1 Apache Lucene 相似度评分
lucence相似度评分公式:
es除了使用上面的默认公式外,还允许用户自定义评分规则。
2 查询重写(query rewrite)
es会对模糊查询(前缀匹配、通配符匹配)进行重写,以提高查询效率。看一下例子。
假设有以下文档
curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/clients/client/1' -d '
{
"id":"1", "name":"Joe"
}'
curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/clients/client/2' -d '
{
"id":"2", "name":"Jane"
}'
curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/clients/client/3' -d '
{
"id":"3", "name":"Jack"
}'
curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/clients/client/4' -d '
{
"id":"4", "name":"Rob"
}'
curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/clients/client/5' -d '
{
"id":"5", "name":"Jannet"
}'进行前缀j查询:
curl -XGET 'localhost:9200/clients/_search?pretty' -d '{
"query" : {
"prefix" : {
"name" : {
"value":"j",
"rewrite" : "constant_score_boolean"
}
}
}
}'将会得到以下结果:
{
...
"hits" : {
"total" : 4,
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [ {
"_index" : "clients",
"_type" : "client",
"_id" : "5",
"_score" : 1.0, "_source" : {"id":"5", "name":"Jannet"}
}, {
"_index" : "clients",
"_type" : "client",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.0, "_source" : {"id":"1", "name":"Joe"}
}, {
"_index" : "clients",
"_type" : "client",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 1.0, "_source" : {"id":"2", "name":"Jane"}
}, {
"_index" : "clients",
"_type" : "client",
"_id" : "3",
"_score" : 1.0, "_source" : {"id":"3", "name":"Jack"}
} ]
}
}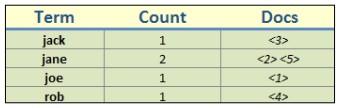
在以上的例子中,是查询name中以j为前缀的所有记录,它重写的过程是这样的:搜索索引表(如上),把相应的模糊查询变成一下形式:

此时,es就会拆分成3个查询分别进行匹配。这种重写的形式,在不同关键词多的索引中效果更明显。
3 概念
Gateway
Gateway存放集群状态、索引配置等信息。
DSL
displine special language 领域专用语言(JSON based
language for building complex queries)。
索引
索引仅在主分片上进行。
mapping
ES的mapping非常类似于静态语言中的数据类型:声明一个变量为int类型的变量, 以后这个变量都只能存储int类型的数据。同样的,一个number类型的mapping字段只能存储number类型的数据。
同语言的数据类型相比,mapping还有一些其他的含义,mapping不仅告诉ES一个field中是什么类型的值, 它还告诉ES如何索引数据以及数据是否能被搜索到。
当你的查询没有返回相应的数据, 你的mapping很有可能有问题。当你拿不准的时候, 直接检查你的mapping。
curl -XGET 'localhost:9200/clients/client/_mapping?pretty'ES能非常聪明的识别出”name”和”description”字段的类型是string, ES默认会创建以下的mapping。
4 排序(Sorting data)
es默认情况是按文档得分排序。当然它允许我们自定义排序规则。排序主要涉及单字段单个值、单字段多个值、嵌套对象三种类型的排序方式。
1. 单字段单个值
{
"query" : {
"terms" : {
"title" : [ "crime", "front", "punishment" ],
"minimum_match" : 1
}
},
"sort" : [
{ "section" : "desc" }
]
}{ “section” : “desc” }表示通过section字段降序排列。
“minimum_match” : 1表示[“crime”, “front”, “punishment” ]3个里面至少要匹配一个。
2. 单字段多个值
单字段多个值的情况涉及部分场景,例如电影在不同国家的首映时间、部门分部的坐落位置等。
下述例子表示以release_dates字段中最小的那个值进行升序排列。
{
"query" : {
"match_all" : {}
},
"sort" : [
{"release_dates" : { "order" : "asc", "mode" : "min" }}
]
}再来看一个地理位置为多个值的例子。
有如下的映射(mappings)结构
{
"mappings": {
"poi": {
"properties": {
"country": { "type": "string" },
"loc": { "type": "geo_point" }
}
}
}
}其中有这样一条数据:
{ "country": "UK", "loc": ["51.511214,-0.119824", "53.479251,
-2.247926", "53.962301,-1.081884"] }通过下式的查询,表示寻找与”loc”: “51.511214,-0.119824”距离最小的点。
{
“sort”: [{
“_geo_distance”: {
“loc”: “51.511214,-0.119824”,
“unit”: “km”,
“mode” : “min”
}
}]
}
可得到如下的结果。其中sort:[0,0],是因为查询的条件与文档的值一模一样。
{
"took" : 21,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 1,
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ {
"_index" : "map",
"_type" : "poi",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : null, "_source" : {
"country": "UK", "loc": ["51.511214,-0.119824",
"53.479251,-2.247926", "53.962301,-1.081884"] }
,
"sort" : [ 0.0 ]
} ]
}
}3. 嵌套对象(Nested object)
假设有如下包含多个嵌套的数据:
{
"country": "PL", "cities": { "name": "Cracow", "votes": {
"users": "A" }}
}
{
"country": "EN", "cities": { "name": "York", "votes": [{"users":
"B"}, { "users": "C" }]}
}
{
"country": "FR", "cities": { "name": "Paris", "votes": {
"users": "D"} }
}那么可以通过嵌套对象形式指定查询的排序规则:
{
"sort": [{ "cities.votes.users": { "order": "desc", "mode":
"min" }}]
}5 filter缓冲
es会为filter字段进行缓存,即存储已经匹配的文档,在下次相同过滤条件时,不需要再次查询索引,以此提高性能。
filter语法:
{
"query" : {
"filtered" : {
"query" : {
"term" : { "name" : "joe" }
},
"filter" : {
"term" : { "year" : 1981 }
}
}
}
}但也不是所有filter es都会为其缓存,以下的filter es就不会缓存:
• numeric_range
• script
• geo_bbox
• geo_distance
• geo_distance_range
• geo_polygon
• geo_shape
• and
• or
• not
6交叉查询(join查询)
例1
有如下记录:
curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/clients/client/1' -d '{
"id":"1", "name":"Joe Doe", "books":["1","3"]
}'
curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/clients/client/2' -d '{
"id":"2", "name":"Jane Doe", "books":["3"]
}'
curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/books/book/1' -d '{
"id":"1", "title":"Test book one"
}'
curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/books/book/2' -d '{
"id":"2", "title":"Test book two"
}'
curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/books/book/3' -d '{
"id":"3", "title":"Test book three"
}'查询用户中id为1的所购买的所有图书:
curl -XGET 'localhost:9200/books/_search' -d '{
"query" : {
"filtered" : {
"query" : {
"match_all" : {}
},
"filter" : {
"terms" : {
"id" : {
"index" : "clients",
"type" : "client",
"id" : "1",
"path" : "books"
},
"_cache_key" : "terms_lookup_client_1_books"
}
}
}
}
}'其思路就是:先在索引为clients,类型为client,id为1,filed为books的记录缓存起来,然后在索引为books下,匹配图书的id是否与缓存中的id相等。
7 小面化(faceting)
之所以采用faceting这个词,是因为为了表述将结果的简单数学统计信息摊牌于一个面上,让人们观看。
faceting的计算数据是依据查询的数据集。如下,将会查看所有文档在price字段价格为30以下以及30以上的简单数学描述信息。
{
"query" : {
"match_all" : {}
},
"filter" : {
"term" : { "category" : "book" }
},
"facets" : {
"price" : {
"range" : {
"field" : "price",
"ranges" : [
{ "to" : 30 },
{ "from" : 30 }
]
}
}
}
}如下,将会查看经过过滤后所有文档在price字段价格为30以下以及30以上的简单数学描述信息。
{
"query" : {
"filtered" : {
"query" : {
"match_all" : {}
},
"filter" : {
"term" : {
"category" : "book" }
}
}
},
"facets" : {
"price" : {
"range" : {
"field" : "price",
"ranges" : [
{ "to" : 30 },
{ "from" : 30 }
]
}
}
}
}那么将会得到如下的结果:
{
...
"hits" : {
"total" : 2,
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [ {
"_index" : "books",
"_type" : "book",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.0, "_source" : {"id":"1", "title":"Test book
1", "category":"book", "price":29.99}
}, {
"_index" : "books",
"_type" : "book",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 1.0, "_source" : {"id":"2", "title":"Test book
2", "category":"book", "price":39.99}
} ]
},
"facets" : {
"price" : {
"_type" : "range",
"ranges" : [ {
"to" : 30.0,
"count" : 1,
"min" : 29.99,
"max" : 29.99,
"total_count" : 1,
"total" : 29.99,
"mean" : 29.99
}, {
"from" : 30.0,
"count" : 1,
"min" : 39.99,
"max" : 39.99,
"total_count" : 1,
"total" : 39.99,
"mean" : 39.99
} ]
}
}
}







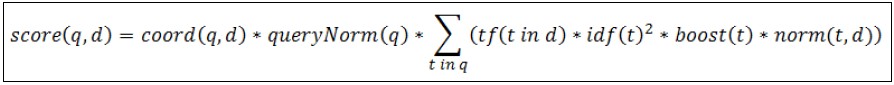














 582
582

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








