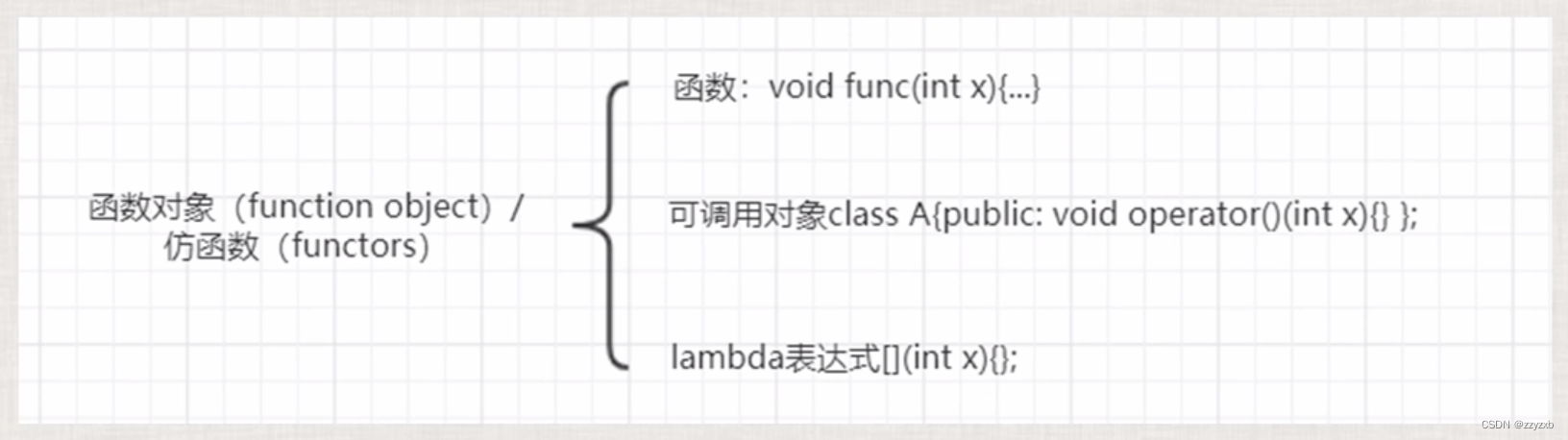
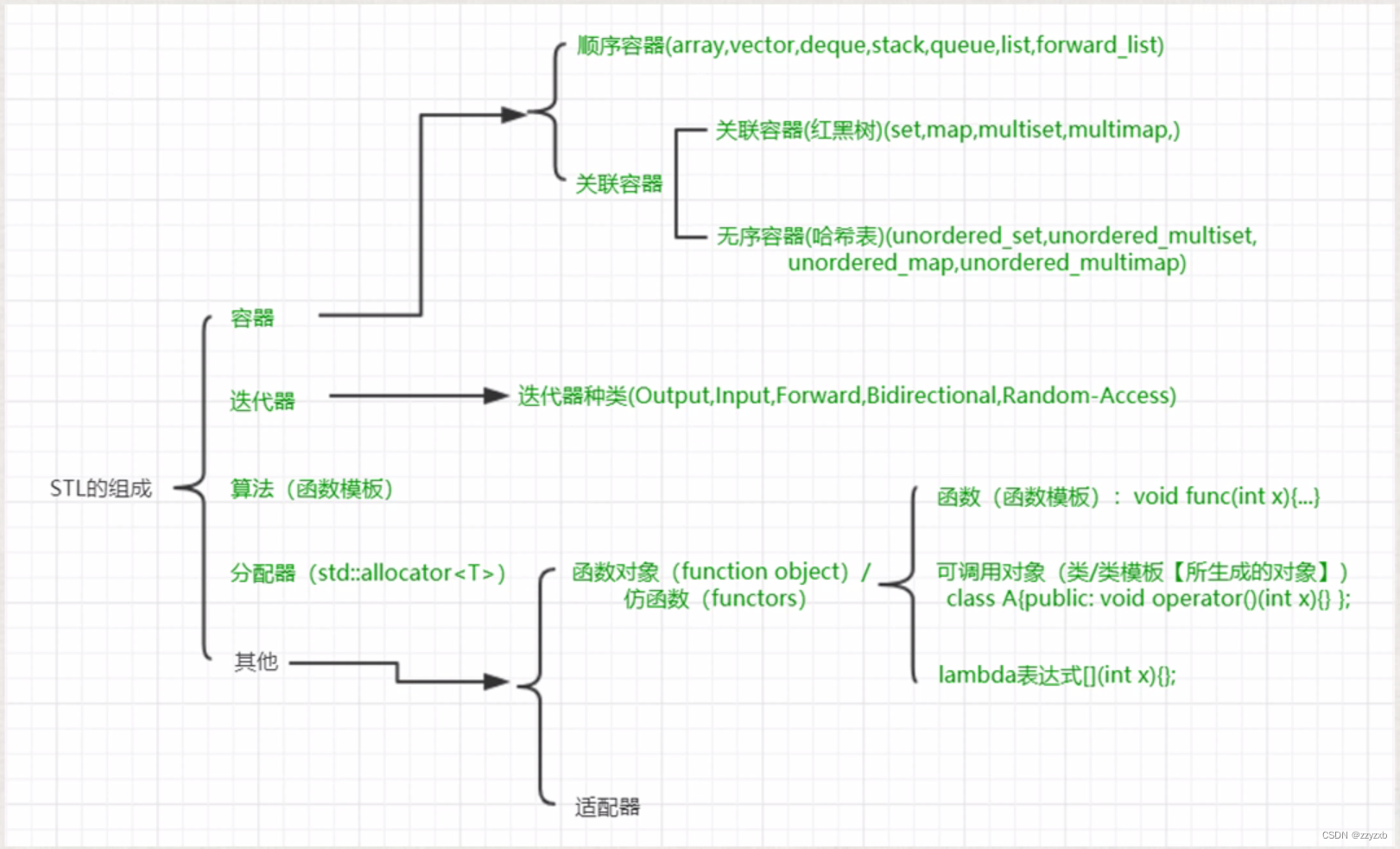
一:函数对象(function object) / 仿函数(functors)回顾
函数对象在stl中,一般都是和算法配合来使用,从而实现一些特定的功能;也就是说,这些函数对象主要用来服务于算法;
函数名(参数列表)
高级话题与新标准第一节、第七节和第八节
#include <map>
#include <list>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <unordered_set>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
bool operator()(int i, int j)
{
return i > j;
}
};
void func()
{
vector<int> myvector = { 50, 15, 80, 30, 46 };
A mya;
sort(myvector.begin(), myvector.end(), mya);
for (auto iter = myvector.begin(); iter != myvector.end(); ++iter)
{
cout << *iter << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
cout << "begin" << endl;
func();
cout << "end" << endl;
return 0;
}
二:标准库中定义的函数对象
标准库中提供了很多可以现成拿来使用的函数对象,使用它们之前;
要包含一个头文件 #include <functional>

函数对象分类:
<1>算术运算类:6
<2>关系运算类:6
<3>逻辑运算类:3
<4>位运算类:3
void func()
{
plus<int>(); //加圆括号是生成一个临时对象,就是个可调用对象
plus<int> myplus;
}
三:标准库中定义的函数对象范例
#include <map>
#include <list>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
#include <unordered_set>
using namespace std;
void func()
{
vector<int> myvector = { 50, 15, 80, 30, 46 };
//sort(myvector.begin(), myvector.end(), greater<int>()); //greater<int>()产生临时对象
sort(myvector.begin(), myvector.end(), less<int>());
for (auto iter = myvector.begin(); iter != myvector.end(); ++iter)
{
cout << *iter << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
cout << "begin" << endl;
func();
cout << "end" << endl;
return 0;
}























 115
115











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








