1.3 Is learning feasible
学习可行性:目标函数f是机器学习的最终目的,由于它是未知的,如何在提供的有限信息中确定目标函数呢?
在学习过程中,目标函数f通过数据集合D学习得到,对于训练数据之外的事件不能保证预测结果,这样的过程只能说是在记忆,而不是学习,也就是说真正的学习过程就是在数据中学习且能预测未知事件结果。(书中举了一个例子大家可以学习下,理解上述过程)
一个学习系统是否成功的标准:预测值与真实值非常接近。
本节举了一个例子,假设瓶子里装了无限数量的红色和绿色小球,随机选取红色球的概率为u,绿色球的概率为1-u,随机选取N个独立的小球,其中红色球的比例v,我们是否能从v中得到真实红色球的分布值u?
根据上述假设,可以得出v与u的关系度准则:Hoeffding Inequality
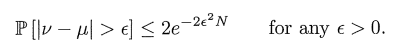
其中,P[.]表示事件的概率,衡量v与u的接近程度(记住Hoeffding Inequality 准则,下面内容推到原型),上述过程与假设学习过程相似,同样的问题,通过学习数据集得到目标函数,预测未知事件。
下图为加入概率的学习模型:
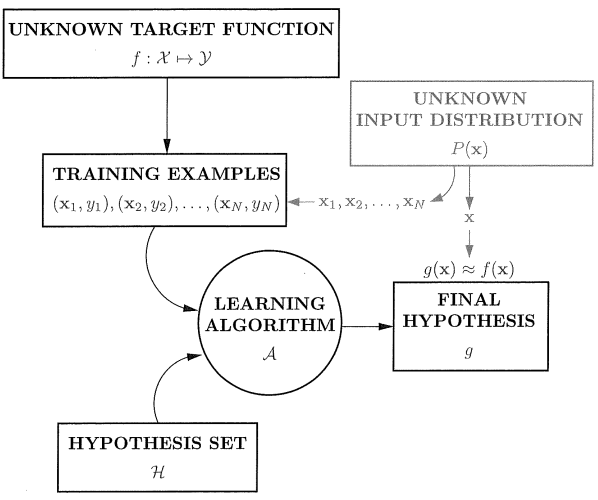
接下来作者引入两个误差准则:

样本内误差
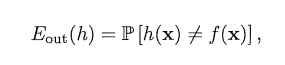
样本外误差
根据Hoeffding Inequality可以写成:
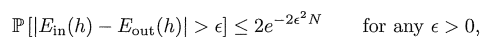
样本内误差就像抽取概率v,依靠样本的随机变量,样本外误差就像球的分布概率u未知但不是随机。
两个误差符合:1、两个误差尽可能接近。2、样本内误差尽可能小。
1.4 Error and Noise
讨论误差和噪声之间的不同:
误差主要取决于假设与实际的接近程度,就像在指纹系统中有误识率或者错误接受率等等。而噪声就像高中时的电路物力实验,电流和电压的关系,本来是一条直线,但是正是因为电路中电阻什么的变化影响,导致输入电流与输出电压不一致。
《Learning From Data》第一章(二)读书笔记
最新推荐文章于 2023-09-11 15:54:24 发布






















 839
839

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








