1. 成员函数
1) 类内实现成员函数——inline函数
//示例
#include<iostream>
usingnamespace std;
classTest
{
public:
intx_;
inlinevoid setX(int x)
{
x_= x;
}
inlinevoid setY(int y)
{
y_= y;
}
inlinevoid setZ(int z)
{
z_= z;
}
inlineint getX()
{
returnx_;
}
inlineint getY()
{
returny_;
}
inlineint getZ()
{
returnz_;
}
protected:
inty_;
private:
intz_;
};
intmain()
{
Testt;
t.x_= 5;
t.setY(6);
t.setZ(7);
cout<< "t.x: " << t.x_ << endl;
cout<< "t.y: " << t.getY() << endl;
cout<< "t.z: " << t.getZ() << endl;
return0;
}
2) 类外实现成员函数
示例:
[main.cpp]
#include<iostream>
#include"Test.h"
usingnamespace std;
intmain()
{
Test test;
test.x_ = 5;
//test.y_ = 6;//私有成员,类外不能访问
//test.z_ = 7;//保护成员,类外不能访问
test.init(4, 6, 7);
test.display();
return 0;
}
[Test.cpp]
#include"Test.h"
#include<iostream>
usingnamespace std;
voidTest::init(int x, int y, int z)
{
x_ = x;
y_ = y;
z_ = z;
}
voidTest:: display()
{
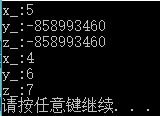
cout << "x_:" << x_<<endl;
cout << "y_:" << y_<<endl;
cout << "z_:" << z_<<endl;
}
[Test.h]
#ifndef_TEST_H_
#define_TEST_H_
classTest
{
public:
int x_;
void init(int x, int y, int z);
void display();
private:
int y_;
//int y_ =10;//该成员不能在类内初始化,只有静态常量整型数据成员才可以在类中初始化
protected:
int z_;
};
#endify_、z_是私有、保护成员,类外不可调用并且未初始化,所以是任意值
3) 成员函数的重载及默认参数






















 1288
1288

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








