网站的购物车(Shopping Cat)系统。一个最简单的情况就是把所有货品的单价乘上数量,但是实际情况肯定比这要复杂。
比如:
- 本网站可能对所有的儿童类图书实行每本一元的折扣;
- 对计算机类图书提供每本7%的促销折扣,而对电子类图书有3%的折扣;
- 对其余的图书没有折扣。
- 未来可能还会有新的打折策略。
由于有这样复杂的折扣算法,使得价格计算问题需要系统地解决。
方案一:业务逻辑放在各具体子类

 /**/
/*
/**/
/* *各子类实现销售价格算法
*各子类实现销售价格算法 */
*/

 public
abstract
class
Book
...
{
public
abstract
class
Book
...
{ private double price;
private double price; private String name;
private String name;

 public String getName() ...{
public String getName() ...{ return name;
return name; }
}
 public void setName(String name) ...{
public void setName(String name) ...{ this.name = name;
this.name = name; }
}
 public double getPrice() ...{
public double getPrice() ...{ return price;
return price; }
}
 public void setPrice(double price) ...{
public void setPrice(double price) ...{ this.price = price;
this.price = price; }
}
 public abstract double getSalePrice() ;
public abstract double getSalePrice() ;
 }
}


 public
class
CsBook
extends
Book
...
{
public
class
CsBook
extends
Book
...
{ public CsBook(String name,double price)
public CsBook(String name,double price)
 ...{
...{ this.setName(name);
this.setName(name); this.setPrice(price);
this.setPrice(price); }
}
 public double getSalePrice()
public double getSalePrice()
 ...{
...{ return this.getPrice()*0.93;
return this.getPrice()*0.93; }
} }
}


 public
class
ChildrenBook
extends
Book
...
{
public
class
ChildrenBook
extends
Book
...
{

 public ChildrenBook(String name, double price) ...{
public ChildrenBook(String name, double price) ...{ this.setName(name);
this.setName(name); this.setPrice(price);
this.setPrice(price); }
}

 public double getSalePrice() ...{
public double getSalePrice() ...{ return this.getPrice() - 1;
return this.getPrice() - 1; }
} }
}


 public
class
Client
...
{
public
class
Client
...
{
 public static void main(String args[])
public static void main(String args[])
 ...{
...{ Book csBook1=new CsBook("Think in java",45);
Book csBook1=new CsBook("Think in java",45); Book childrenBook1=new ChildrenBook("Hello",20);
Book childrenBook1=new ChildrenBook("Hello",20);
 System.out.println(csBook1.getName()+":"+csBook1.getSalePrice());
System.out.println(csBook1.getName()+":"+csBook1.getSalePrice()); System.out.println(childrenBook1.getName()+":"+childrenBook1.getSalePrice());
System.out.println(childrenBook1.getName()+":"+childrenBook1.getSalePrice()); }
} }
}
问题:每个子类必须都各自实现打折算法,即使打折算法相同。所以code reuse不好
方案二:
 //
把打折策略代码提到父类来实现code reuse
//
把打折策略代码提到父类来实现code reuse

 public
abstract
class
Book
...
{
public
abstract
class
Book
...
{ private double price;
private double price; private String name;
private String name;

 public String getName() ...{
public String getName() ...{ return name;
return name; }
}
 public void setName(String name) ...{
public void setName(String name) ...{ this.name = name;
this.name = name; }
}
 public double getPrice() ...{
public double getPrice() ...{ return price;
return price; }
}
 public void setPrice(double price) ...{
public void setPrice(double price) ...{ this.price = price;
this.price = price; }
}
 // 销售价格
// 销售价格 public static double toSalePrice(Book book)
public static double toSalePrice(Book book)
 ...{
...{ if (book instanceof ChildrenBook)
if (book instanceof ChildrenBook)
 ...{
...{ return book.getPrice()-1;
return book.getPrice()-1; }
} else if (book instanceof CsBook)
else if (book instanceof CsBook)
 ...{
...{ return book.getPrice()*0.93;
return book.getPrice()*0.93; }
} return 0;
return 0; }
} }
}



 public
class
Client
...
{
public
class
Client
...
{

 public static void main(String args[])
public static void main(String args[])
 ...{
...{ Book csBook1=new CsBook("Think in java",45);
Book csBook1=new CsBook("Think in java",45); Book childrenBook1=new ChildrenBook("Hello",20);
Book childrenBook1=new ChildrenBook("Hello",20); System.out.println(csBook1.getName()+":"+Book.toSalePrice(csBook1));
System.out.println(csBook1.getName()+":"+Book.toSalePrice(csBook1)); System.out.println(childrenBook1.getName()+":"+Book.toSalePrice(childrenBook1));
System.out.println(childrenBook1.getName()+":"+Book.toSalePrice(childrenBook1)); }
} }
}

toSalePrice方法是比较容易change的地方,如果策略复杂用if判断比较乱,并且策略修改或增加时需改变原代码。
方案三:策略模式
code reuse时最好用合成(HAS-A)而不用(IS-A),更加灵活。

 public
abstract
class
Book
...
{
public
abstract
class
Book
...
{ private double price;
private double price; private String name;
private String name; private DiscountStrategy discountStrategy;//折扣策略
private DiscountStrategy discountStrategy;//折扣策略

 public String getName() ...{
public String getName() ...{ return name;
return name; }
}
 public void setName(String name) ...{
public void setName(String name) ...{ this.name = name;
this.name = name; }
}
 public double getPrice() ...{
public double getPrice() ...{ return price;
return price; }
}
 public void setPrice(double price) ...{
public void setPrice(double price) ...{ this.price = price;
this.price = price; }
}

 public DiscountStrategy getDiscountStrategy() ...{
public DiscountStrategy getDiscountStrategy() ...{ return discountStrategy;
return discountStrategy; }
}
 public void setDiscountStrategy(DiscountStrategy discountStrategy) ...{
public void setDiscountStrategy(DiscountStrategy discountStrategy) ...{ this.discountStrategy = discountStrategy;
this.discountStrategy = discountStrategy; }
} public double getSalePrice()
public double getSalePrice() 
 ...{
...{ return discountStrategy.getSalePrice(price);
return discountStrategy.getSalePrice(price); }
}
 }
}


 public
class
CsBook
extends
Book
...
{
public
class
CsBook
extends
Book
...
{ public CsBook(String name,double price)
public CsBook(String name,double price)
 ...{
...{ this.setName(name);
this.setName(name); this.setPrice(price);
this.setPrice(price); }
} }
}


 public
abstract
class
DiscountStrategy
...
{
public
abstract
class
DiscountStrategy
...
{ public abstract double getSalePrice(double orgPrice) ;
public abstract double getSalePrice(double orgPrice) ; }
}


 /**/
/*
/**/
/* * 按折扣率打折
* 按折扣率打折 */
*/

 public
class
PercentDiscountStrategy
extends
DiscountStrategy
...
{
public
class
PercentDiscountStrategy
extends
DiscountStrategy
...
{
 private double percent;//折扣率
private double percent;//折扣率 public PercentDiscountStrategy(double percent)
public PercentDiscountStrategy(double percent)
 ...{
...{ this.percent=percent;
this.percent=percent; }
}
 public double getPercent() ...{
public double getPercent() ...{ return percent;
return percent; }
}
 public void setPercent(double percent) ...{
public void setPercent(double percent) ...{ this.percent = percent;
this.percent = percent; }
}
 public double getSalePrice(double orgPrice)
public double getSalePrice(double orgPrice) 
 ...{
...{ return orgPrice*percent;
return orgPrice*percent; }
} }
}



 public
class
Client
...
{
public
class
Client
...
{
 public static void main(String args[])
public static void main(String args[])
 ...{
...{ Book csBook1=new CsBook("Think in java",45);
Book csBook1=new CsBook("Think in java",45); csBook1.setDiscountStrategy(new NoDiscountStrategy());
csBook1.setDiscountStrategy(new NoDiscountStrategy()); System.out.println(csBook1.getName()+":"+csBook1.getSalePrice());
System.out.println(csBook1.getName()+":"+csBook1.getSalePrice()); csBook1.setDiscountStrategy(new PercentDiscountStrategy(0.95));
csBook1.setDiscountStrategy(new PercentDiscountStrategy(0.95)); System.out.println(csBook1.getName()+":"+csBook1.getSalePrice());
System.out.println(csBook1.getName()+":"+csBook1.getSalePrice()); Book childrenBook1=new ChildrenBook("Hello",20);
Book childrenBook1=new ChildrenBook("Hello",20);
 childrenBook1.setDiscountStrategy(new PercentDiscountStrategy(0.9));
childrenBook1.setDiscountStrategy(new PercentDiscountStrategy(0.9)); System.out.println(childrenBook1.getName()+":"+childrenBook1.getSalePrice());
System.out.println(childrenBook1.getName()+":"+childrenBook1.getSalePrice()); }
} }
}
三:结构
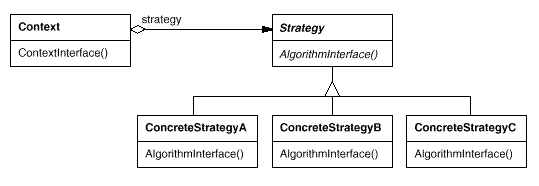
四:实际应用
- AWT中的 LayoutManager
五:适用情形
Use the Strategy pattern when
- many related classes differ only in their behavior. Strategies provide a way to configure a class with one of many behaviors.
- you need different variants of an algorithm. For example, you might define algorithms reflecting different space/time trade-offs. Strategies can be used when these variants are implemented as a class hierarchy of algorithms .
- an algorithm uses data that clients shouldn't know about. Use the Strategy pattern to avoid exposing complex, algorithm-specific data structures.
- a class defines many behaviors, and these appear as multiple conditional statements in its operations. Instead of many conditionals, move related conditional branches into their own Strategy class.
参考文献:
1:阎宏,《Java与模式》,电子工业出版社
2:Eric Freeman & Elisabeth Freeman,《Head First Design Pattern》,O'REILLY
3:GOF ,《designpatterns-elements.of.reuseable.object-oriented.software》






















 907
907











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








