注:本系列属于学习笔记,学习内容主要来自于刘望舒的博客,特此声明
1.视图坐标系
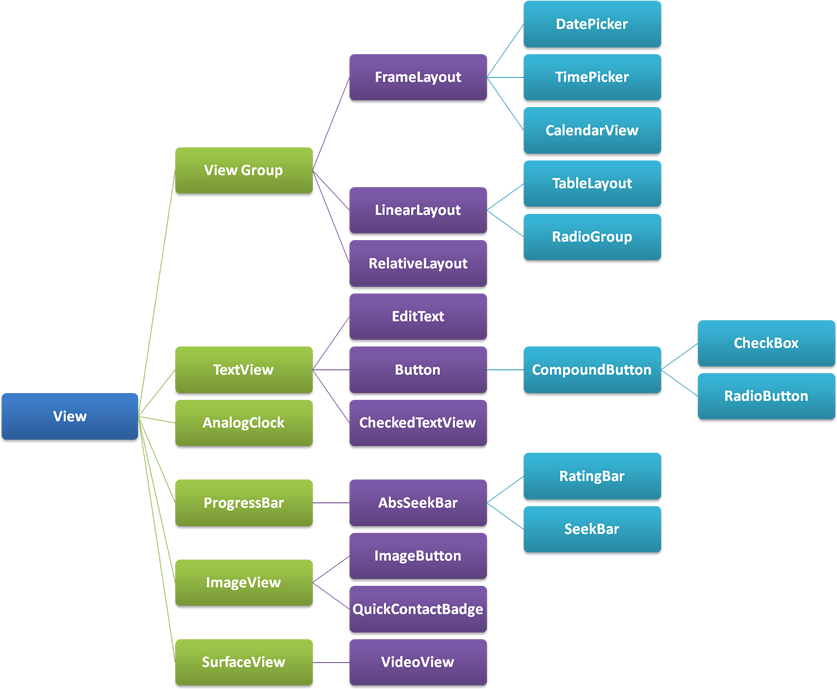
Android中所有控件都是继承View类的,下图可以看到其中的关系
2.Android坐标系
Android中有两种坐标系:Android坐标系、视图坐标系
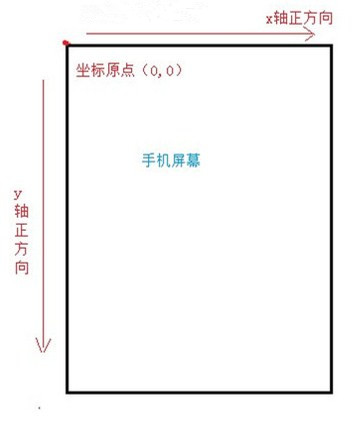
2.1 Android坐标系
在Android中,将屏幕的左上角的顶点作为Android坐标系的原点,这个原点向右是X轴正方向,原点向下是Y轴正方向
在Android中,MotionEvent中提供的getRawX()和getRawY()获取的坐标都是Android坐标系的坐标
2.2 视图坐标系
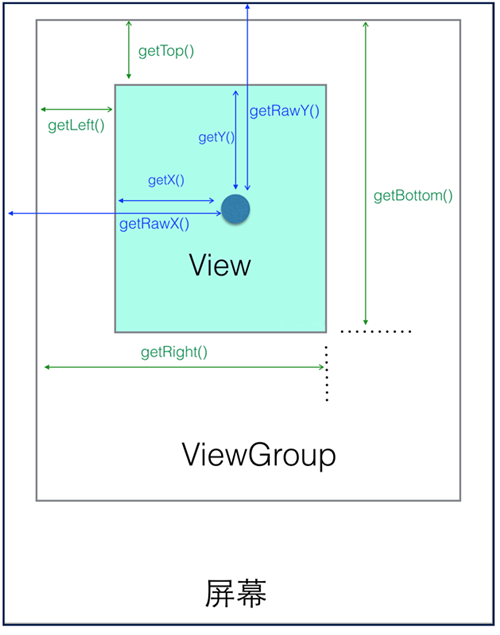
View获取自身高度
- getHeight():获取View自身高度
- getWidth():获取View自身宽度
View自身坐标
通过如下方法可以获得View到其父控件(ViewGroup)的距离:
- getTop():获取View自身顶边到其父布局顶边的距离
- getLeft()、getRight():获取View自身左边到其父布局左边的距离(或右边)
- getBottom():获取View自身底边到其父布局底边的距离
MotionEvent提供的方法
我们看上图那个深蓝色的点,假设就是我们触摸的点,我们知道无论是View还是ViewGroup,最终的点击事件都会由onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event)方法来处理,MotionEvent也提供了各种获取焦点坐标的方法:
- getX()、getY():获取点击事件距离控件左边的距离,即视图坐标
- getRawX()、getRawY():获取点击事件距离整个屏幕左边距离,即绝对坐标
二、实现View滑动的六种方法
其实不管是那种滑动的方式基本思想都是类似的:当触摸事件传到View时,系统记下触摸点的坐标,手指移动时系统记下移动后的触摸的坐标并算出偏移量,并通过偏移量来修改View的坐标
1. Layout()
view进行绘制的时候会调用onLayout()方法来设置显示的位置,因此我们同样也可以通过修改View的left、top、right、bottom这四种属性来控制View的坐标
Step 1: 自定义一个View,在onTouchEvent()方法中获取触摸点的坐标
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event){
// 获取到手指处的横纵坐标
int x = (int)event.getX();
int y = (int)event.getY();
switch (event.getAction()){
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
lastX = x;
lastY = Y;
break;
}
...
}Step 2: 在ACTION_MOVE事件中计算偏移量,再调用layout()方法重新放置这个自定义View的位置
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
//计算移动的距离
int offsetX = x - lastX;
int offsetY = y - lastY;
//调用layout方法来重新放置它的位置
layout(getLeft()+offsetX, getTop()+offsetY, getRight()+offsetX , getBottom()+offsetY);
break;Step Example(1) : 自定义View的全部代码
package zhongshijie.viewsystem.CustomView;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
/**
* 可以跟随手指拖动的自定义View
* Created by ZhongShijie on 2017/8/7.
*/
public class MoveTouchView extends View {
private int lastX;
private int lastY;
public MoveTouchView(Context context, AttributeSet attributeSet, int defStyleAttr){
super(context, attributeSet, defStyleAttr);
}
public MoveTouchView(Context context,AttributeSet attributeSet){
super(context, attributeSet);
}
public MoveTouchView(Context context){
super(context);
}
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event){
//获取到手指处的横坐标和纵坐标
int x = (int) event.getX();
int y = (int) event.getY();
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
lastX = x;
lastY = y;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
//计算移动的距离
int offsetX = x - lastX;
int offsetY = y - lastY;
//调用layout方法来重新放置它的位置
layout(getLeft()+offsetX, getTop()+offsetY,
getRight()+offsetX , getBottom()+offsetY);
break;
}
return true;
}
}Step Example(2) : 布局中引用自定义View
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="zhongshijie.viewsystem.MainActivity">
<zhongshijie.viewsystem.CustomView.MoveTouchView
android:layout_width="80dp"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:background="@color/colorAccent"/>
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>2. offsetLeftAndRight() 与 offsetTopAndBottom()
这两种方法和layout()方法效果方法差不多,使用也差不多,我们将ACTION_MOVE中的代码替换成如下代码:
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
//计算移动的距离
int offsetX = x - lastX;
int offsetY = y - lastY;
//对left和right进行偏移
offsetLeftAndRight(offsetX);
//对top和bottom进行偏移
offsetTopAndBottom(offsetY);
break;根据这两种方法,我们可以完成:跟随手指拖动而移动的View只进行单一左右移动或者上下移动
3. LayoutParams(改变布局参数)
LayoutParams主要保存了一个View的布局参数,因此我们可以通过LayoutParams来改变View的布局的参数从而达到了改变View的位置的效果。同样的我们将ACTION_MOVE中的代码替换成如下代码:
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
//计算移动的距离
int offsetX = x - lastX;
int offsetY = y - lastY;
//改变布局参数
LinearLayout.LayoutParams layoutParams= (LinearLayout.LayoutParams) getLayoutParams();
layoutParams.leftMargin = getLeft() + offsetX;
layoutParams.topMargin = getTop() + offsetY;
setLayoutParams(layoutParams);
break;此处的LinearLayout是该自定义View的父控件,如果你的自定义View的父控件是RelativeLayout,则需要改为RelativeLayout
注:同时,除了使用LayoutParams外,还可以用ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams来实现,将上面的LinearLayout.LayoutParams替换为ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams即可实现。
4. 动画
- 可以采用View动画来移动
Step 1 : 在res目录新建anim文件夹并创建translate.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<translate android:fromXDelta="0" android:toXDelta="300" android:duration="1000"/>
</set>Step 2 : 在Java代码中引用
mCustomView.setAnimation(AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this, R.anim.translate)
- 当然也可以采用属性动画
Step 1 : 在Activity中获取到控件mCustomView后,使用属性动画
ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mCustomView,"translationX",0,300).setDuration(1000).start();5. scollTo与scollBy
scollTo(x,y)表示移动到一个具体的坐标点,而scollBy(dx,dy)则表示移动的增量为dx、dy
其实,scollBy最终也是要调用scollTo的。另外,这两个方法都是针对View的内容的,如果在ViewGroup中使用则是移动他的子View
Step 1 : 将ACTION_MOVE中的代码替换成如下代码
// 实现CustomView随着我们手指移动的效果,需要将偏移量设置为负值
((View)getParent()).scrollBy(-offsetX,-offsetY);6. Scroller
可以使用Scroller来实现过度效果的滑动。但是,Scroller本身是不能实现View的滑动的,需要配合View的滑动,它需要配合view的computeScroll()方法才能弹性滑动的效果。
Step 1 :在自定义View的构造函数中,初始化Scroller
public MoveTouchView(Context context,AttributeSet attributeSet){
super(context, attributeSet);
mScroller = new Scroller(context);
}Step 2 : 重写自定义view中的computeScroll()方法
该方法中我们调用父类的scrollTo()方法,通过Scroller来不断获取当前的滚动值,每滑动一小段距离我们就调用invalidate()方法不断的进行重绘,重绘就会调用computeScroll()方法,这样我们就通过不断的移动一个小的距离并连贯起来就实现了平滑移动的效果
@Override
public void computeScroll() {
super.computeScroll();
if(mScroller.computeScrollOffset()){
((View) getParent()).scrollTo(mScroller.getCurrX(),mScroller.getCurrY());
//通过不断的重绘不断的调用computeScroll方法
invalidate();
}
}Step 3 : 在CustomView中写一个smoothScrollTo()方法,调用Scroller.startScroll()方法,在2000毫秒内沿X轴平移delta像素
public void smoothScrollTo(int destX,int destY){
int scrollX=getScrollX();
int delta=destX-scrollX;
//1000秒内滑向destX
mScroller.startScroll(scrollX,0,delta,0,2000);
invalidate();
}Step 4 : 在ViewSlideActivity.java中调用CustomView的smoothScrollTo()方法:
//使用Scroll来进行平滑移动
mCustomView.smoothScrollTo(-400,0);





















 3063
3063

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








