第一部分:
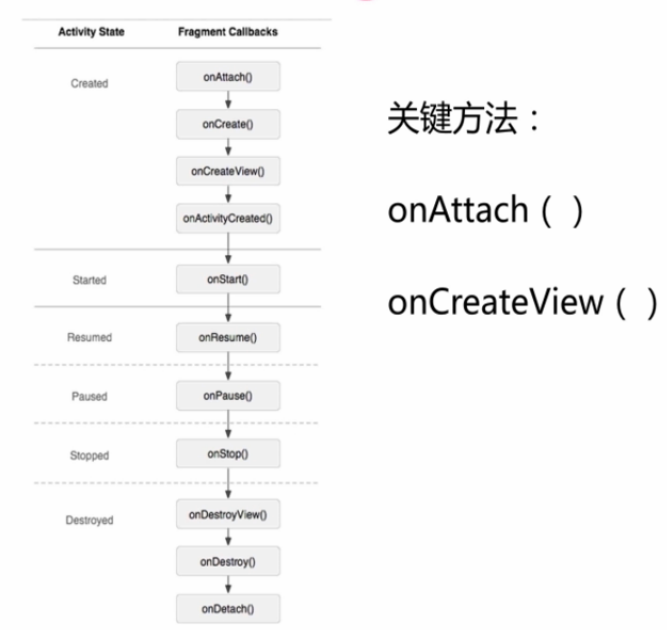
1. Fragment的生命周期:
2. 案例:
第一步:创建布局fragment2,用来作为Fragment3和Fragment4的布局。只包含一个TextView控件,其中ID为text。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="text" />
</LinearLayout>
package com.example.fragment;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MyFragment3 extends Fragment{
/*
* 每次创建都会绘制Fragment的View组件时回调该方法。
* */
@Override
// 加载自己的布局
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// 把layout布局文件转换成View对象
// 第一个参数resource:Fragment需要加载的布局文件
// 第二个参数root:加载layout的父ViewGroup
// attactToRoot:false,不返回父ViewGroup
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment2, container, false);
TextView tv = (TextView)view.findViewById(R.id.text);// 这里加了view是因为返回对象必须是一个view。
tv.setText("第一个Fragment");
Log.i("Main", "Fragment1---onCreateView()");
return view;
}
/*
* 当Fragment被添加到Activity的时候会回调这个方法,这个方法只会去调用一次。
* */
@Override
public void onAttach(Activity activity) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onAttach(activity);
Log.i("Main", "Fragment1---onAttach()");
}
/*
* 创建Fragment时会调用。只会调用一次
* */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
Log.i("Main", "Fragment1---onCreate()");
}
/*
* 创建以后的一个状态,当Fragment所在的Activity启动完成后调用。
* */
@Override
public void onActivityCreated(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState);
Log.i("Main", "Fragment1---onActivityCreated()");
}
/*
* 启动Fragment。
* */
@Override
public void onStart() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onStart();
Log.i("Main", "Fragment1---onStart()");
}
/*
* 恢复Fragment时会被回调,调用onStart()方法后面一定会调用这个方法。
* */
@Override
public void onResume() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onResume();
Log.i("Main", "Fragment1---onResume()");
}
/*
* 暂停Fragment。
* */
@Override
public void onPause() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onPause();
Log.i("Main", "Fragment1---onPause()");
}
/*
* 停止Fragment。
* */
@Override
public void onStop() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onStop();
Log.i("Main", "Fragment1---onStop()");
}
/*
* 销毁Fragment所包含的View组件时调用,与CreateView对应。
* */
@Override
public void onDestroyView() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onDestroyView();
Log.i("Main", "Fragment1---onDestroyView()");
}
/*
* 销毁Fragment时会被回调。
* */
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onDestroy();
Log.i("Main", "Fragment1---onDestroy()");
}
/*
* Fragment从Activity中删除时会回调该方法,并且这个方法只会调用一次。
* */
@Override
public void onDetach() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onDetach();
Log.i("Main", "Fragment1---onDetach()");
}
}
package com.example.fragment;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MyFragment4 extends Fragment{
@Override
// 加载自己的布局
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// 把layout布局文件转换成View对象
// 第一个参数resource:Fragment需要加载的布局文件
// 第二个参数root:加载layout的父ViewGroup
// attactToRoot:false,不返回父ViewGroup
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment2, container, false);
TextView tv = (TextView)view.findViewById(R.id.text);
tv.setText("第二个Fragment");
Log.i("Main", "Fragment2---onCreateView()");
return view;
}
@Override
public void onAttach(Activity activity) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onAttach(activity);
Log.i("Main", "Fragment2---onAttach()");
}
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
Log.i("Main", "Fragment2---onCreate()");
}
@Override
public void onActivityCreated(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onActivityCreated(savedInstanceState);
Log.i("Main", "Fragment2---onActivityCreated()");
}
@Override
public void onStart() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onStart();
Log.i("Main", "Fragment2---onStart()");
}
@Override
public void onResume() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onResume();
Log.i("Main", "Fragment2---onResume()");
}
@Override
public void onPause() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onPause();
Log.i("Main", "Fragment2---onPause()");
}
@Override
public void onStop() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onStop();
Log.i("Main", "Fragment2---onStop()");
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onDestroy();
Log.i("Main", "Fragment2---onDestroy()");
}
@Override
public void onDetach() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onDetach();
Log.i("Main", "Fragment2---onDetach()");
}
}
第五步:创建main3布局文件,是为下面的MainActivity3提供布局页面的:只有一个Button按钮。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:id="@+id/layout">
<Button
android:text="切换Fragment"
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
</Button>
</LinearLayout>package com.example.fragment;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.FragmentManager;
import android.app.FragmentTransaction;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity3 extends Activity{
private Button button;
private boolean flag = true;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main3);
init();
button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button);
button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction beginTransaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
// 点击按钮时,Fragment4和Fragment3之间相互转换。是动态加在的
if(flag){
MyFragment4 frag4 = new MyFragment4();
// 这个layout是在main3中的LinearLayout。
beginTransaction.replace(R.id.layout, frag4);
flag = false;
}
else{
MyFragment3 frag3 = new MyFragment3();
beginTransaction.replace(R.id.layout, frag3);
flag = true;
}
beginTransaction.commit();
}
});
}
private void init() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getFragmentManager();// 动态生成Fragment3,默认生成这个。
FragmentTransaction beginTransaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
MyFragment3 frag3 = new MyFragment3();
beginTransaction.add(R.id.layout,frag3);
beginTransaction.commit();
}
}
第五步:去MainActivity中设置switch跳转:
package com.example.fragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.FragmentManager;
import android.app.FragmentTransaction;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.widget.CompoundButton;
import android.widget.CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener;
import android.widget.RadioGroup;
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements android.widget.RadioGroup.OnCheckedChangeListener{
private RadioGroup group;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
group = (RadioGroup) findViewById(R.id.radiogroup);
group.setOnCheckedChangeListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(RadioGroup group, int checkedId) {
//
switch(checkedId){
case R.id.first:
Intent intent = new Intent(this,MainActivity2.class);
startActivity(intent);
break;
case R.id.second:
MyFragment2 fragment2 = new MyFragment2();
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction beginTransaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
// 第一个参数是说你要把fragment2加载到布局的ID,例子中frame在main布局文件中定义。
// 第二个参数是说
beginTransaction.add(R.id.frame, fragment2);
beginTransaction.addToBackStack(null); // 返回键就可以返回了。
beginTransaction.commit();
break;
case R.id.third:
Intent intent1 = new Intent(this,MainActivity3.class);
startActivity(intent1);
break;
case R.id.fourth:
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
查看Log日志:
完全是个线性变化,不会打断,一直都是从头到尾的。开始会从onAttach()到onResume(),退出走后面的。
我们下面走一个流程:
启动Fragment
屏幕锁屏
屏幕解屏
切换到其他Fragment
回到桌面
回到应用
退出Fragment
第二部分:
3. Fragment与Activity通信:
案例一:Activity向Fragment传送信息:
第一步:在MainActivity文件中设置switch,进行点击跳转:
package com.example.fragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.FragmentManager;
import android.app.FragmentTransaction;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.widget.CompoundButton;
import android.widget.CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener;
import android.widget.RadioGroup;
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements android.widget.RadioGroup.OnCheckedChangeListener{
private RadioGroup group;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
group = (RadioGroup) findViewById(R.id.radiogroup);
group.setOnCheckedChangeListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(RadioGroup group, int checkedId) {
//
switch(checkedId){
case R.id.first:
Intent intent = new Intent(this,MainActivity2.class);
startActivity(intent);
break;
case R.id.second:
MyFragment2 fragment2 = new MyFragment2();
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction beginTransaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
// 第一个参数是说你要把fragment2加载到布局的ID,例子中frame在main布局文件中定义。
// 第二个参数是说
beginTransaction.add(R.id.frame, fragment2);
beginTransaction.addToBackStack(null); // 返回键就可以返回了。
beginTransaction.commit();
break;
case R.id.third:
Intent intent1 = new Intent(this,MainActivity3.class);
startActivity(intent1);
break;
case R.id.fourth:
Intent intent2 = new Intent(this,MainActivity4.class);
startActivity(intent2);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
package com.example.fragment;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MyFragment5 extends Fragment{
@Override
// 加载自己的布局
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// 把layout布局文件转换成View对象
// 第一个参数resource:Fragment需要加载的布局文件
// 第二个参数root:加载layout的父ViewGroup
// attactToRoot:false,不返回父ViewGroup
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment2, container, false);
TextView tv = (TextView)view.findViewById(R.id.text);
String text = getArguments().get("name")+" ";// 获取它所在的Activity,然后接收从Activity中传来的信息,然后用Toast显示处理。
tv.setText(text);
Toast.makeText(getActivity(), "已成功接收到"+text, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return view;
}
}
第三步:创建一个与下面活动对应的布局文件main4,其中包含一个EditText和Button。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:id="@+id/layout"
>
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/editText"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="发送"
android:id="@+id/send"
/>
</LinearLayout>package com.example.fragment;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.FragmentManager;
import android.app.FragmentTransaction;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity4 extends Activity{
private EditText editext;
private Button send;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main4);
editext = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText);
send = (Button) findViewById(R.id.send);
send.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String text = editext.getText().toString();
MyFragment5 fragment5 = new MyFragment5();
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString("name", text);// 用这个方法从Activity给Fragment发送信息,信息名称为name
fragment5.setArguments(bundle);// Fragment从这里向Activity接收信息
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getFragmentManager();// 动态创建Fragment。
FragmentTransaction beginTransaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
beginTransaction.add(R.id.layout,fragment5,"fragment5");
beginTransaction.commit();
Toast.makeText(MainActivity4.this, "向Fragment发送数据"+text, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
}
}
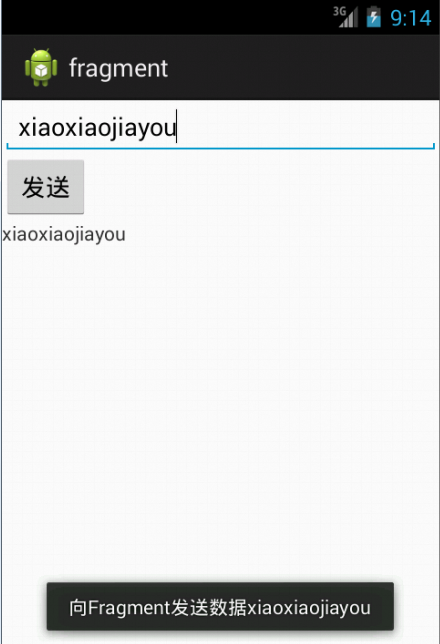
案例二:案例二包括了双方的收发:
第一步:改写MyFragment5文件:定义一个接口,让MainActivity4去实现,通过接口来传递信息。
就是Fragment通过onattach方法获取了当前的Activity,然后Activity调用自己实现的方法thank将数据传回去。
package com.example.fragment;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MyFragment5 extends Fragment {
public MyListener listener;
private String code = "Thank you!";
// 定义一个接口,在MainActivity4中实现。
public interface MyListener {
public void thank(String code);
}
// 当Fragment添加到Activity中时调用的一个方法。也就是通过这个方法,Fragment获取了当前的Activity。
@Override
public void onAttach(Activity activity) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
listener = (MyListener) activity; // 所以这里Activity也就是那个Activity。
super.onAttach(activity);
}
@Override
// 加载自己的布局
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// 把layout布局文件转换成View对象
// 第一个参数resource:Fragment需要加载的布局文件
// 第二个参数root:加载layout的父ViewGroup
// attactToRoot:false,不返回父ViewGroup
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment2, container, false);
TextView tv = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.text);
String text = getArguments().get("name") + " ";
tv.setText(text);
Toast.makeText(getActivity(), "已成功接收到" + text, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT)
.show();
Toast.makeText(getActivity(), "向Activity发送" + code, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT)
.show();
listener.thank(code); // 这样就把字符串传给了Activity。相当于Activity通过自己实现的方法thank将数据传了回去,thank函数是Activity中的。
return view;
}
}
package com.example.fragment;
import com.example.fragment.MyFragment5.MyListener;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.FragmentManager;
import android.app.FragmentTransaction;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast;
// 实现在MyFragment5中定义的接口MyListener
public class MainActivity4 extends Activity implements MyListener {
private EditText editext;
private Button send;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main4);
editext = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText);
send = (Button) findViewById(R.id.send);
send.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String text = editext.getText().toString();
MyFragment5 fragment5 = new MyFragment5();
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString("name", text);
fragment5.setArguments(bundle);
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction beginTransaction = fragmentManager
.beginTransaction();
beginTransaction.add(R.id.layout, fragment5, "fragment5");
beginTransaction.commit();
Toast.makeText(MainActivity4.this, "向Fragment发送数据" + text,
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
}
@Override
public void thank(String code) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Toast.makeText(MainActivity4.this, "Think" + code, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT)
.show();
}
}


































 935
935

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








