图形图像处理-之-一个复杂度为常数的快速局部自适应算法 上篇
HouSisong@GMail.com 2008.04.12
(2009.03.10 可以到这里下载完整的可以编译的项目源代码: http://cid-10fa89dec380323f.skydrive.live.com/browse.aspx/.Public?uc=4
tag: 图像二值化,局部自适应,二维模板
摘要: 图像处理中,某些算法在对一个像素的处理都需要根据周围很多像素的综合信息
来做处理,这类算法一般叫做局部自适应算法,用以得到更好的处理效果;但很多时候
这都可能成为一个性能瓶颈,因为对一个像素点都需要做大量的处理;本文将提供我使
用的一个复杂度为常数的快速局部自适应算法。
(当然,某些二维模板不一定能够拆解成常数算法,但很多还是可以拆解成线性算法的)
正文:
代码使用C++,编译器:VC2005
测试平台:(CPU:AMD64x2 4200+(2.37G); 内存:DDR2 677(双通道); 编译器:VC2005)
A:像素使用ARGB32颜色类型,颜色和图片的数据定义:
typedef unsigned long TUInt32;
struct TARGB32 // 32 bit color
{
TUInt8 b,g,r,a; // a is alpha
};
struct TPicRegion // 一块颜色数据区的描述,便于参数传递
{
TARGB32 * pdata; // 颜色数据首地址
long byte_width; // 一行数据的物理宽度(字节宽度);
// 注意: abs(byte_width)有可能大于等于width*sizeof(TARGB32);
unsigned long width; // 像素宽度
unsigned long height; // 像素高度
};
// 那么访问一个点的函数可以写为:
inline TARGB32 & Pixels( const TPicRegion & pic, const long x, const long y)
{
return ( (TARGB32 * )((TUInt8 * )pic.pdata + pic.byte_width * y) )[x];
}
B:图像二值化的一个简单实现
函数的作用是将一幅彩色图像转化成黑白两色的图像;
算法很简单,像素的亮度值大于127(也可以预先统计出源图片的平均亮度值作
为阈值)的转换为白色,否则设置为黑色,实现如下:
const double cs_gray_green = 0.587 ;
const double cs_gray_blue = 0.114 ;
inline long getGray0( const TARGB32 & color) // 获得颜色的亮度
{
return ( long )(color.r * cs_gray_red + color.g * cs_gray_green + color.b * cs_gray_blue);
}
void threshold0( const TPicRegion & dst, const TPicRegion & src)
{
long width = dst.width;
if (src.width < width) width = src.width;
long height = dst.height;
if (src.height < height) height = src.height;
TARGB32 * srcLine = src.pdata;
TARGB32 * dstLine = dst.pdata;
for ( long y = 0 ;y < height; ++ y)
{
for ( long x = 0 ;x < width; ++ x)
{
long light = getGray0(srcLine[x]);
if (light >= 127 ) // 设置为白色
{
dstLine[x].b = 255 ;
dstLine[x].g = 255 ;
dstLine[x].r = 255 ;
dstLine[x].a = 255 ;
}
else // 设置为黑色
{
dstLine[x].b = 0 ;
dstLine[x].g = 0 ;
dstLine[x].r = 0 ;
dstLine[x].a = 0 ;
}
}
(TUInt8 *& )srcLine += src.byte_width; // 下一行颜色
(TUInt8 *& )dstLine += dst.byte_width; // 下一行颜色
}
}
原图像(图像大小: 640x480):
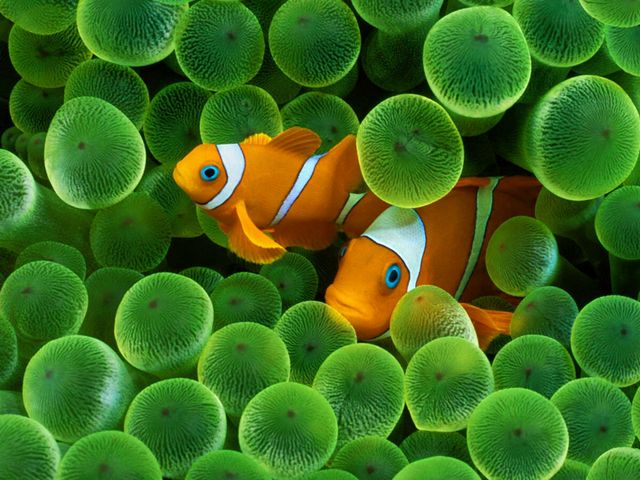

函数效果:
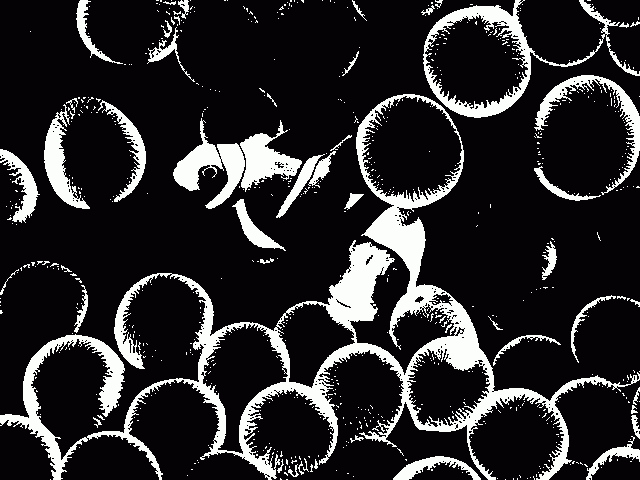
速度测试:
//
//threshold0 177.1 FPS
//
C:我们来简单优化一下threshold0的速度
getGray0涉及到浮点计算和浮点数取整,可以改写为一个整数定点数算法(见代
码中的getGrayInt函数);
在取黑白值的时候涉及到一个逻辑判断,从而生成了一个分支,可以优化掉;
在写颜色值的时候可以一次写入4个颜色分量;
详细的代码如下:
const long cs_gray_green_16 = ( long )(cs_gray_green * ( 1 << 16 ));
const long cs_gray_blue_16 = ( long )(cs_gray_blue * ( 1 << 16 ));
inline long getGrayInt( const TARGB32 & color)
{
return (color.r * cs_gray_red_16 + color.g * cs_gray_green_16 + color.b * cs_gray_blue_16) >> 16 ;
}
void threshold1( const TPicRegion & dst, const TPicRegion & src)
{
long width = dst.width;
if (src.width < width) width = src.width;
long height = dst.height;
if (src.height < height) height = src.height;
TARGB32 * srcLine = src.pdata;
TARGB32 * dstLine = dst.pdata;
for ( long y = 0 ;y < height; ++ y)
{
for ( long x = 0 ;x < width; ++ x)
{
long light = getGrayInt(srcLine[x]);
TUInt32 color = (( 127 - light) >> 31 ); // 利用了整数的编码方式来消除了分支
((TUInt32 * )dstLine)[x] = color; // 一次写4个字节
}
(TUInt8 *& )srcLine += src.byte_width;
(TUInt8 *& )dstLine += dst.byte_width;
}
}
threshold1实现的功能和threshold0完全相同;threshold1的速度为:
//
//threshold1 747.6 FPS
//
(当然,该函数还可以继续优化的,比如使用MMX、SSE等指令,可以得到更快的速度;)
D:一个局部自适应图像二值化算法的实现
局部自适应二值化:对于某个像素p,求其周围MxM范围内的像素的平均亮
度I, 若像素p的亮度大于I,则该像素设置为白色,否则设置为黑色;
在边界处,统计周围亮度的时候可能会访问到图像以外,为了在边界处也得到好的效果,
可以返回一个图像内的对应映射像素,完成该功能的函数为getMapBorderColor;
实现如下:
inline const TARGB32 & getMapBorderColor( const TPicRegion & src, long x, long y)
{
if (x < 0 ) x =- x - 1 ;
long width2 = src.width * 2 ;
while (x >= width2) x -= width2;
if (x >= src.width) x = width2 - x - 1 ;
if (y < 0 ) y =- y - 1 ;
long height2 = src.height * 2 ;
while (y >= height2) y -= height2;
if (y >= src.height) y = height2 - y - 1 ;
return Pixels(src,x,y);
}
// 返回图片src中以(x0,y0)为中心距离localHalfWidth以内的所有像素的亮度和
long getLocalLight_quadratic( const TPicRegion & src, long x0, long y0, long localHalfWidth)
{
long sumLight = 0 ;
for ( long y = y0 - localHalfWidth;y <= y0 + localHalfWidth; ++ y)
{
for ( long x = x0 - localHalfWidth;x <= x0 + localHalfWidth; ++ x)
{
const TARGB32 & mapBorderColor = getMapBorderColor(src,x,y);
sumLight += getGrayInt(mapBorderColor);
}
}
return sumLight;
}
void localAdaptiveThreshold_quadratic( const TPicRegion & dst, const TPicRegion & src, long localWidth)
{
long width = dst.width;
if (src.width < width) width = src.width;
long height = dst.height;
if (src.height < height) height = src.height;
TARGB32 * srcLine = src.pdata;
TARGB32 * dstLine = dst.pdata;
long localHalfWidth = localWidth / 2 ;
long tLocalWidth = localHalfWidth * 2 + 1 ;
long tLocalWidthSqr = tLocalWidth * tLocalWidth;
for ( long y = 0 ;y < height; ++ y)
{
for ( long x = 0 ;x < width; ++ x)
{
long sumLight = getLocalLight_quadratic(src,x,y,localHalfWidth);
long light = getGrayInt(srcLine[x]);
// localWidth^2*255<=(2^31-1) => localWidth<=2901
TUInt32 color = ((sumLight - light * tLocalWidthSqr) >> 31 );
((TUInt32 * )dstLine)[x] = color;
}
(TUInt8 *& )srcLine += src.byte_width;
(TUInt8 *& )dstLine += dst.byte_width;
}
}
函数效果:
localWidth=151

localWidth=51

localWidth=17

localWidth=5

恩,效果不错:)
速度测试:
//
// localWidth= 5 | 17 | 51 | 151
//------------------------------------------------------------
//localAdaptiveThreshold_quadratic 9.33 1.04 0.12 0.012FPS
//
可以看到随着模板大小的增长,速度在成平方的减小
(文章的下篇将开始优化localAdaptiveThreshold_quadratic的速度,得到线性算法
和常数算法)





















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








