对本书进行了几天的学习,每个章节内容比较长,偏于理论,对于机器学习初学者掌握其中的内容非常重要,只是理解起来比较困难,第一章分为两部分进行学习。
1 The Learning Problem
1.1. Problem Setup
1.1.1. Components of Learning
1.1.2 A Simple Learning Model
1.1.3 Learning versus Design
1.2 Type of Learning
1.2.1 Supervised Learning
1.2.2 Reingorcement Learning
1.2.3 Unspervised Learning
1.2.4 Other Views of Learning
对于学习的定义,作者举例孩童对树的认识,我们看到过树,然后知道这是树,当我们再次看到其他的树时,我们会准确的辨别出这是一棵树,这就相当于我们在数据中进行学习。
1.1 Problem setup
著名DVD租赁公司Netflix举行一个竞赛,提高公司的推荐性能,每提高%10,奖励100百万美元
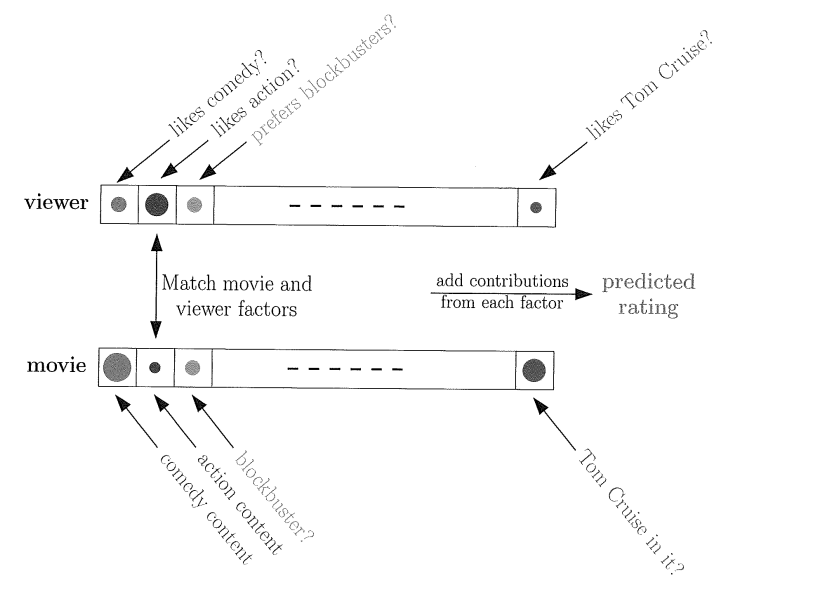
上图是一个简单的用户推荐系统,每个电影都有自己的关键词,比如电影类型是喜剧片,动作片还是爱情片?有没有帅气的明星(汤姆克鲁斯啊,宝强啊)。。。。等等等,这些影片特征我们可以看做输入,客户对其相应输入进行打分,比如喜欢动作片,那么动作片这一项的分数相应高些,比如你觉得宝强比阿汤哥帅,那么宝强项分数会高一些,阿汤哥的分数会小。这样就构成了一个简单的评价系统
1.1.1. Components of Learning
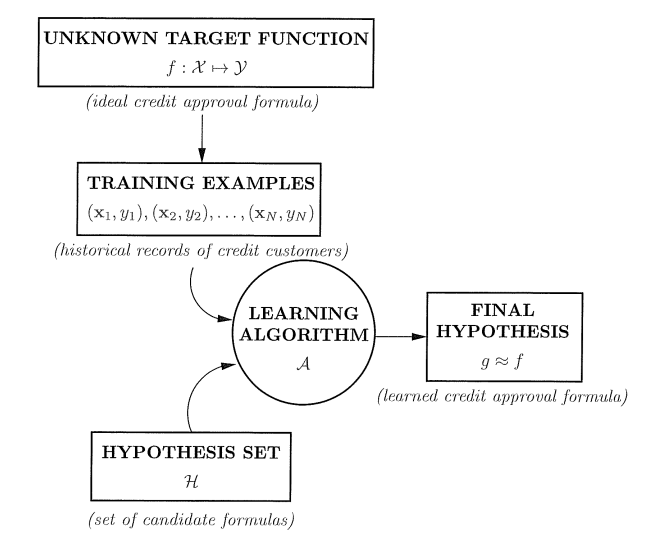
既然要学习,就必然有“教材”,所以我们需要输入元素x(影片的特征,申请信用卡用户信息等),有了原因就要有结果,所以这里还有输出y(影片分数,是否申请成功等),我们学习的目的要智能自动发现数据的规律,在现有的数据中发现这样的规律,所以需要学习得到目标函数f:X->Y(X为输入集合,Y为输出集合),输入数据集合D:(
x1,y1
),(
x2,y2
)….,(
xN,yN
),目标函数符合
yn=f(xn)
,其中n=1,2,…,N,但是目标函数是未知的,此时我们需要在已知的数据D中学习得到g:X->Y来近似目标函数f,g由候选函数集中选取,成为假设集合H,我们在H中找到能够拟合数据。在新的数据输入时,可以用g代替目标函数f拟合数据,下图为学习流程图:
1.1.2 A Simple Learning Model
感知器算法:假设
X=Rd
,其中
Rd
为d维欧式空间,输出为Y={-1,+1},比如信用卡申请系统
X=Rd
为输入向量(薪水,居住年限,又无外债以及其他申请信息),我们在假设集合中选取一个假设
h∈H
,函数h(x)针对不同x选取不同权重:
If 申请成功:
∑i=d1wixi>threshold
If 申请失败:
∑i=d1wixi<threshold
假设函数为:
h(x)=sign((
∑i=d1wixi
)+b) (1)
令
w0
=b,故权值向量w=[
w0
,
w1
,…,
wd
]T
,
x0
=1,式(1)改成:
h(x)=sign(
wT
x) (2).
感知器学习算法目标由数据通过迭代方法得到合适的权值向量w。假设当前权值矩阵为w(t),t=0,1,2…..,如果样本分类错误,y(t)!=sign(
wT
(t)x(t)),则进行更新:
w(t+1)=w(t)+y(t)x(t) (3)
1.1.3 Learning versus Design
简而言之,就是设计特征选择,输入相应数据进行学习。比如硬币面值判定,我们选取尺寸和重量特征。
1.2 Type of Learning
监督学习
无监督学习
加强学习






















 828
828

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








