本文主要参考Xlinx的Device Driver Programmer Guide
Device Driver特点
- 提供最大的兼容性
- 使用标准的C语言编写
- 设备驱动层和操作系统层、处理器分离
- 支持FPGA重配置
- 支持动态重配置
- 不复制代码可以例化多个设备
- 支持简单和复杂的使用方法
- 可根据需求去调整面积与速度的优化
- 方便使用和维护
- 不同的设备驱动API都有着相似的风格
Device Driver结构
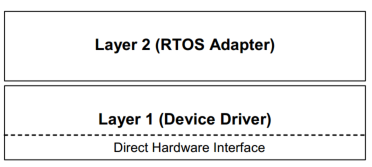
带有API函数的是Layer1和Layer2,Direct Hardware Interface只有一些宏定义的常量
Layer 2 (RTOS Adapter)
- Adapters 典型特点.
- Communicates directly to the RTOS as well as the Layer 1 interface of the device driver.
- References functions and identifiers specific to the RTOS. This layer is therefore not portable across operating systems.
- Can use memory management
- Can use RTOS services such as threading, inter-task communication, etc.
- Can be simple or complex depending on the RTOS interface and requirements for the device driver
Layer 1 (Device Driver)
- Device Driver典型特点
- Consistent API that gives the user an “out-of-the-box” solution. The abstract API helps isolate the user from hardware changes.
- No RTOS or processor dependencies, making the device driver highly portable
- Run-time error checking such as assertion of input arguments, and provides the ability to compile away asserts.
- Comprehensive support of device features
- Supports device configuration parameters to handle FPGA-based parameterization of hardware devices.
- Supports multiple instances of a device while managing unique characteristics on a per instance basis.
- Polled and interrupt driven I/O
- Non-blocking function calls to aid complex applications
- May have a large memory footprint
- Typically provides buffer interfaces for data transfers as opposed to byte interfaces. This makes the API easier to use for complex applications.
- Does not communicate directly to Layer 2 adapters or application software. Utilizes asynchronous callbacks for upward communication.
Direct Hardware Interface
- 典型特点
- Constants that define the device register offsets and bit fields, and simple macros that give the user access to the hardware registers
- Small memory footprint
- Little to no error checking is performed
- Minimal abstraction such that the API typically matches the device registers. The API is therefore less isolated from hardware device changes.
- No support of device configuration parameters
- Supports multiple instances of a device with base address input to the API
- No, or minimal, state is maintained
- Polled I/O only
- Blocking functions for simple use cases
- Typically provides byte interfaces
命名规则
外部标识符(External Identifiers)
External Name Pattern:
X[driver_name]_VariableName;
X[driver_name]_FunctionName(ArgumentType Argument)
X[driver_name]_TypeName;
For example, a driver named XUartLite (for the UART Lite device driver) would have constants that begin with XUL_, and a driver named XEmac (for the Ethernet 10/100 device driver) would have constants that begin with XEM_.
文件命名规则(File Naming Conventions)
- Driver Source File Names
每一个文件都有一个小写的 “x” - Implementation Source Files (*.c)
Source File Naming Pattern:
x[driver_name].c main source file
x[driver_name]_functionality.c secondary source file - Header Source Files (*.h)
- The high-level, abstract interface (Layer 1) for a driver is contained in a header file with the file name format x[driver_name].h.
- The direct hardware interface is contained in a header file with the file name format x_hw.h (or x[driver_name]_l.h).
- The internal interfaces are contained in a header file with the file name format
x[driver_name]_i.h.
Device Driver Layers
Example File Names
The following source file names illustrates an example which is complex enough to utilize multiple C source files.
xuartns550.c Main implementation file
xuartns550_intr.c Secondary implementation file for interrupt handling
xuartns550.h High level external interfaces header file
xuartns550_i.h Internal identifiers header file
xuartns550_l.h Low level external interfaces header file
xuartns550_l.c Low level implementation file
xuartns550_g.c Generated file controlling parameterized
instances and, xuartns550_sio_adapter.c VxWorks Serial I/O (SIO) adapter
上面文件的命名规则
Layer 1 and the direct hardware interface (i.e., high-level and low-level driver interfaces) are bundled together in a directory. The direct hardware interface files are named x[driver_name]_hw.h (or _l.h) and sometimes x[driver_name]_hw.c (or _l.c). The “_hw” indicates hardware-specific definitions. Layer 2 RTOS adapter files typically include the word “adapter” in the file name, such as x[driver_name]_adapter.h and x[driver_name]_adapter.c.These are stored in a different directory name (e.g., one specific to the RTOS) than the device driver files.
更多关于zynq开发相关的文章和问题请点击:
http://www.osrc.cn/forum.php?mod=forumdisplay&fid=292
http://blog.csdn.net/rzjmpb
























 9259
9259











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








